This document discusses SQL and database connectivity using Python. It covers SQL statements like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE. It describes database tables like orders and parts with sample data. It also explains how to connect to databases using Python DB-API modules, execute queries, retrieve and manipulate result sets. Key methods like cursor.execute, fetchall are demonstrated along with transaction handling.






![www.SunilOS.com 16
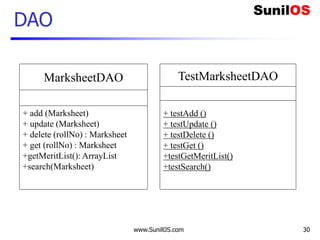
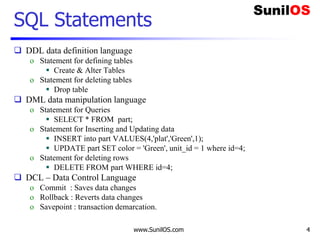
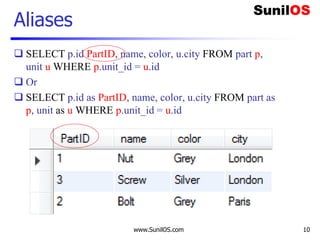
MYSQL – Get Data
import pymysql
result=""
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='root',db='test')
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
sql = "select * from part"
cursor.execute(sql)
result= cursor.fetchall()
connection.close()
for d in result:
print(d[0]," ",d[1],"t", d[2])
Column value by index
SQL Query
DB URL Login ID PWD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdbc-211115105151/85/PDBC-16-320.jpg)








![www.SunilOS.com 28
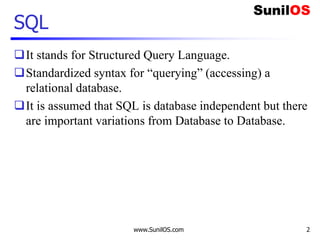
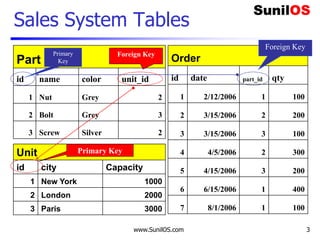
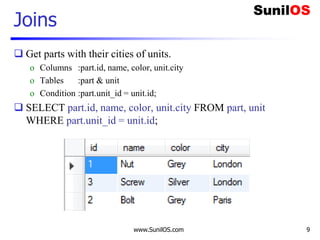
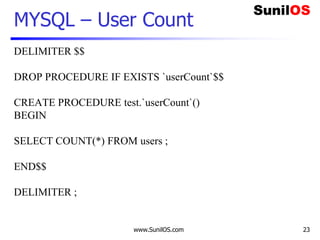
Metadata – Data about Data
import pymysql
connection = pymysql.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='root',db='abc')
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("select * from company ")
cursor.fetchall()
meta=cursor.description
for data in meta:
print("t",data[0],end="")
connection.close()
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdbc-211115105151/85/PDBC-28-320.jpg)