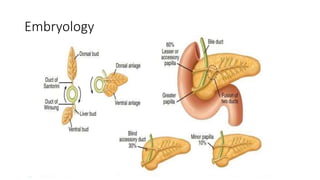
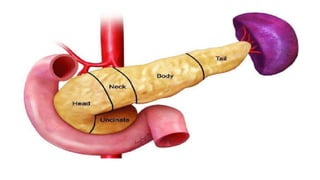
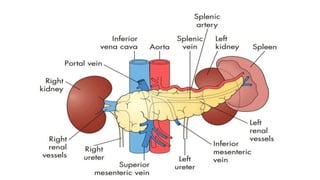
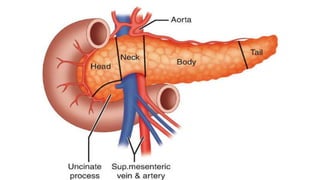
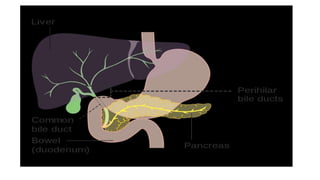
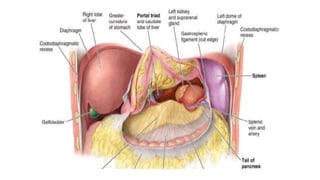
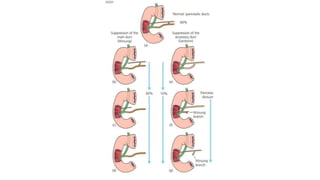
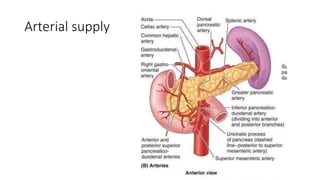
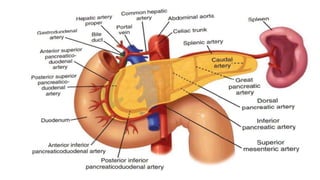
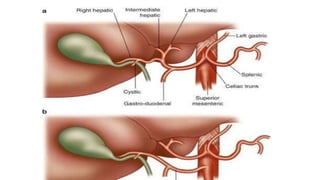
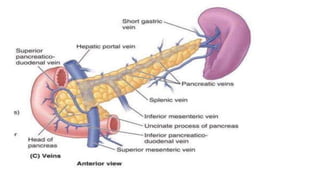
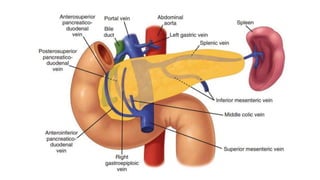
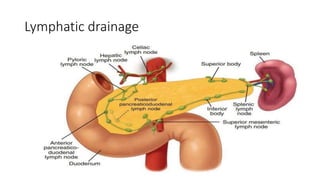
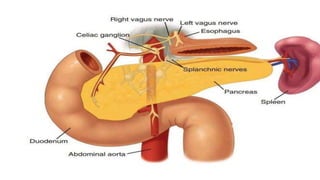
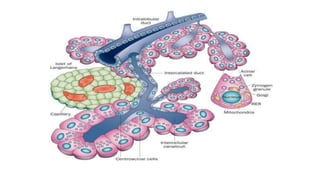
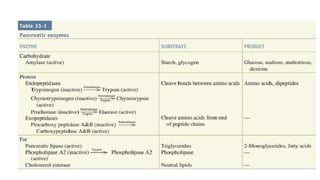
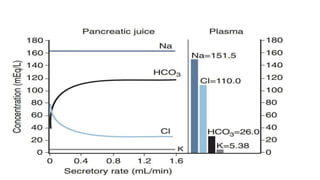
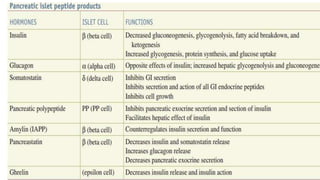
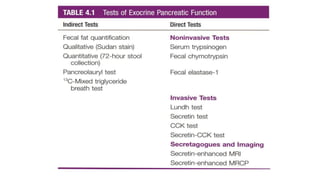
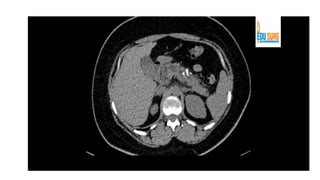
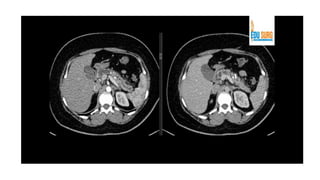
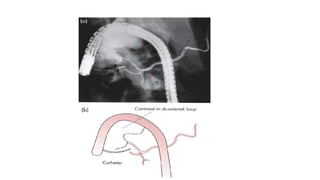
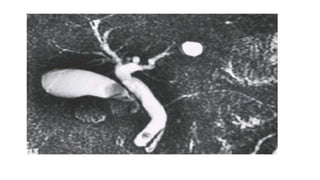
The pancreas has four regions - the head, neck, body, and tail. The head is nestled near the duodenum and contains the pancreatic duct which drains into the common bile duct. The neck lies at the level of L1-L2 near the portal vein. The body and tail are located near the spleen. Arterial blood supply comes from branches of the celiac and superior mesenteric arteries, while venous drainage involves the portal vein. The exocrine pancreas secretes enzymes to aid digestion, and the endocrine islets of Langerhans produce hormones like insulin and glucagon to regulate metabolism. Imaging techniques like ultrasound and CT are important for evaluating pancreatic anatomy and function.