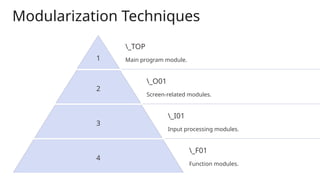
This training session introduces ABAP module pool programming, focusing on creating custom screens for user interactions and supporting complex business processes. Key concepts include PBO (Process Before Output) and PAI (Process After Input), with tools like the Screen Painter for designing screens. Participants will learn to create a simple module pool program through practical examples and coding snippets.