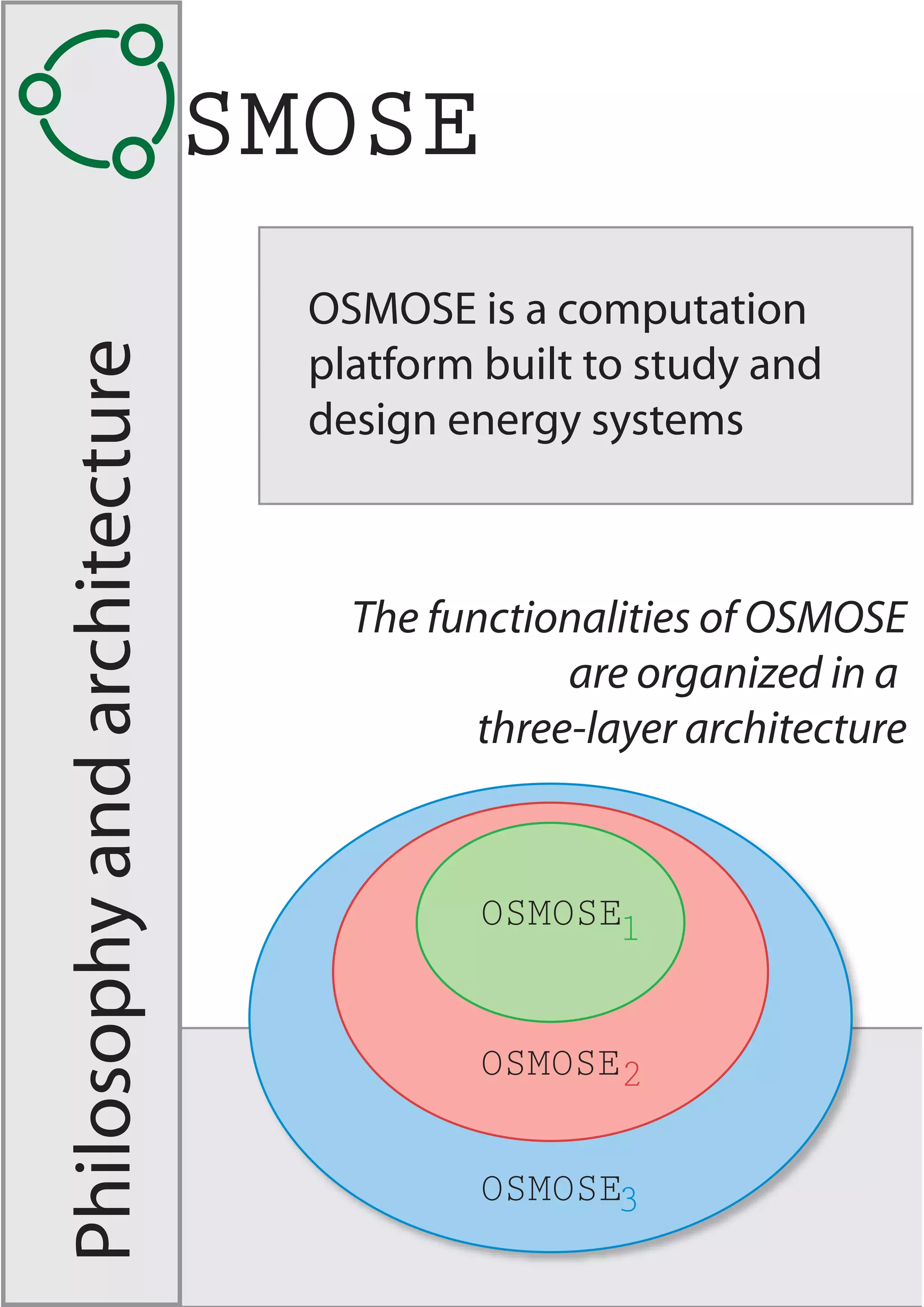
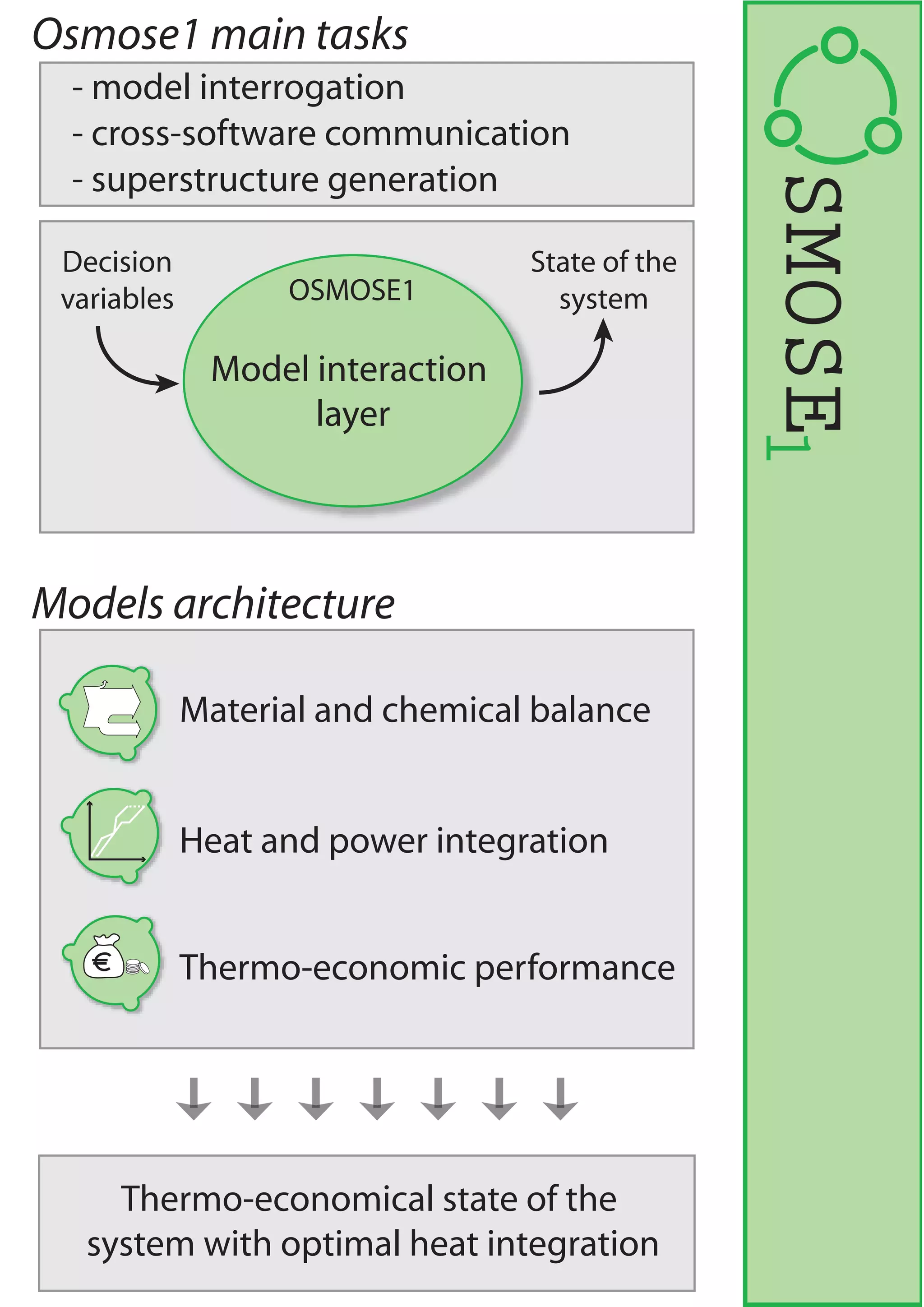
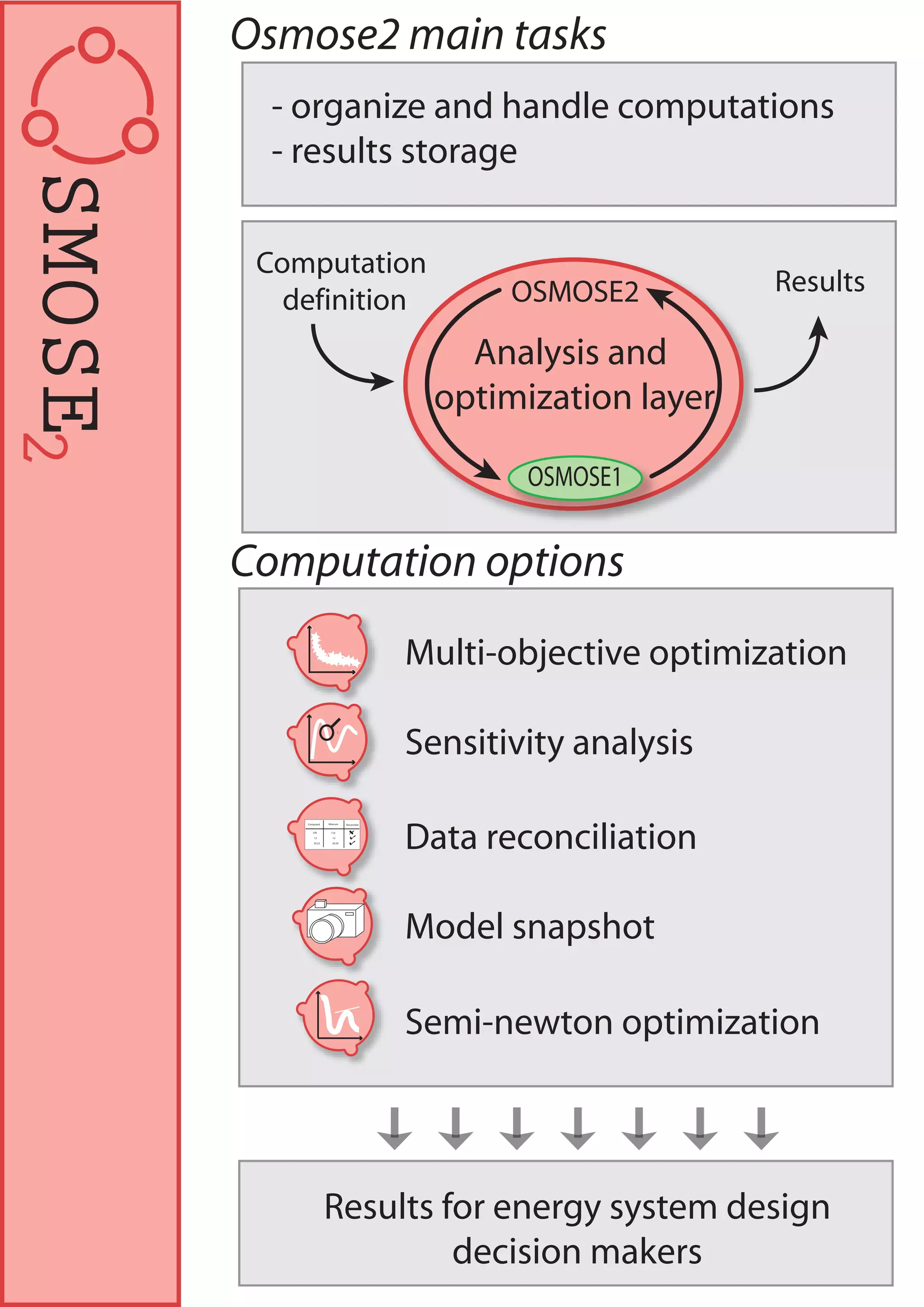
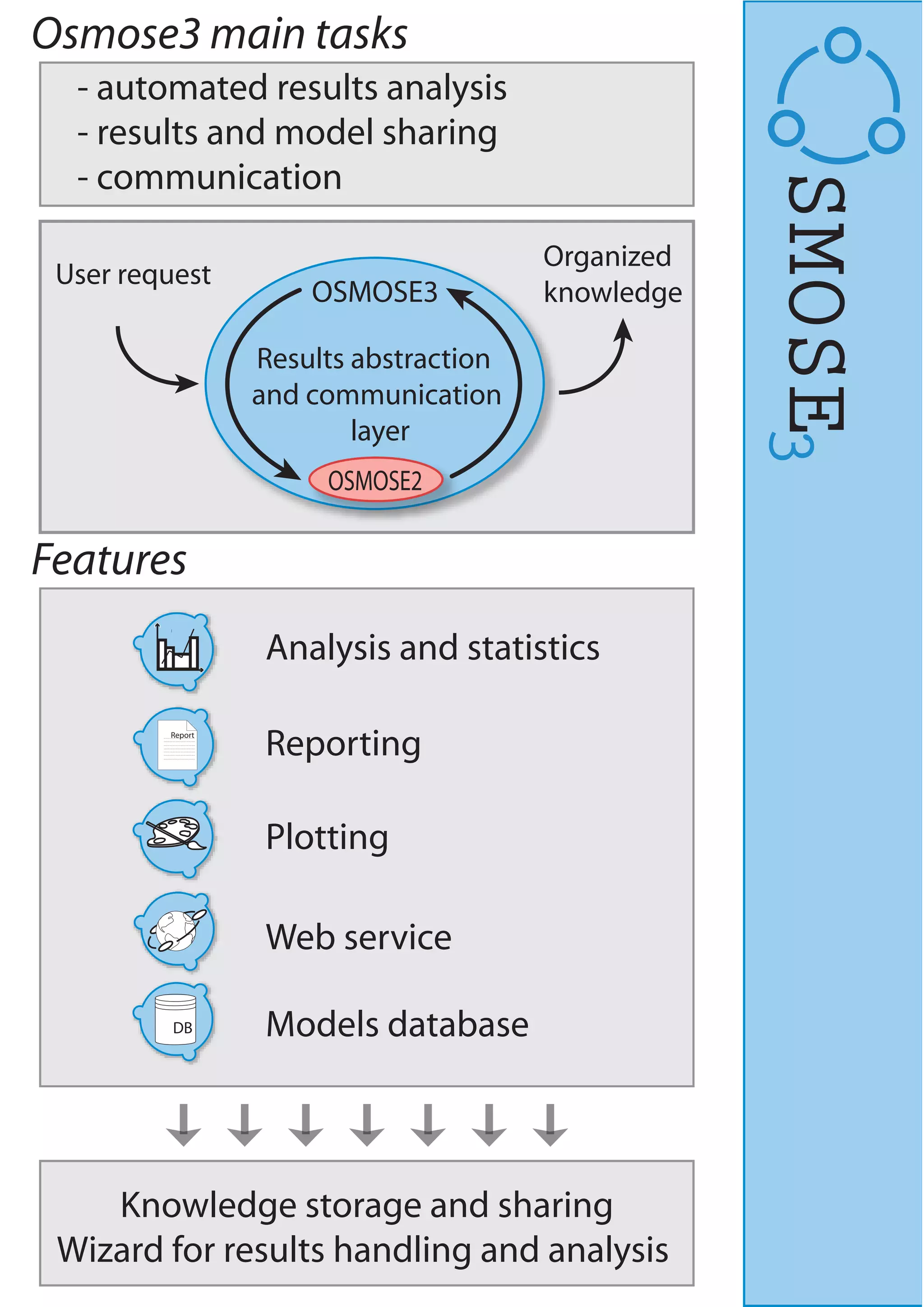
LENI Systems developed OSMOSE, a computation platform for designing and analyzing integrated energy systems. OSMOSE has a three-layer architecture for organizing models, computations, and results. It allows for model interrogation, heat and power integration analysis, multi-objective optimization, and results sharing through a web interface. The tool has been used to study advanced power plant design, fuel cell systems, and hybrid solid oxide fuel cell and gas turbine systems.