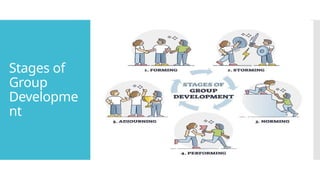
The document outlines the stages of group development: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning, each characterized by specific dynamics and challenges. Successful group behavior, according to Richard Hackman, depends on being a real group, having compelling directions, enabling structure, supportive context, and expert coaching. These elements are crucial for the successful functioning and eventual completion of group tasks.