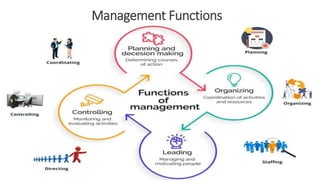
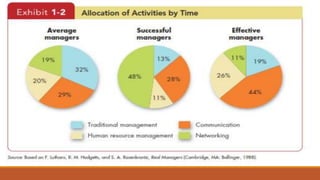
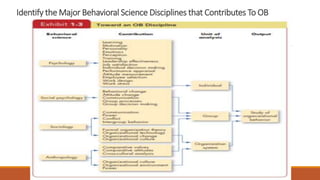
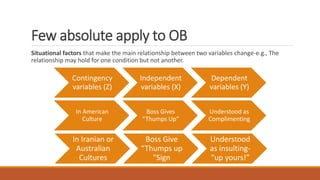
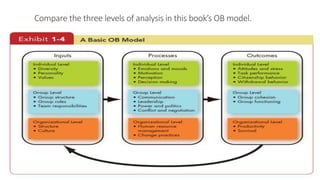
This chapter introduces organizational behavior (OB) and defines it as the study of how individuals and groups act within organizations and how their behaviors affect organizational performance. It discusses the importance of interpersonal skills for managers and describes managers' roles and functions. The chapter also identifies the major behavioral science disciplines that contribute to OB, such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Finally, it outlines challenges and opportunities for applying OB concepts, like managing diversity and stimulating innovation, and compares the three levels of analysis in the book's OB model: inputs, processes, and outcomes.