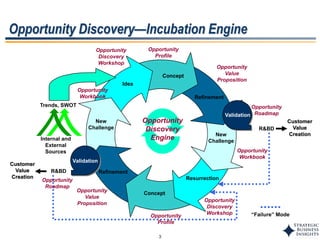
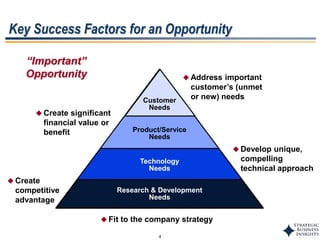
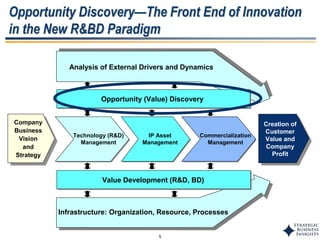
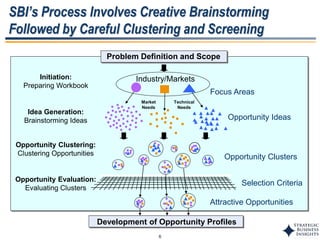
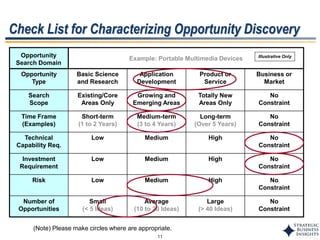
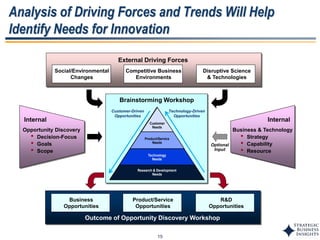
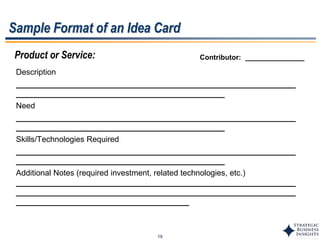
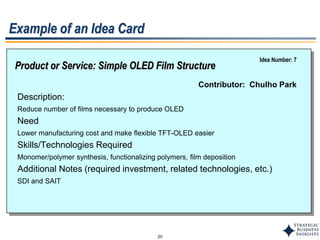
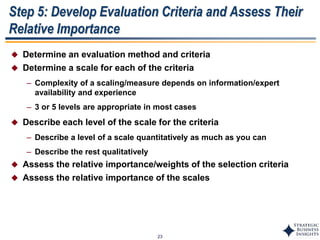
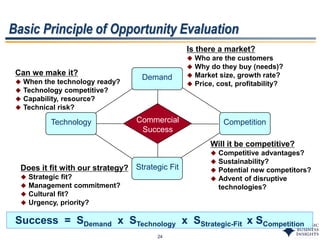
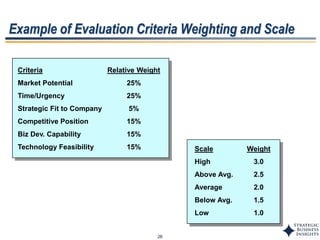
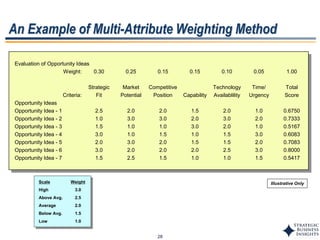
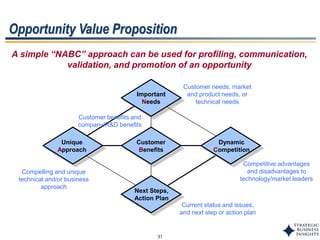
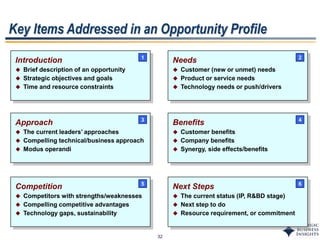
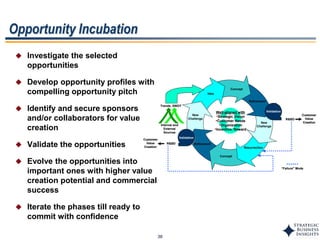
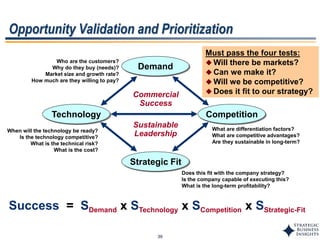
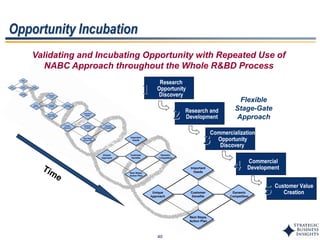
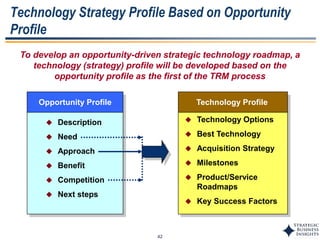
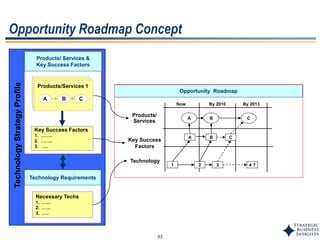
This document outlines SBI's opportunity discovery process (ODP). The process involves creative brainstorming to generate new business and research opportunities, followed by clustering and screening of ideas. Ideas are evaluated against criteria like market potential, strategic fit, and technical feasibility. Top opportunities are selected and refined for further development. The goal is to incubate new opportunities through a structured, multidisciplinary process of identifying customer needs, trends, and technologies.