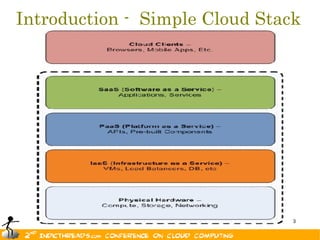
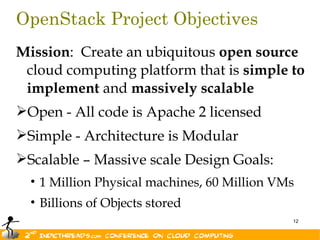
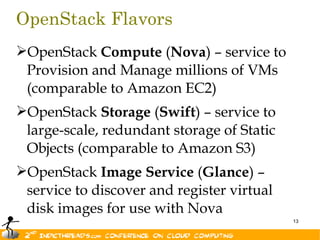
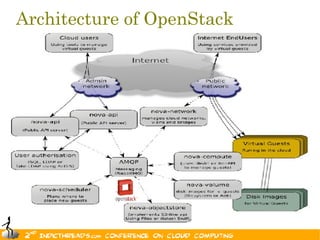
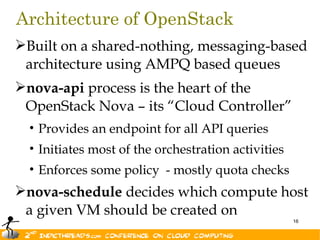
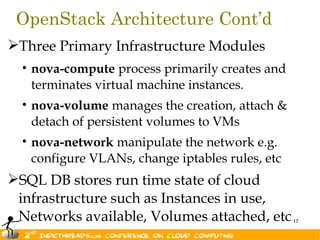
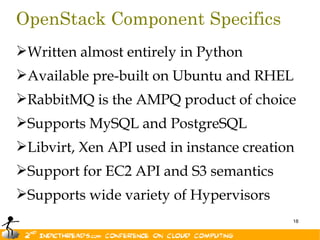
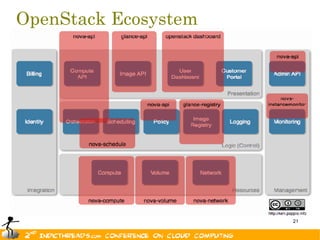
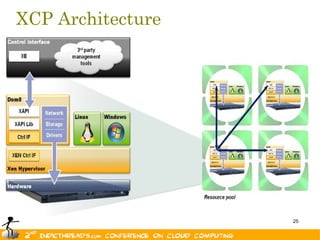
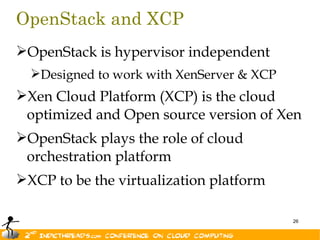
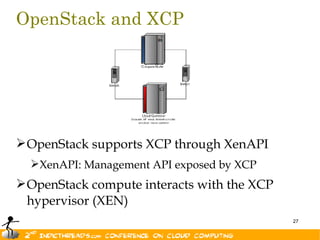
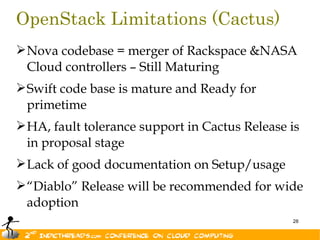
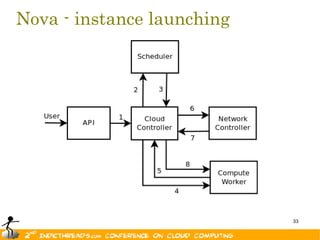
The document discusses the evolution of OpenStack as a significant IaaS platform, detailing its inception in collaboration between Rackspace and NASA, aimed at enabling scalable cloud services. It outlines the features and architecture of OpenStack, its components like Nova and Swift, and its compatibility with various hypervisors, notably Xen. Additionally, it emphasizes OpenStack's growing ecosystem and partnerships, positioning it as a strong competitor in the cloud computing landscape.