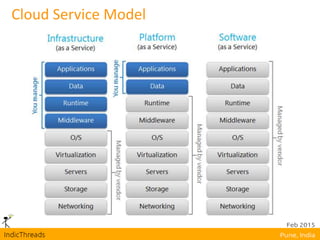
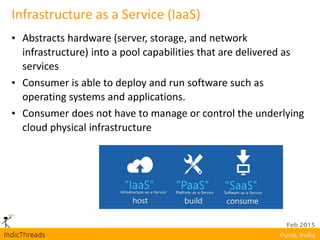
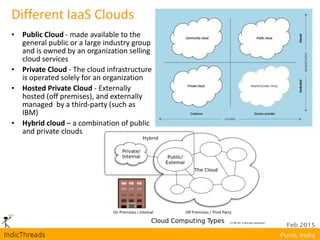
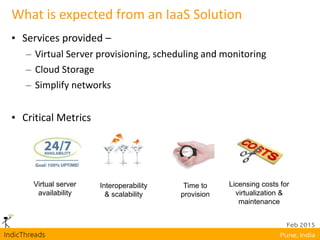
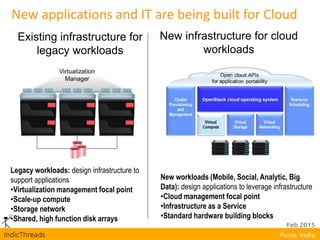
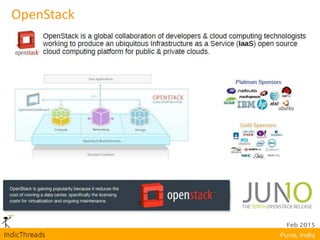
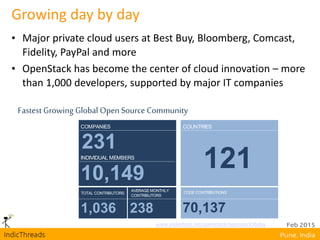
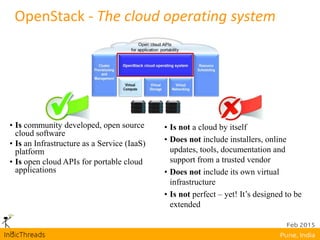
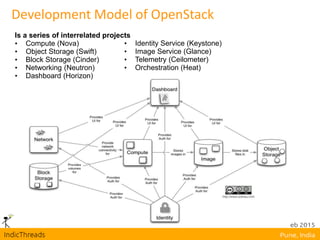
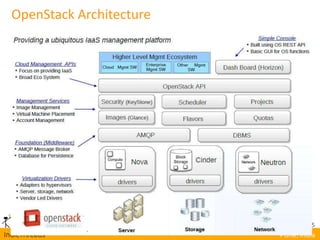
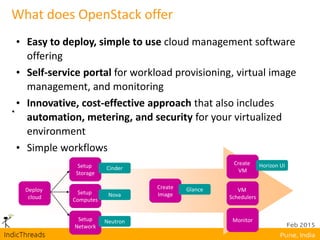
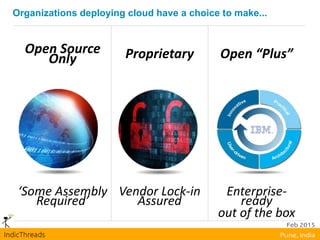
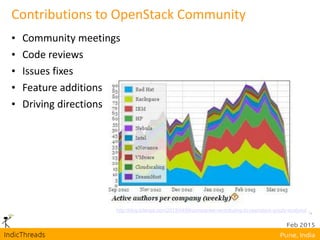
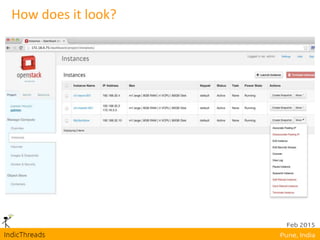
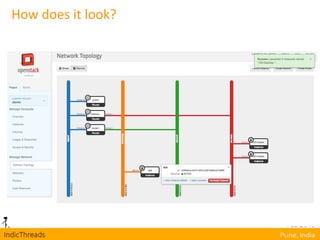
OpenStack is an open-source Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) platform that abstracts hardware into a pool of services, allowing users to deploy and manage applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. It has evolved into a significant player in cloud innovation, supported by a large developer community and organizations such as Best Buy and PayPal. OpenStack offers a user-friendly self-service portal for managing cloud resources and is suitable for various organizations, including universities and banks, seeking to establish private or public cloud solutions.