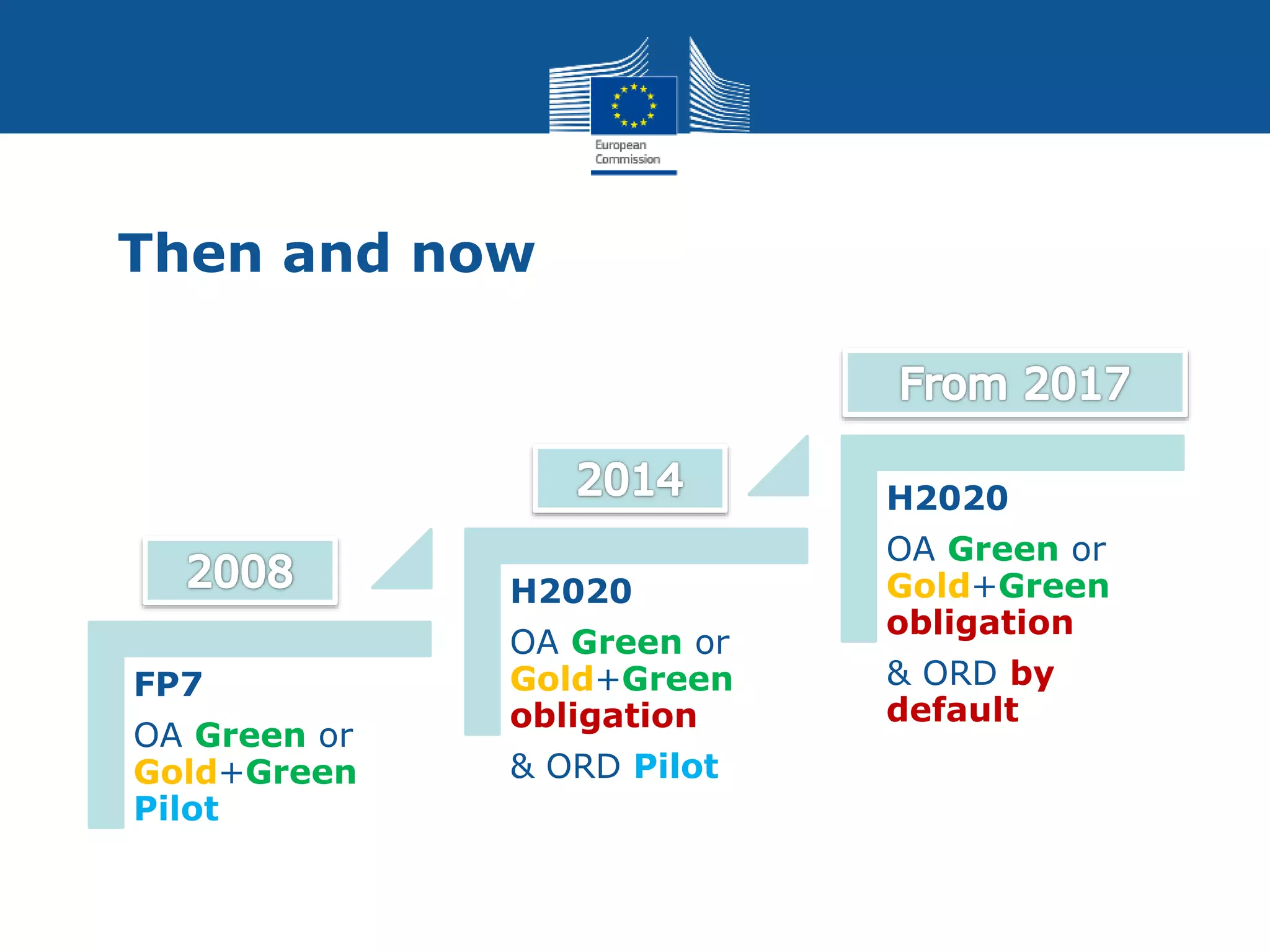
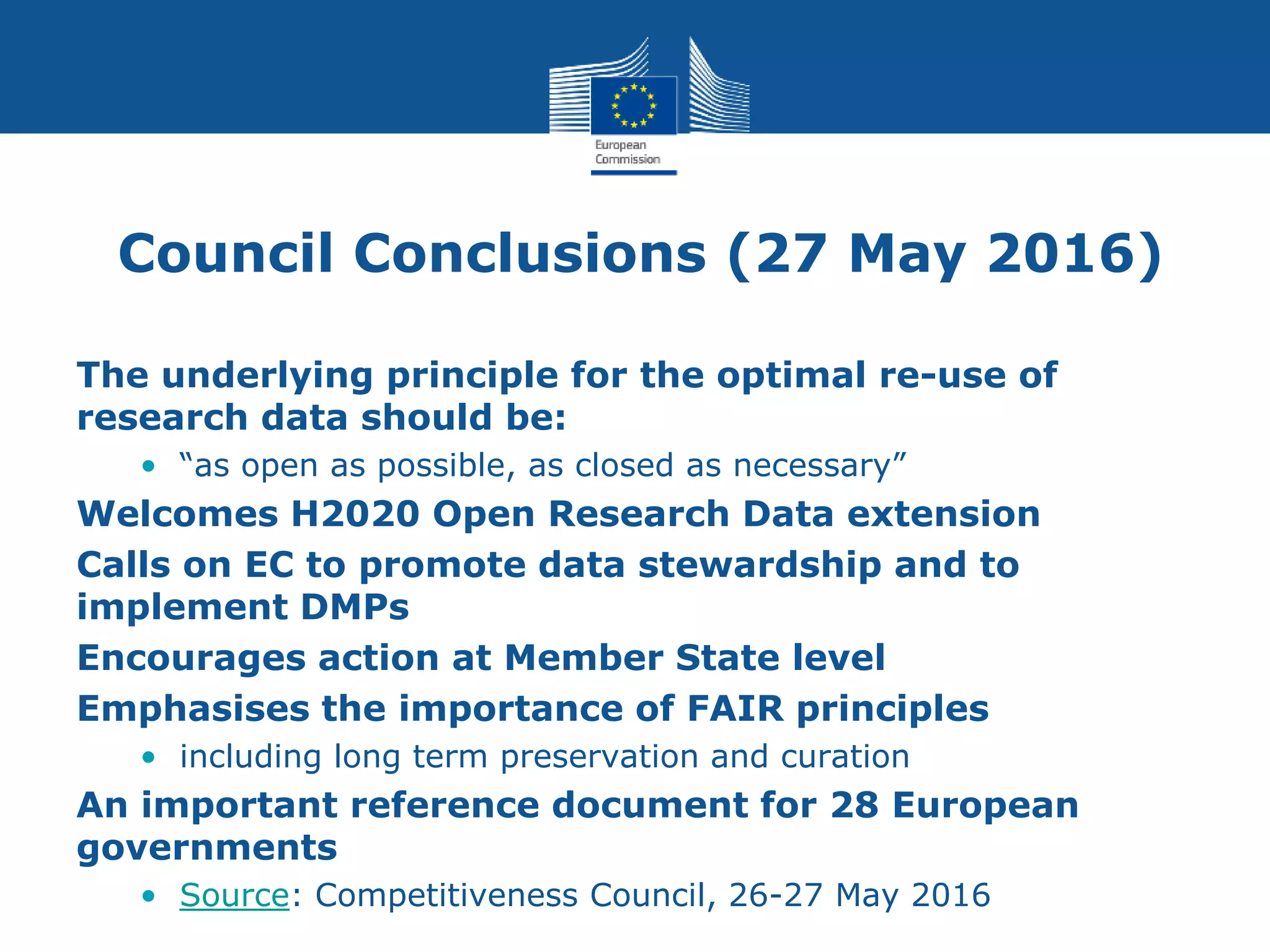
The document discusses the challenges and solutions around open access to research data in Europe. It summarizes that Horizon 2020 now mandates open access to publications and open access to research data by default from 2017. It describes how grantees are required to deposit data in repositories and take measures to grant open access, with the ability to opt-out for certain reasons. The approach has been tested in a Horizon 2020 pilot and will expand in 2017 to cover all areas with the same rules, aiming for research data to be as open as possible while allowing necessary closures.