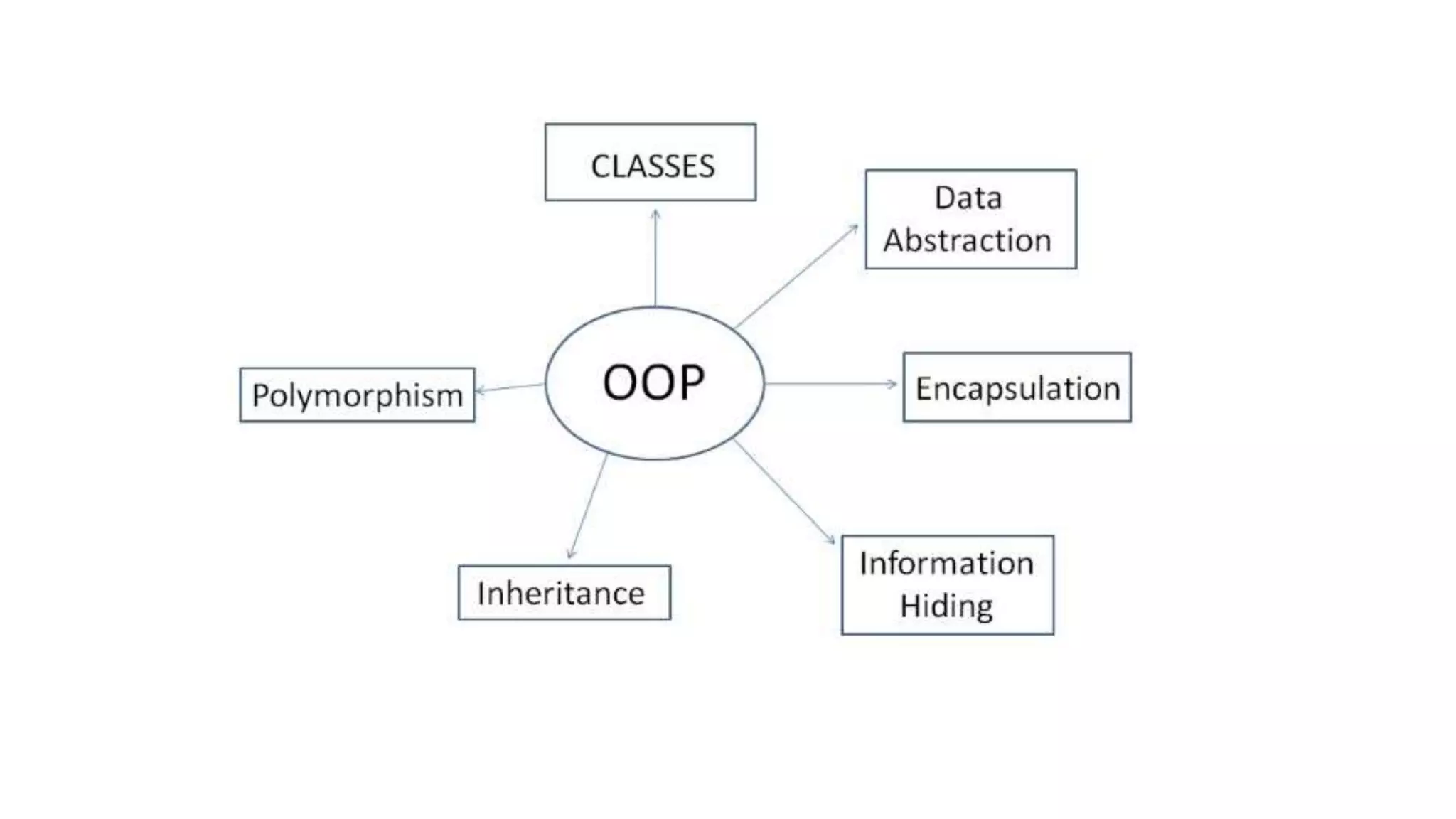
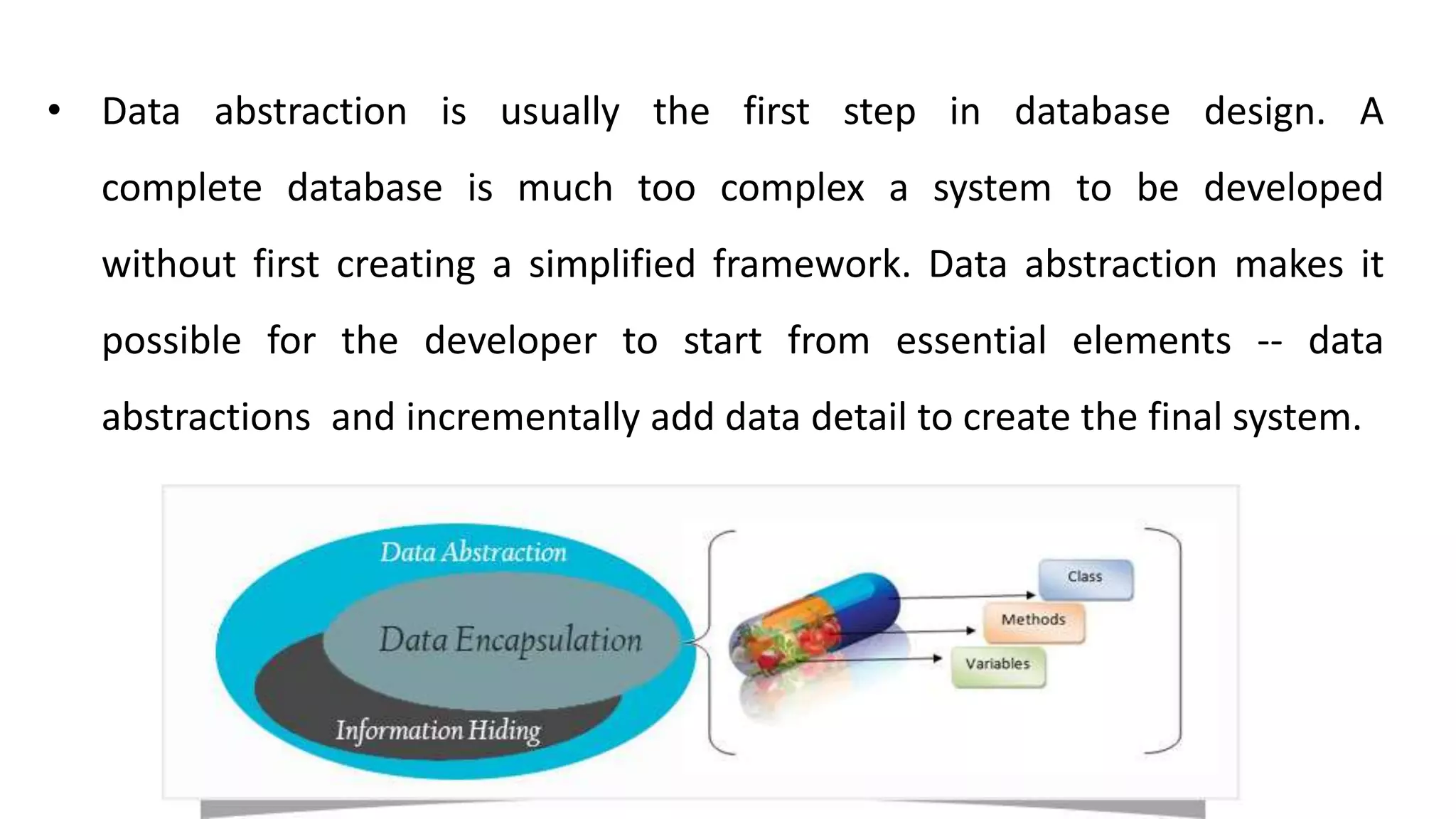
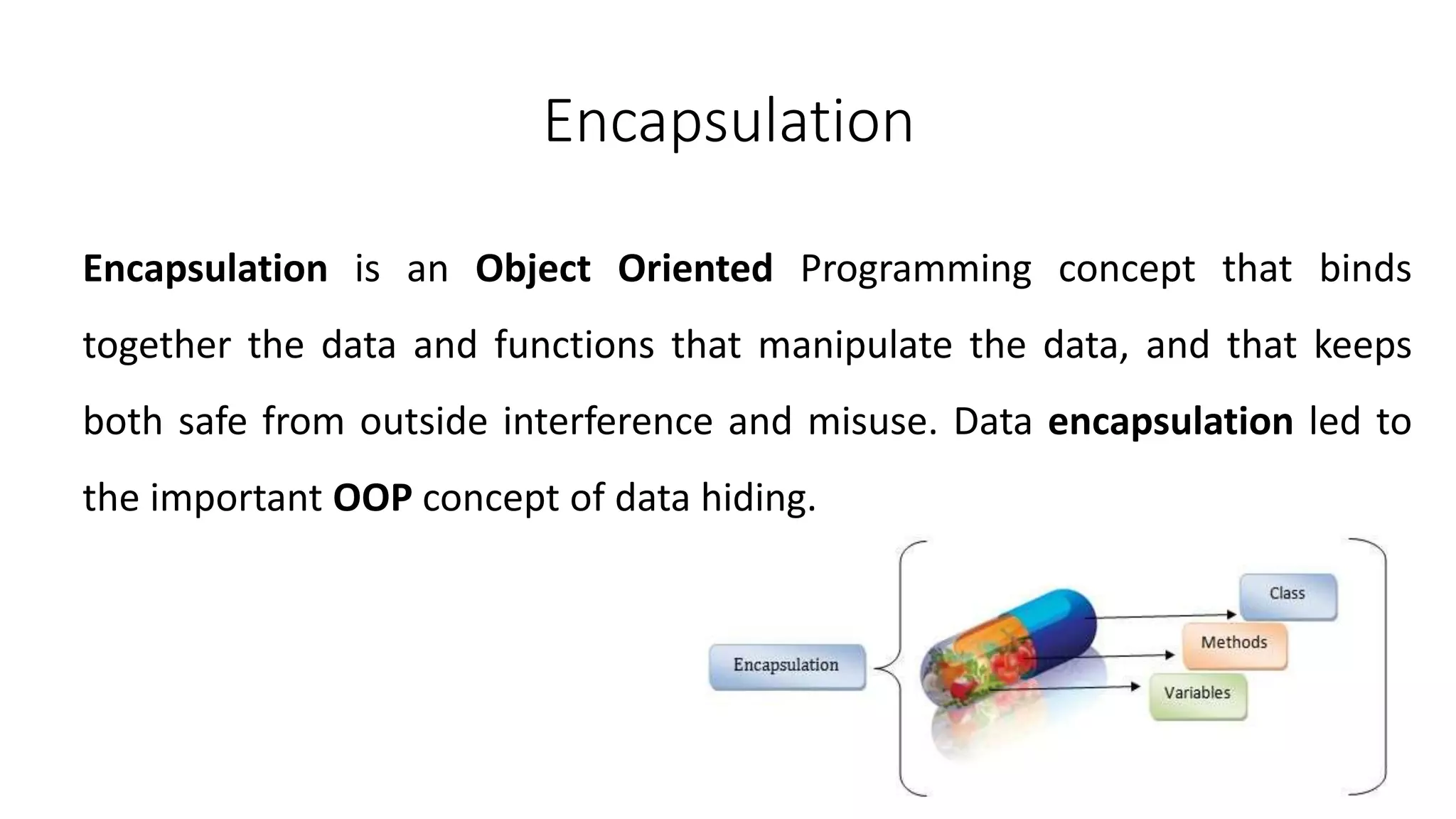
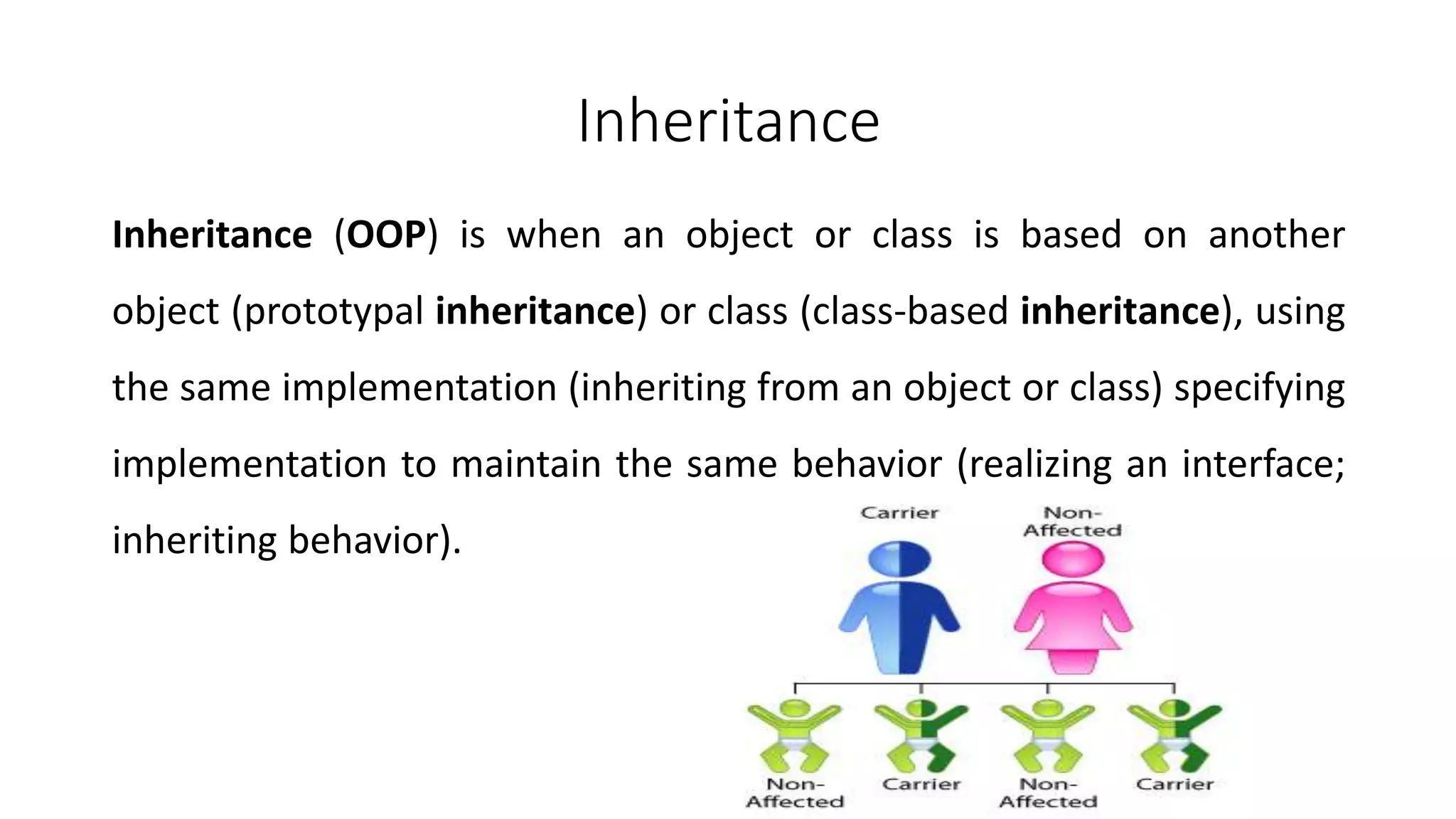
1. The document discusses key object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts in C++ including objects, classes, data abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
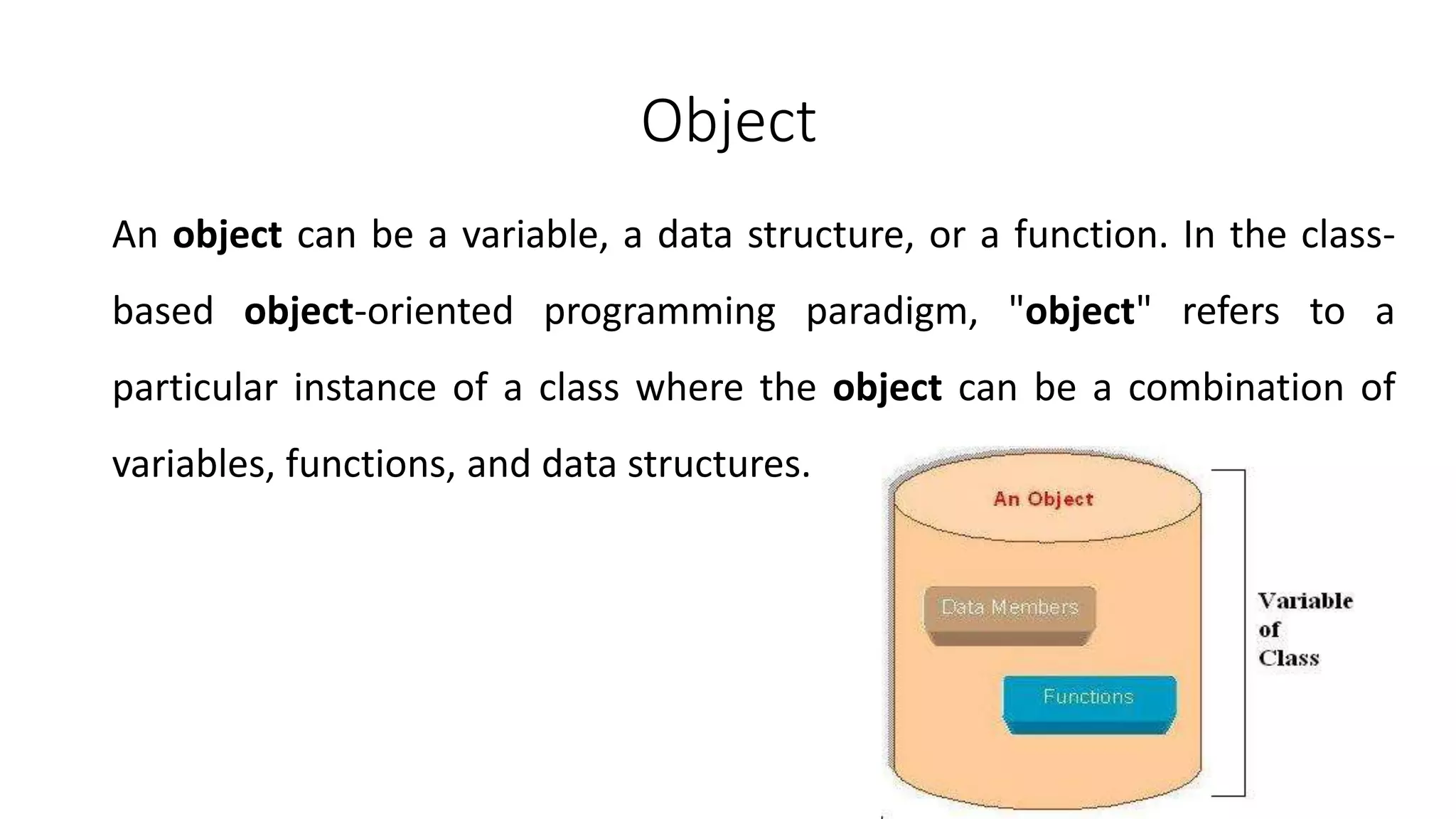
2. An object can be a variable, data structure, or function, and in class-based OOP refers to an instance of a class containing variables, functions, and data structures.
3. A C++ class declares a user-defined type with data members and member functions (methods), with access controlled by private, protected, or public specifiers.