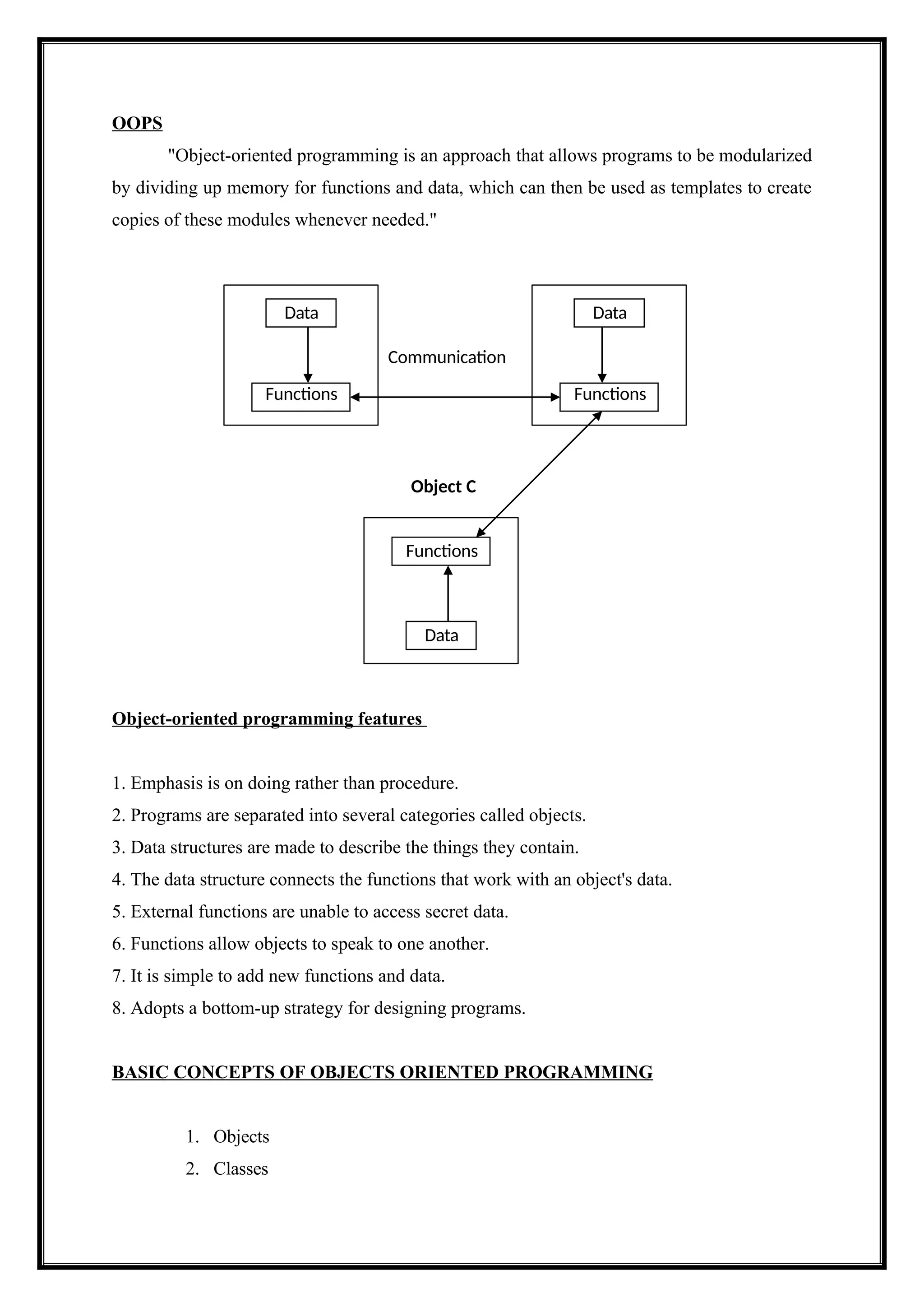
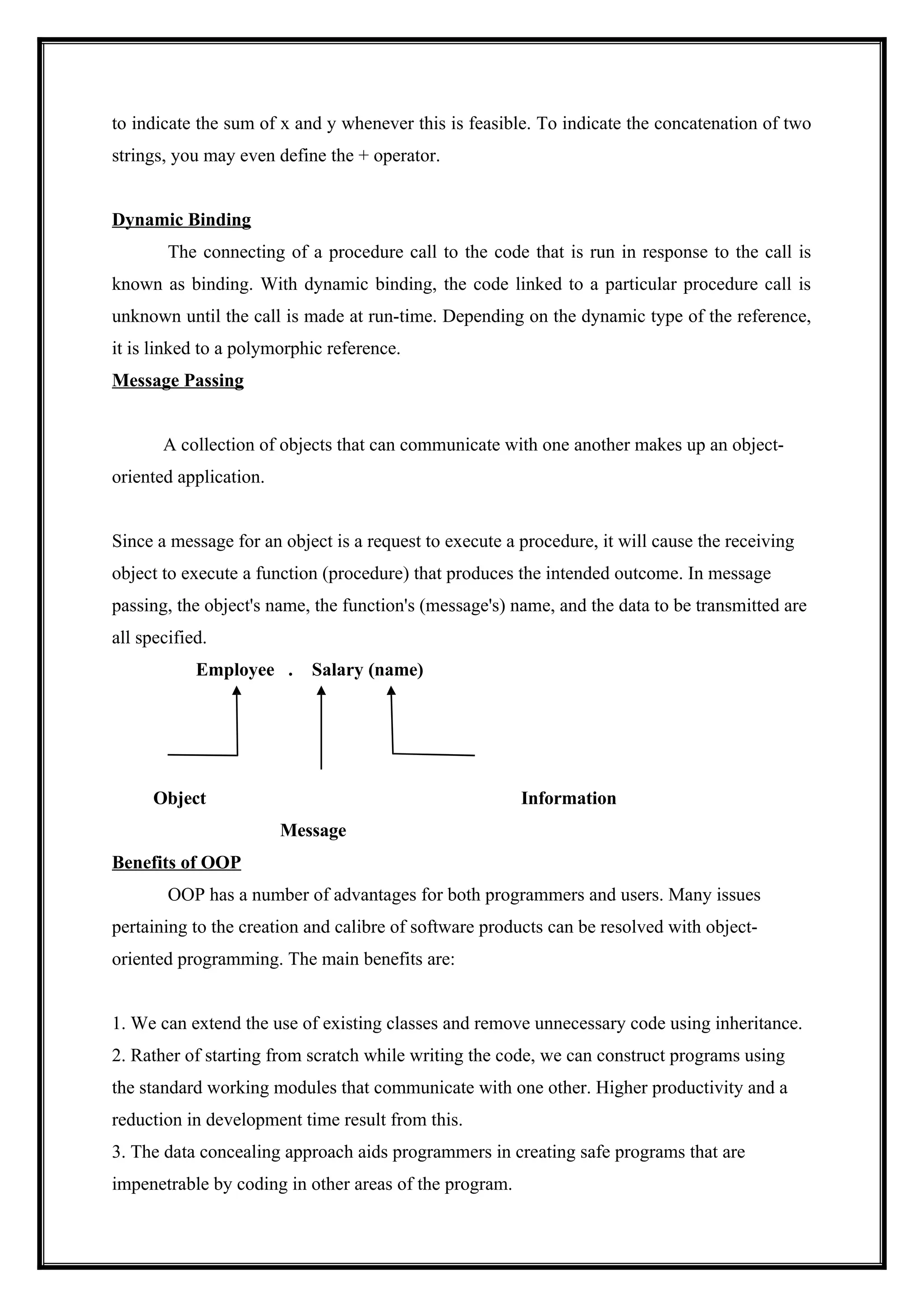
Applications and computer programs are designed using "objects" in the OOP programming paradigm. It centers on the idea of organizing data and the operations performed on it into objects that may communicate with one another. This method encourages programming that is modular, reusable, and maintainable.