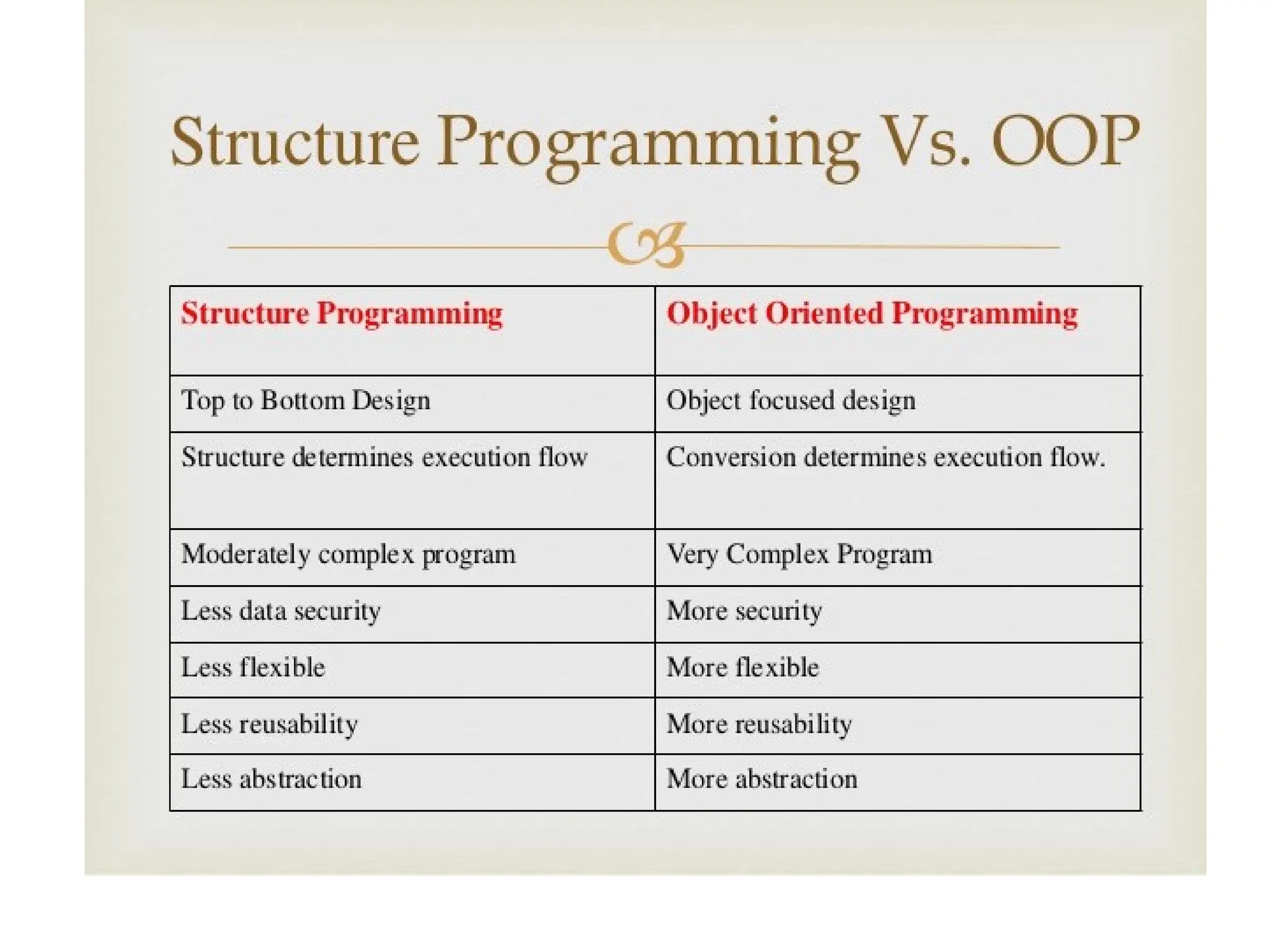
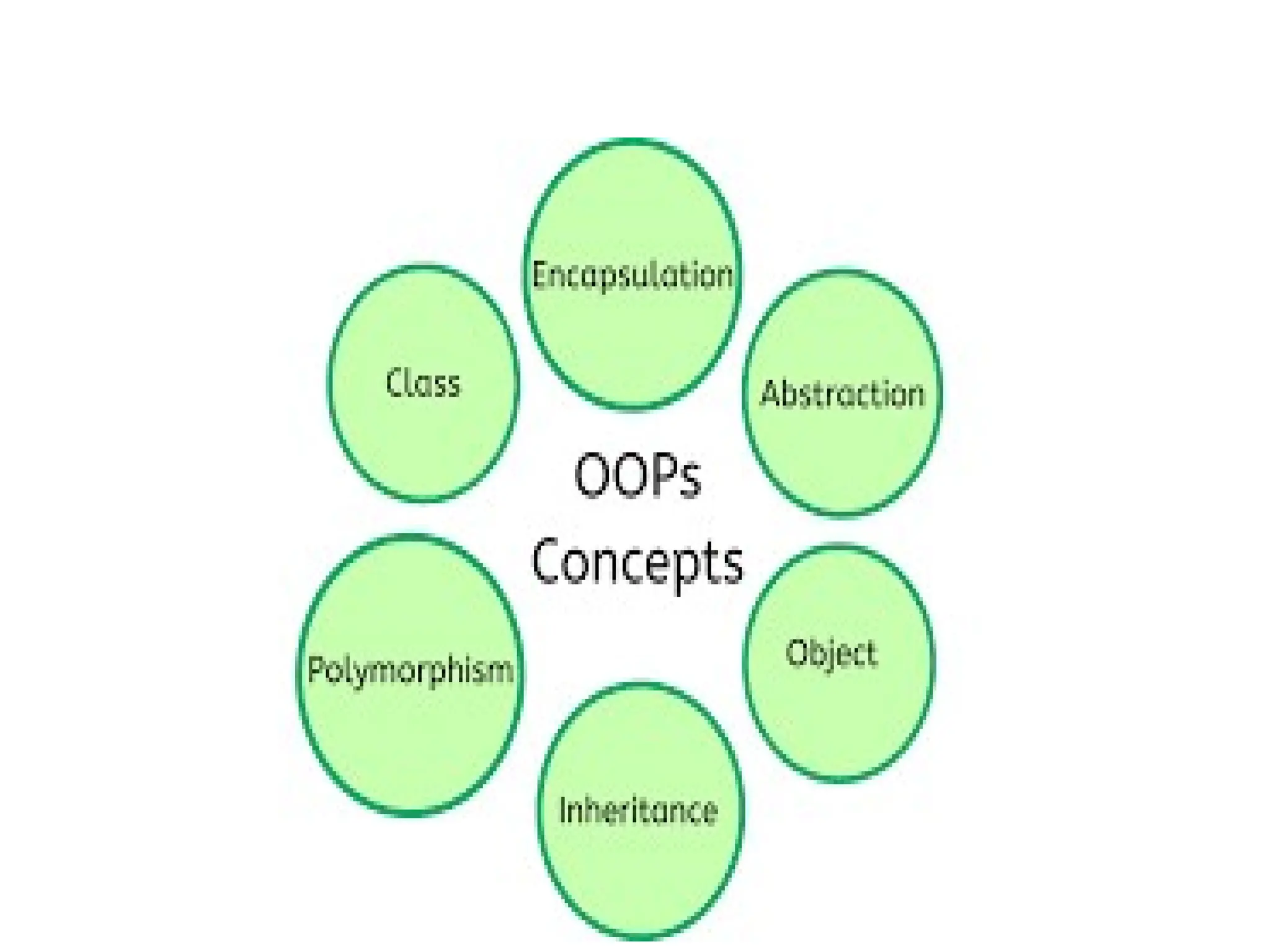
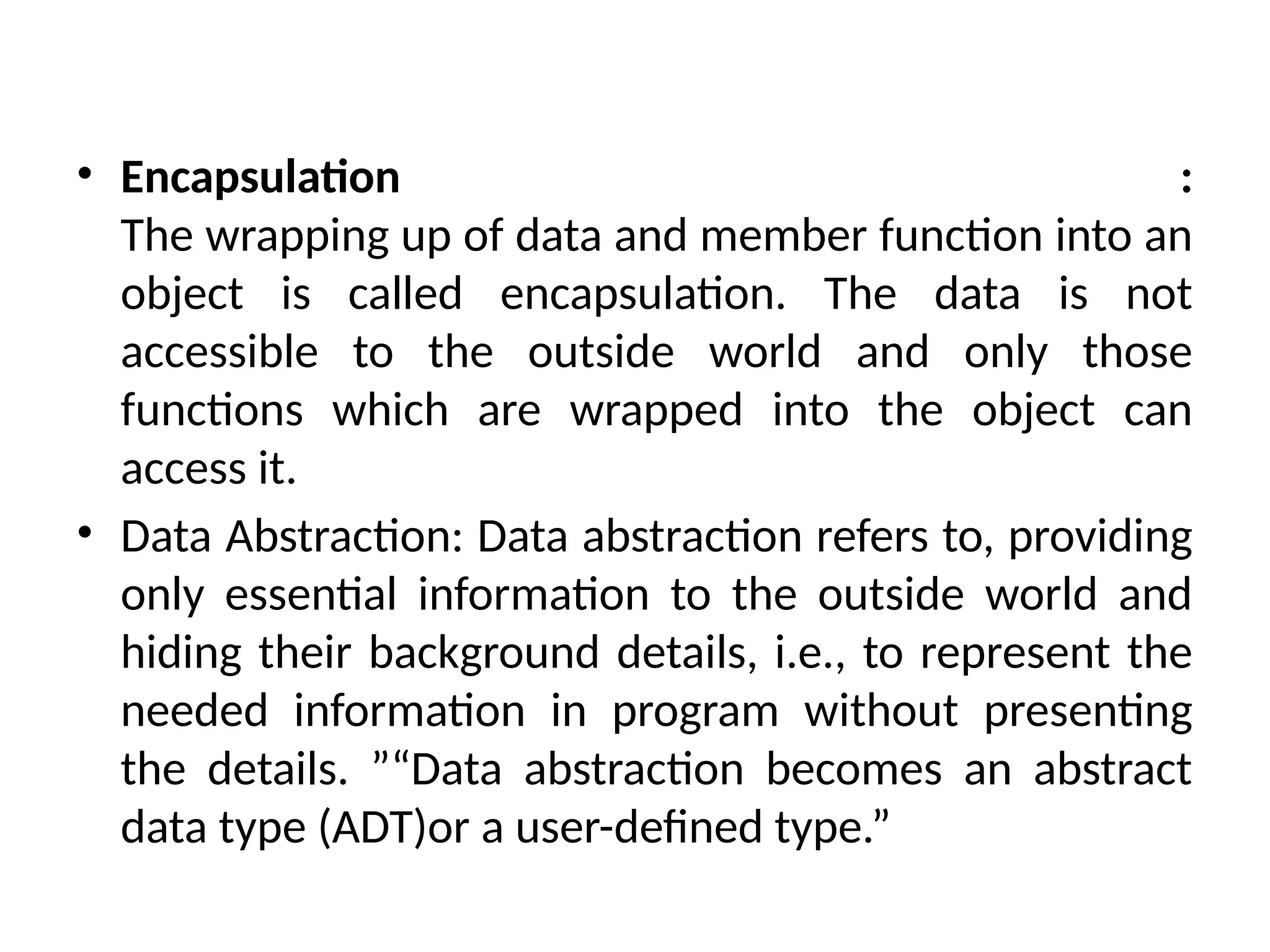
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming methodology that focuses on creating objects that encapsulate both data and functions. Key elements of OOP include objects, classes, encapsulation, data abstraction, inheritance, polymorphism, dynamic binding, and message passing. These concepts enable the representation of data with associated behaviors, promote reusability, and facilitate interaction between objects.