In this presentation I talk about Object Oriented Design Concepts and Core concepts in java
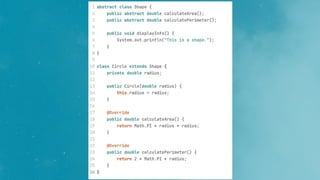
Class
Object
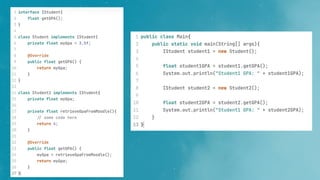
Java Access Keywords
Abstraction
Encapsulation
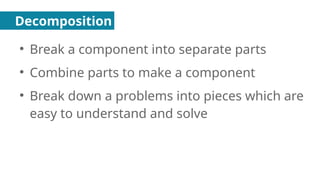
Decomposition
Generalization
Association
- some relation / interaction
Aggregation
- belongs
Composition
- contains (whole cannot exist without parts)
Polymorphism
Cohesion
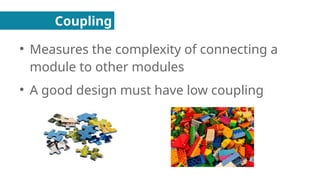
Coupling








![Java Access keywords
●
Most commonly used ones are
– public – Allows methods and attributes to be
accessed by anyone inside / outside the class
– private – Allows the methods and attribute
access within the class
– [default] – Allows the methods and attribute
access within the package](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopdesign-250801174800-392ed7fc/85/Object-Oriented-Design-and-Concepts-related-to-Object-Oriented-Programming-9-320.jpg)