The document contains programs written in C programming language to solve problems using numerical methods like Bisection method, False position method, Trapezoidal rule, Simpson's rule, Runge-Kutta method, Euler's method, and Lagrange interpolation. The programs take user input, perform the respective calculations, and output the results. They provide examples of implementing numerical techniques to find roots of equations, compute integrals, and solve differential equations.
![PROGRAM
/*program for legranges interpolation method*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
float x[20],y[20],unknown,temp,result=0,n,i,j;
clrscr();
printf("nntLEGRANGES INTERPOLATION -FIRST ORDERn");
printf("nt---------------------------------------n");
printf("nEnter the limitn");
scanf("%f",&n);
printf("Enter the values for xn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%f",&x[i]);
}
printf("Enter the values of yn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%f",&y[i]);
}
printf("Enter the value whose f(x) to be foundn");
scanf("%f",&unknown);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
temp=1;
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i!=j)
{
temp*=((unknown-x[j])/(x[i]-x[j]));
}
}
result+=temp*y[i];
}
printf("f( %f )= ",unknown);
printf("%f",result);
getch();
}
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-1-320.jpg)

![PROGRAM
/* program to claculate the integral using trezoidal rule*/
#define f(x) (1/(x+1))
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
float h,a,b,result=0,temp=0;
int i,j,n;
float x[50],y[50];
clrscr();
printf("Enter the Lower & Upper limit a&bn");
scanf("%f %f",&a,&b);
printf("nEnter the number of intervalsn");
scanf("%d", &n);
h=(b-a)/n;
printf("nCOMPUTING INTEGRAL USING-TRAPEZOIDAL RULE n");
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
x[i]=a+(i*h);
}
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
y[i]=f(x[i]);
}
printf("xttty");
for(i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n%ftt%f",x[i],y[i]);
}
result=y[0]+y[n];
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
temp+=y[i];
}
result+=(temp*2);
result*=(h/2);
printf("nn%f",result);
getch();
}
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-3-320.jpg)







![PROGRAM
/* program to compute integral using Simpsons rule*/
#define f(x) 1/(1+x)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
float a,b,h,result,temp1=0,temp2=0;
float x[20],y[20];
int i,j,n;
clrscr();
printf("nntSIMPSONS 1/3rd RULEn");
printf("nt---------------------n");
printf("Enter the Lower and Upper limitsn");
scanf("%f %f",&a,&b);
printf("nEnter the number of intervalsn");
scanf("%d",&n);
h=(b-a)/n;
for(i=0;i<=n;++i)
{
x[i]=a+(i*h);
}
for(i=0;i<=n;++i)
{
y[i]=f(x[i]);
}
printf("nnxttyn");
printf("n-------n");
for(i=0;i<=n;++i)
{
printf("n%ft%f",x[i],y[i]);
}
h=(b-a)/(2*n);
result=y[0]+y[n];
for(i=1;i<=n-1;i+=2)
{
temp1=temp1+y[i];
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-11-320.jpg)
![}
result+=(temp1*4);
for(i=2;i<=n-2;i+=2)
{
temp2=temp2+y[i];
}
result+=temp2*2;
result*=h/3;
printf("nntResult = %f",result);
getch();
}
OUTPUT
SIMPSONS 1/3rd RULE
-----------------------------
Enter the Lower and Upper limits
0
1
Enter the number of intervals
2
x y
---------------------------
0.000000 1.000000
0.500000 0.666667
1.000000 0.500000
Result = 0.347222
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-12-320.jpg)









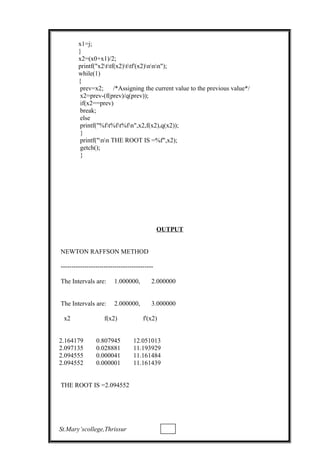
![PROGRAM:
/*program for gauss elimination method…*/
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int m,n,p,q,i,j;
float a[10][10],b[10][10],x,y,z,t; /*…Declaration…*/
clrscr();
printf("nGAUSS ELIMINATION METHODn");
printf("********************************n");
printf("nInput the raw size of first matrix:");
scanf("%d",&m);
printf("Input the column size of first matrix:");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("nInput the %d elements to %d*%d matrix:nn",m*n,m,n);
for(i=0;i<m;i++) /*…For loop…*/
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
scanf("%f",&a[i][j]);
}
}
printf("nnInput the raw size of second matrix:");
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-23-320.jpg)
![scanf("%d",&p);
printf("Input the column size of second matrix:");
scanf("%d",&q);
printf("nInput the %d elements to %d*%d matrix:nn",p*q,p,q);
for(i=0;i<p;i++) /*…For loop…*/
{
for(j=0;j<q;j++)
{
scanf("%f",&b[i][j]);
}
}
printf("ntMatrix A:nn");
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%ft",a[i][j]); /*…Print matrix A…*/
}
printf("n");
}
printf("ntMatrix B:nn");
for(i=0;i<p;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<q;j++)
{
printf("%ft",b[i][j]); /*…Print matrix B…*/
}
printf("n");
}
t=a[0][0];
for(j=0;j<m;j++)
{
a[0][j]/=t;
}
b[0][0]/=t;
for(i=1;i<p;i++)
{
t=a[i][0];
for(j=0;j<m;j++)
{
a[i][j]-=(t*a[0][j]); /*…Calculations…*/
}
b[i][0]-=(t*b[0][0]);
}
t=a[1][1];
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
a[1][j]/=t;
}
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-24-320.jpg)
![b[1][0]/=t;
t=a[2][1];
for(j=1;j<m;j++)
{
a[2][j]-=(t*a[1][j]);
}
b[2][0]-=(t*b[1][0]);
printf("ntThe result is:n");
z=b[2][0]/a[2][2];
y=b[1][0]-(a[1][2]*z); /*…Printing the output…*/
x=b[0][0]-((a[0][1]*y)+(a[0][2]*z));
printf("ntx=%fnty=%fntz=%fn",x,y,z);
getch();
}
OUTPUT:
GAUSS ELIMINATION METHOD
*****************************
Input the raw size of first matrix: 3
Input the column size of first matrix: 3
Input the 9 elements to 3*3 matrix:
4 1 1
3 4 2
2 3 1
Input the raw size of second matrix: 3
Input the column size of second matrix: 1
Input the 3 elements to 3*1 matrix :
11
11
7
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-25-320.jpg)
![Matrix A:
4.000000 1.000000 1.000000
3.000000 4.000000 2.000000
2.000000 3.000000 1.000000
Matrix B:
11.000000
11.000000
7.000000
The result is:
x=2.333333
y=0.333333
z=1.333333
PROGRAM
/* program using Newtons divided difference formula*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<math.h>
void main()
{
float d[100][100],result,temp,unknown;
int m,n,i,j,k;
clrscr();
printf("Enter the limitn");
scanf("%d %d",&m,&n);
printf("Enter the values of xn");
for(i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf("%f",&d[i][0]);
}
printf("Enter the values of yn");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-26-320.jpg)
![scanf("%f",&d[i][1]);
}
printf("Enter the value where f(x) to be foundn");
scanf("%f",&unknown);
printf(" x t y");
for(i=0;i<=(n-2);i++)
{
printf(" ty%d",i);
printf(“---------------------------------------------------------------------“);
}
printf("n");
for(j=2;j<(n+1);j++)
{
k=j-1;
for(i=0;i<(n+1)-j;i++)
{
d[i][j]=(d[i+1][j-1]-d[i][j-1])/(d[k][0]-d[k-(j-1)][0]);
k++;
}
}
k=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("nn");
for(j=0;j<=n-k;j++)
{
printf(" %f ",d[i][j]);
}
k++;
}
result=d[0][1];
for(j=2;j<n+1;j++)
{
temp=1;
for(i=0;i<=j-2;i++)
{
temp=temp*(unknown-d[i][0]);
}
result+=temp*d[0][j];
}
printf("nnf(%f) = %f",unknown,result);
getch();
}
St.Mary’scollege,Thrissur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/n-150505051739-conversion-gate01/85/Numerical-Methods-in-C-27-320.jpg)


