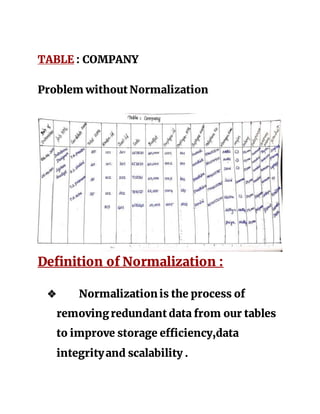
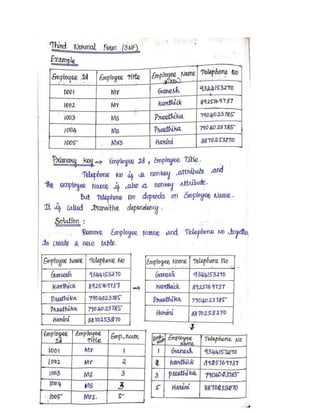
The document discusses database normalization. Normalization is the process of organizing data to avoid data redundancy and inconsistencies. It involves splitting tables and rejoining them through relationships. There are several normal forms that data can be organized into from 1st normal form to 5th normal form, each addressing different types of dependencies and relationships to minimize data anomalies. The goal of normalization is to organize data to reduce storage, improve flexibility, and avoid data problems like duplication, insertion, deletion, and update anomalies.