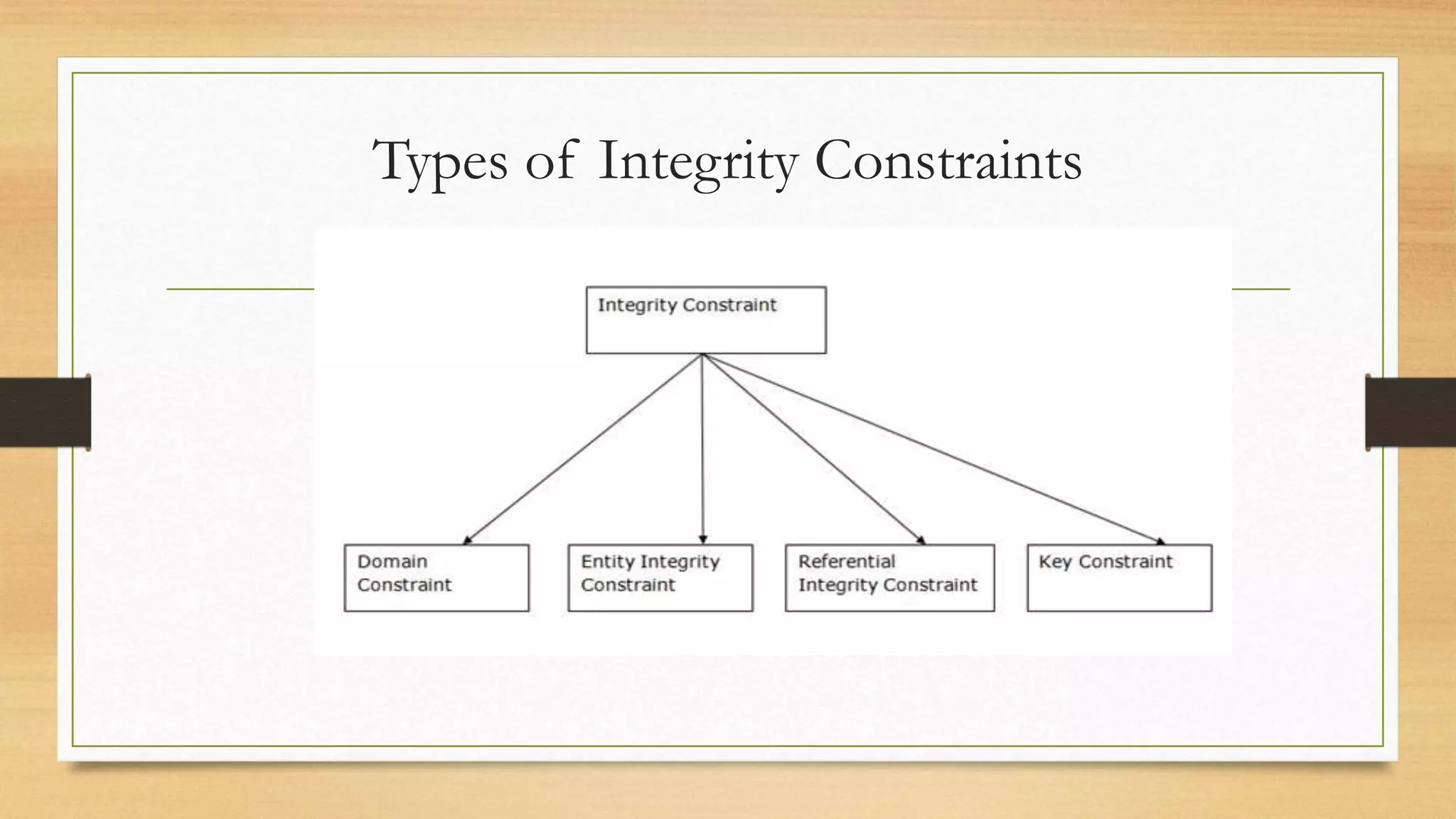
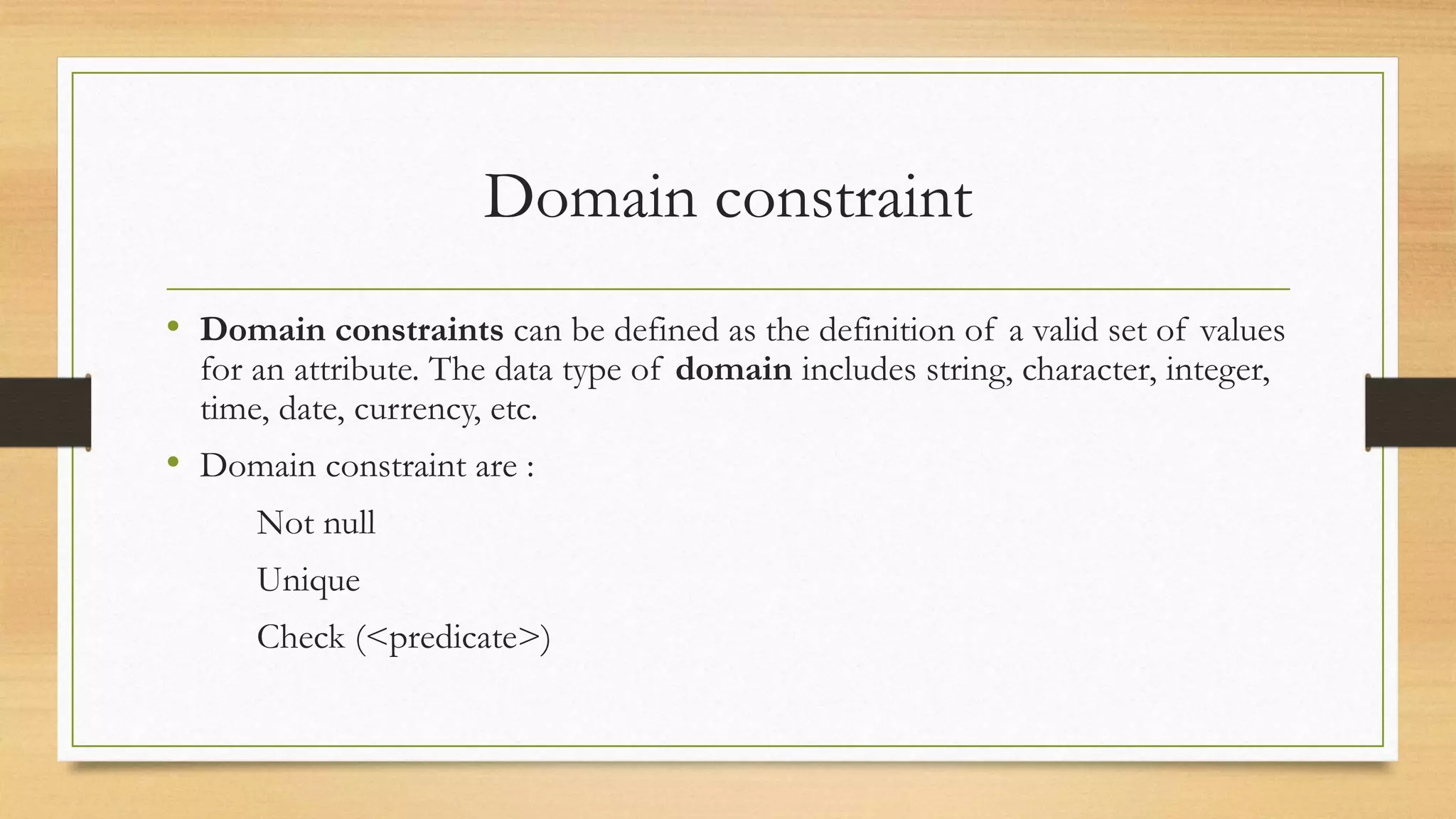
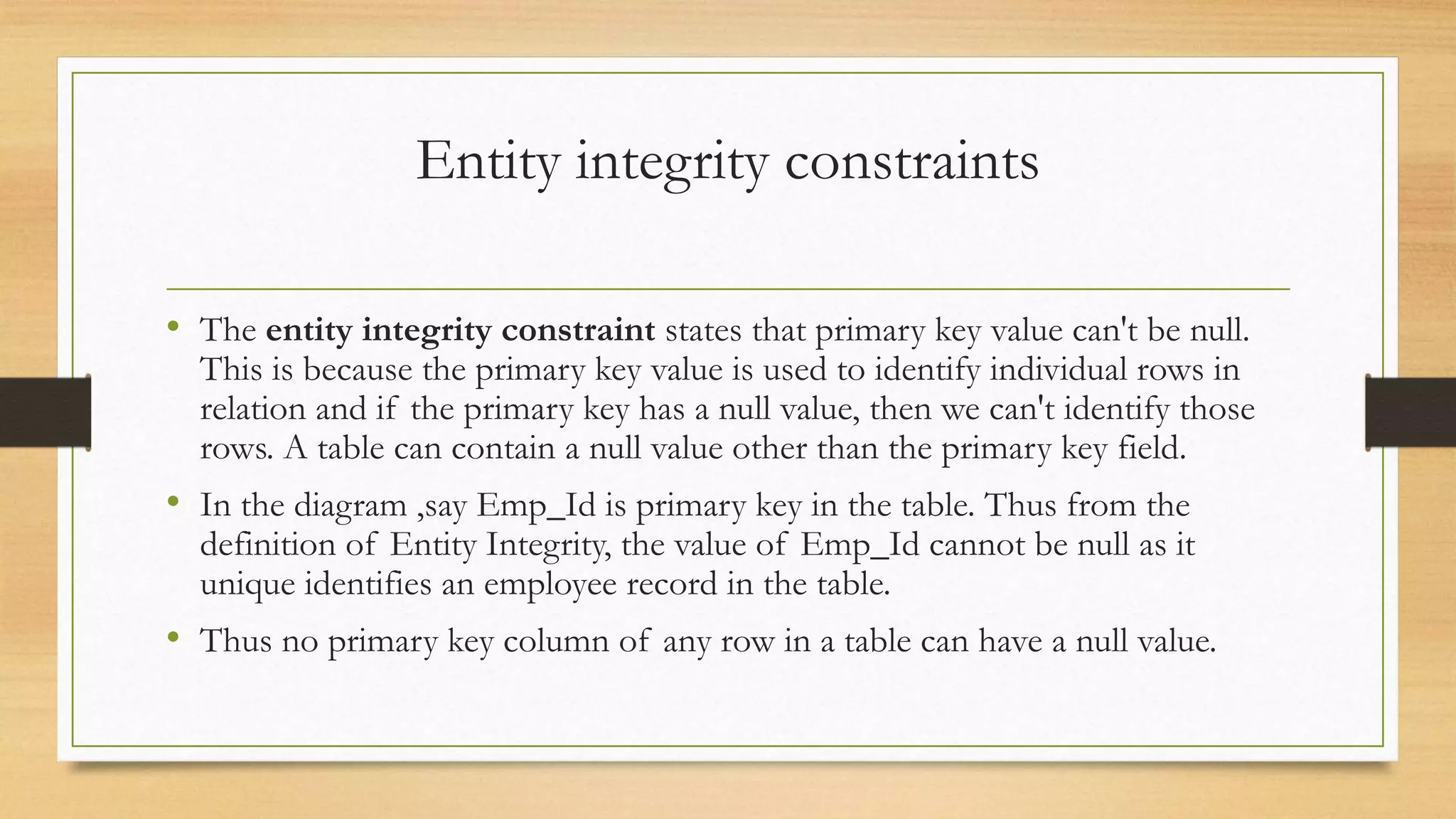
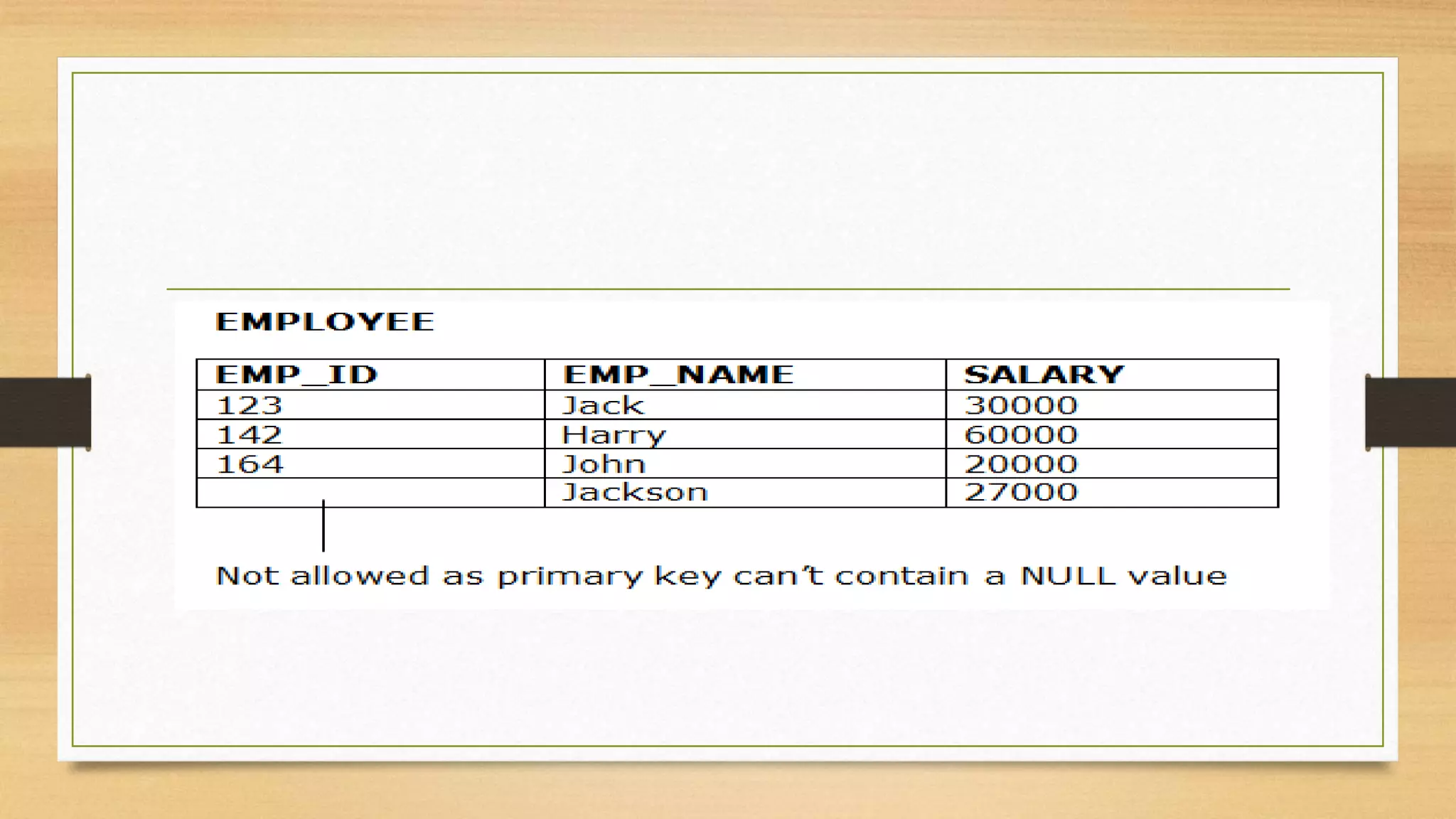
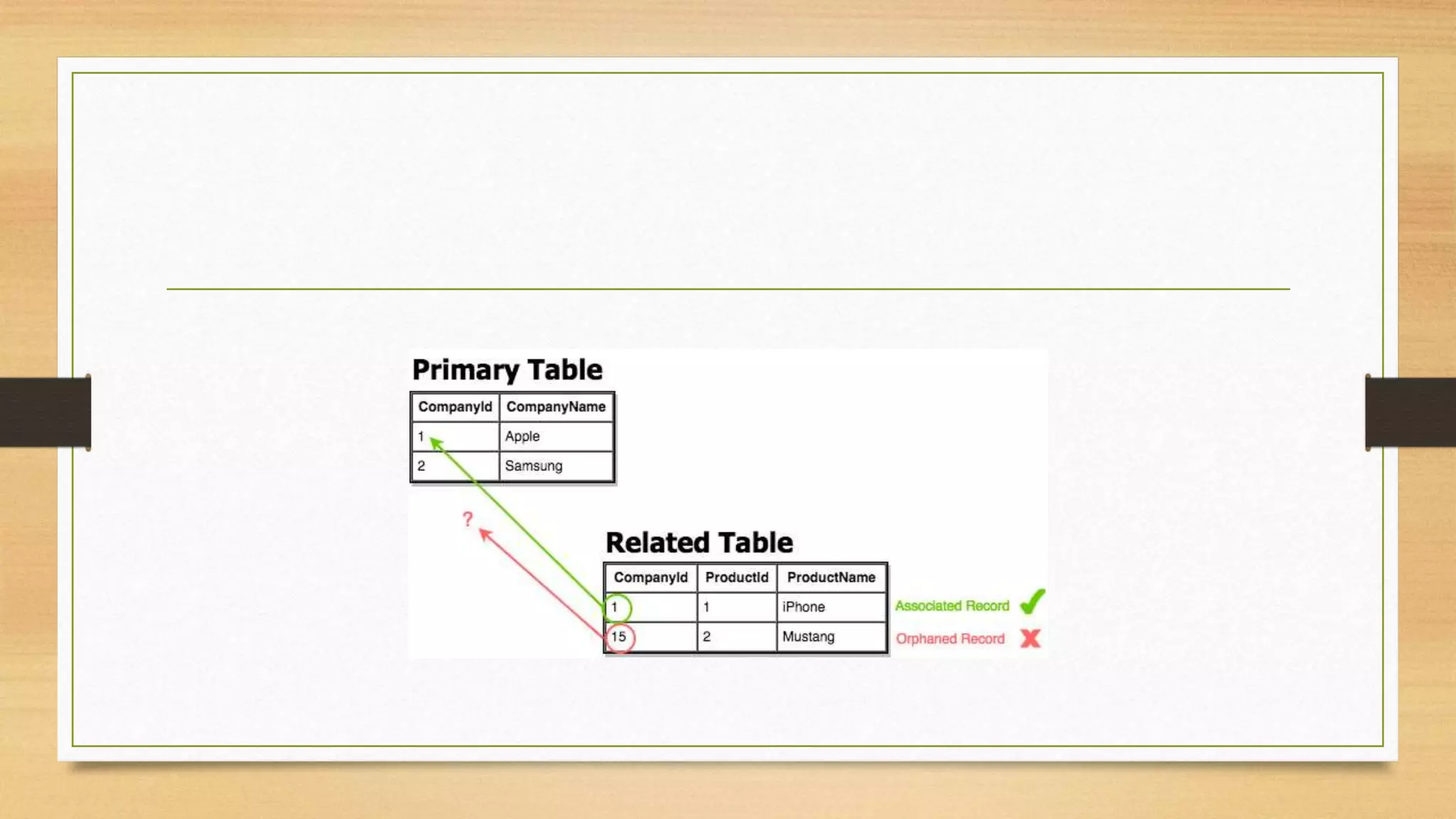
Integrity constraints are rules used to maintain data quality and ensure accuracy in a relational database. The main types of integrity constraints are domain constraints, which define valid value sets for attributes; NOT NULL constraints, which enforce non-null values; UNIQUE constraints, which require unique values; and CHECK constraints, which specify value ranges. Referential integrity links data between tables through foreign keys, preventing orphaned records. Integrity constraints are enforced by the database to guard against accidental data damage.