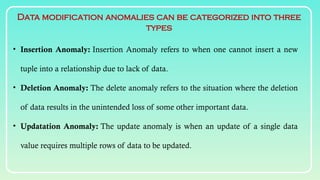
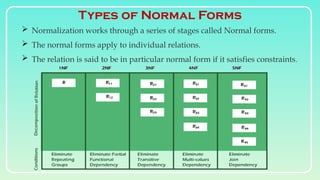
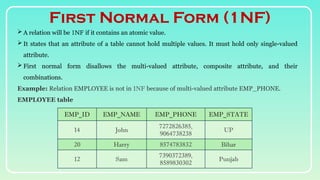
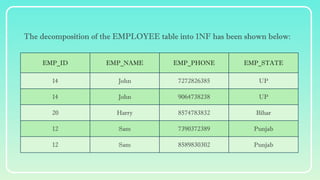
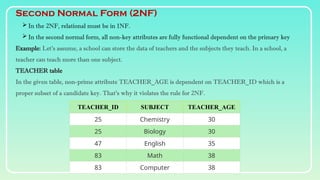
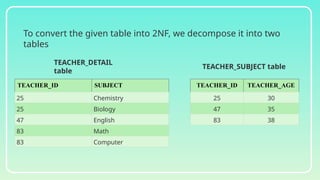
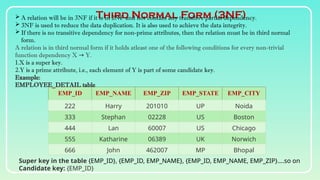
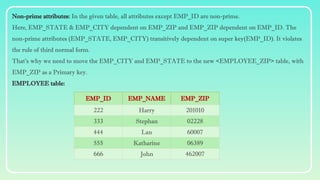
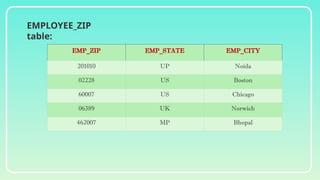
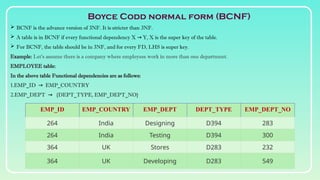
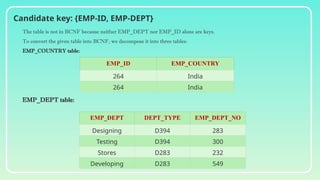
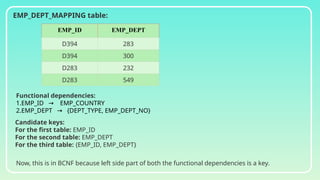
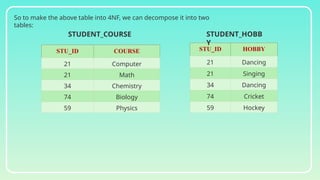
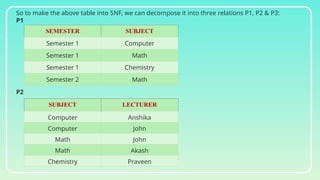
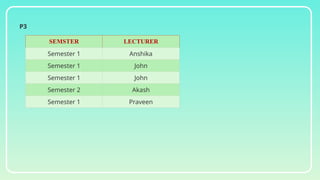
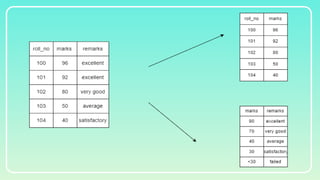
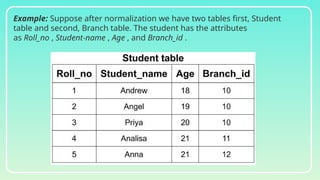
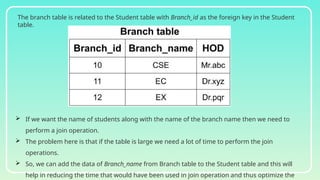
Database normalization is the process of organizing data to minimize redundancy and eliminate anomalies such as insertion, update, and deletion issues. It involves dividing larger tables into smaller ones and applying various normal forms (1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF, 4NF, 5NF) to ensure data integrity and consistency. While normalization has significant advantages in terms of data organization and integrity, it can also lead to performance degradation and increased complexity during database design.