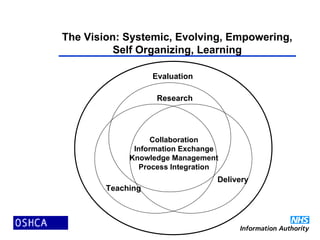
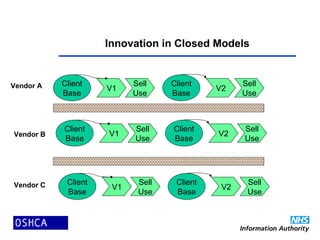
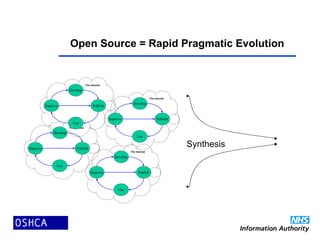
1) The document discusses the propagation of open source software in healthcare and argues that it is inevitable. It provides an overview of open source, how and why it works, examples of open source healthcare projects, and where open source in healthcare is heading.
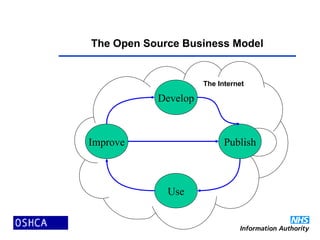
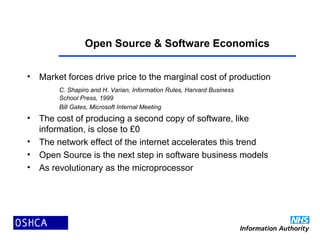
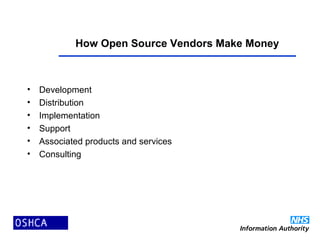
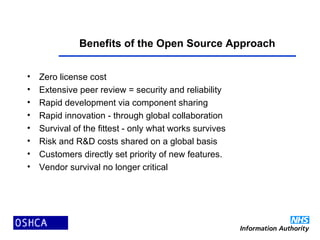
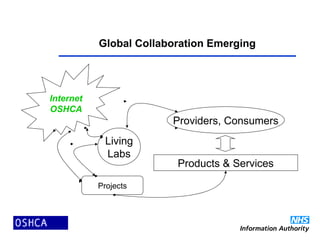
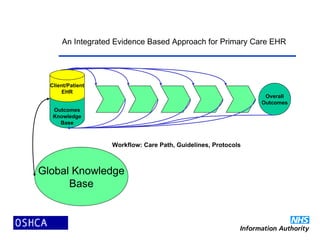
2) Open source software is developed and improved through global collaboration, with the source code freely available. It allows for rapid innovation and customization to user needs at low cost. Examples of emerging open source healthcare projects and alliances are described.
3) The propagation of open source models in healthcare will create virtuous spirals of shared learning and cost reduction. It lever