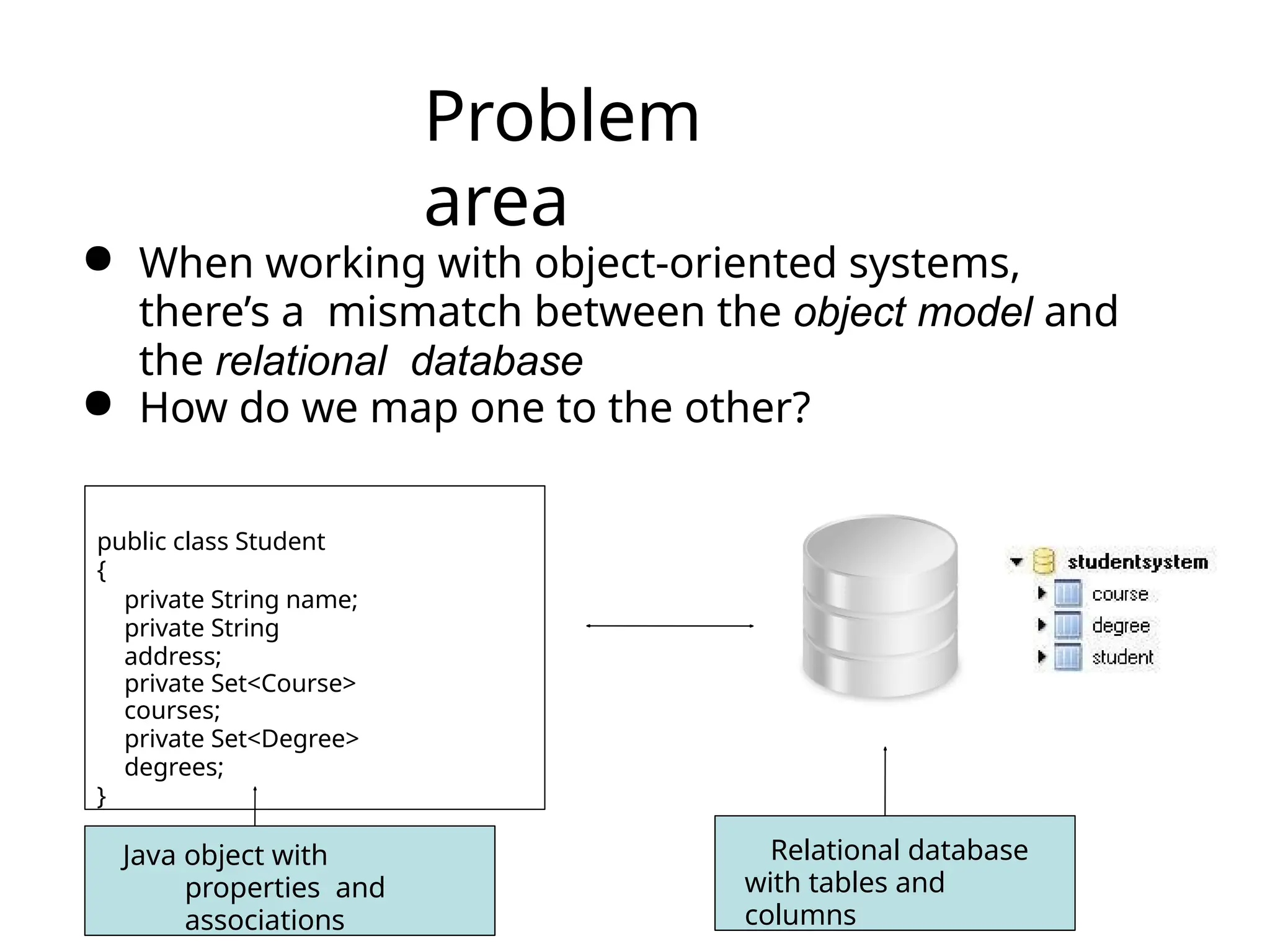
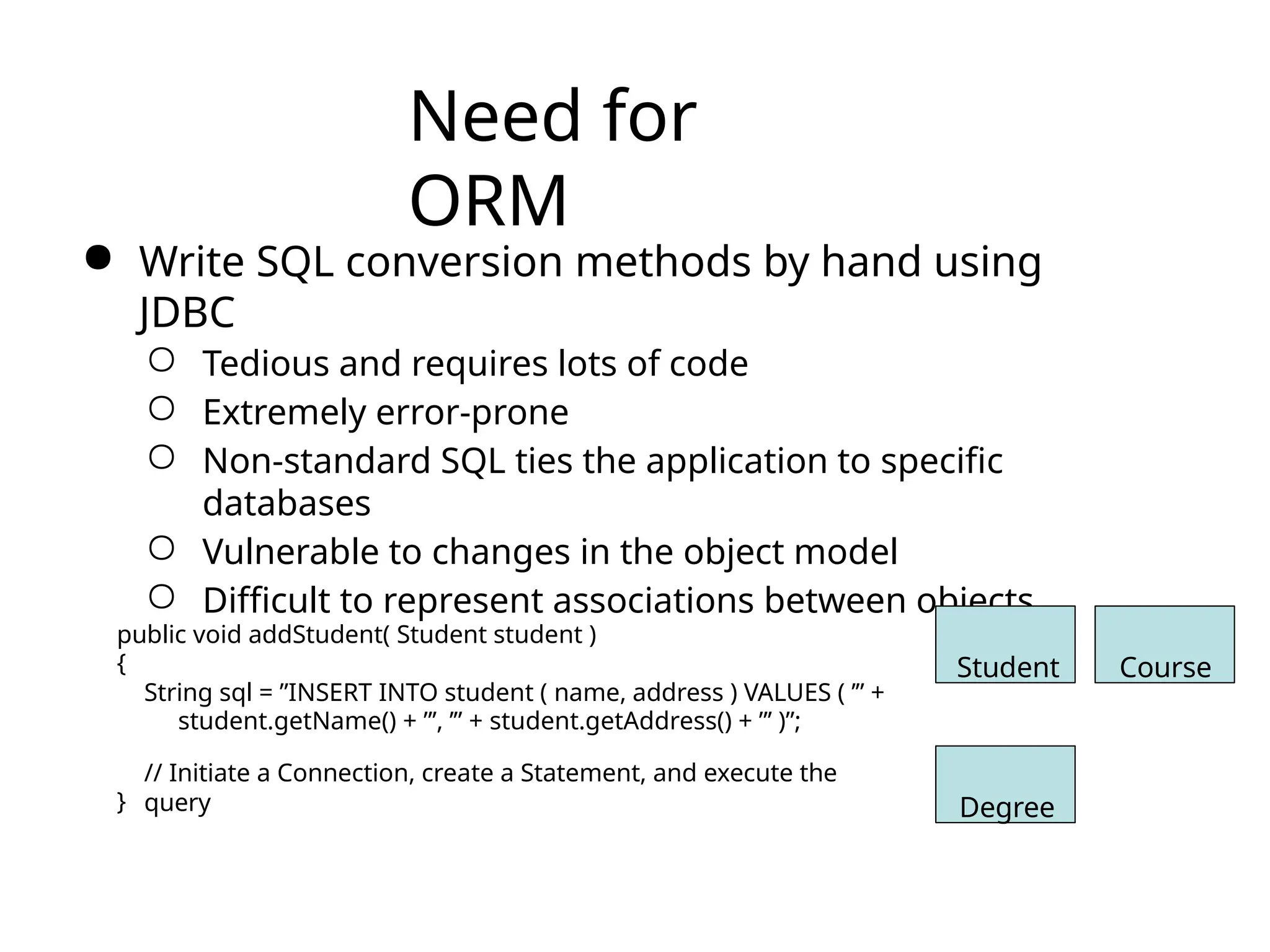
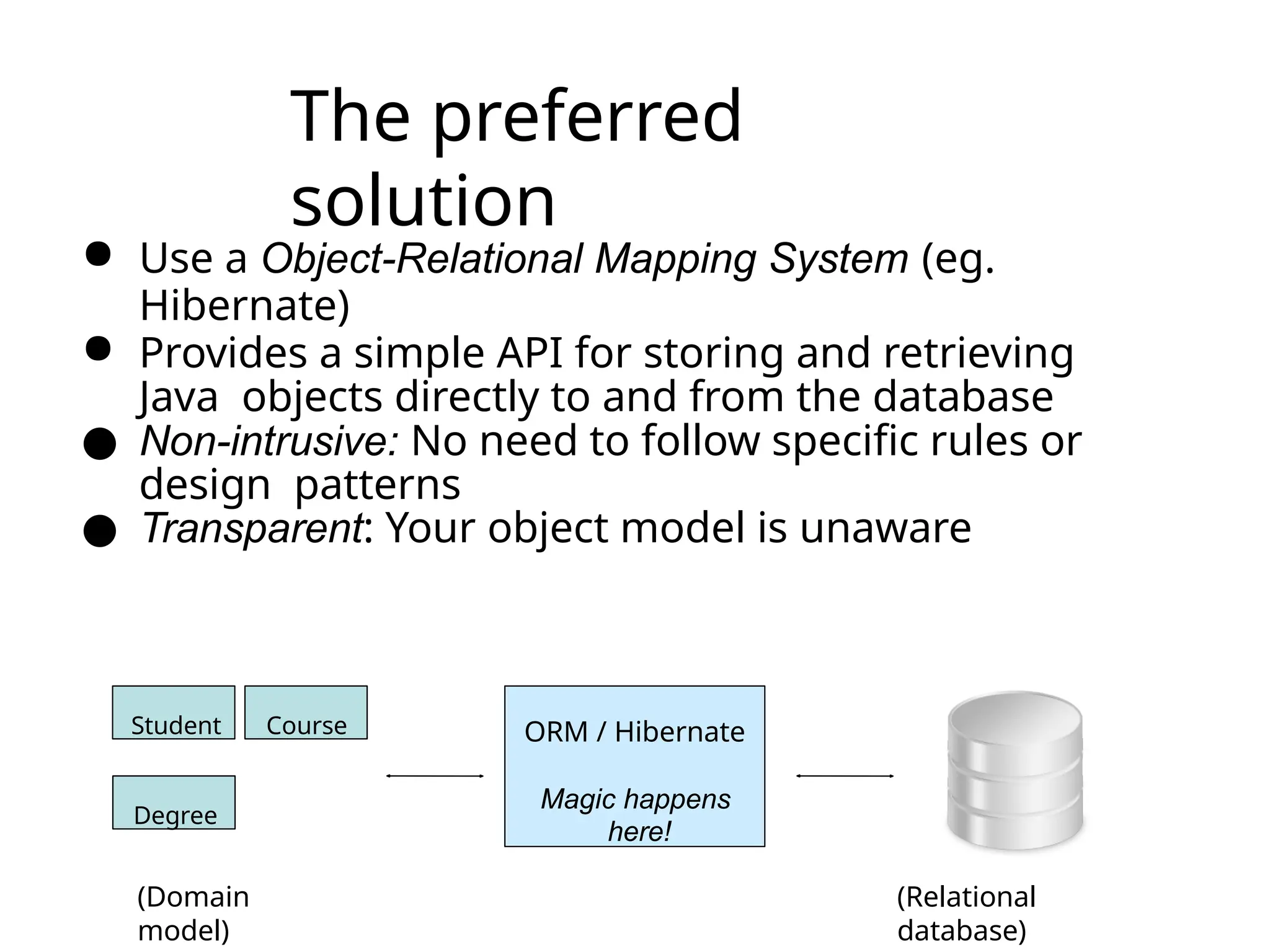
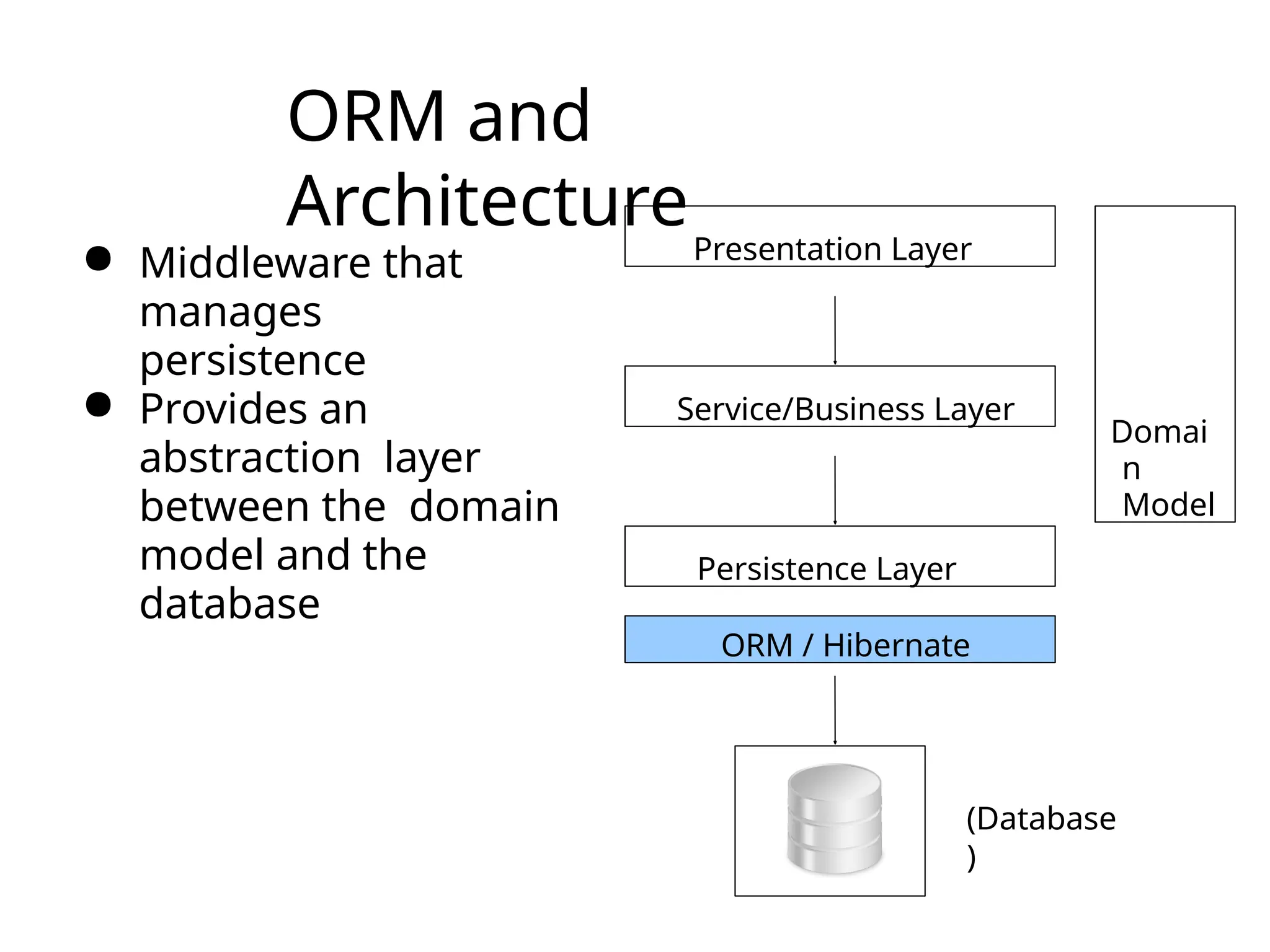
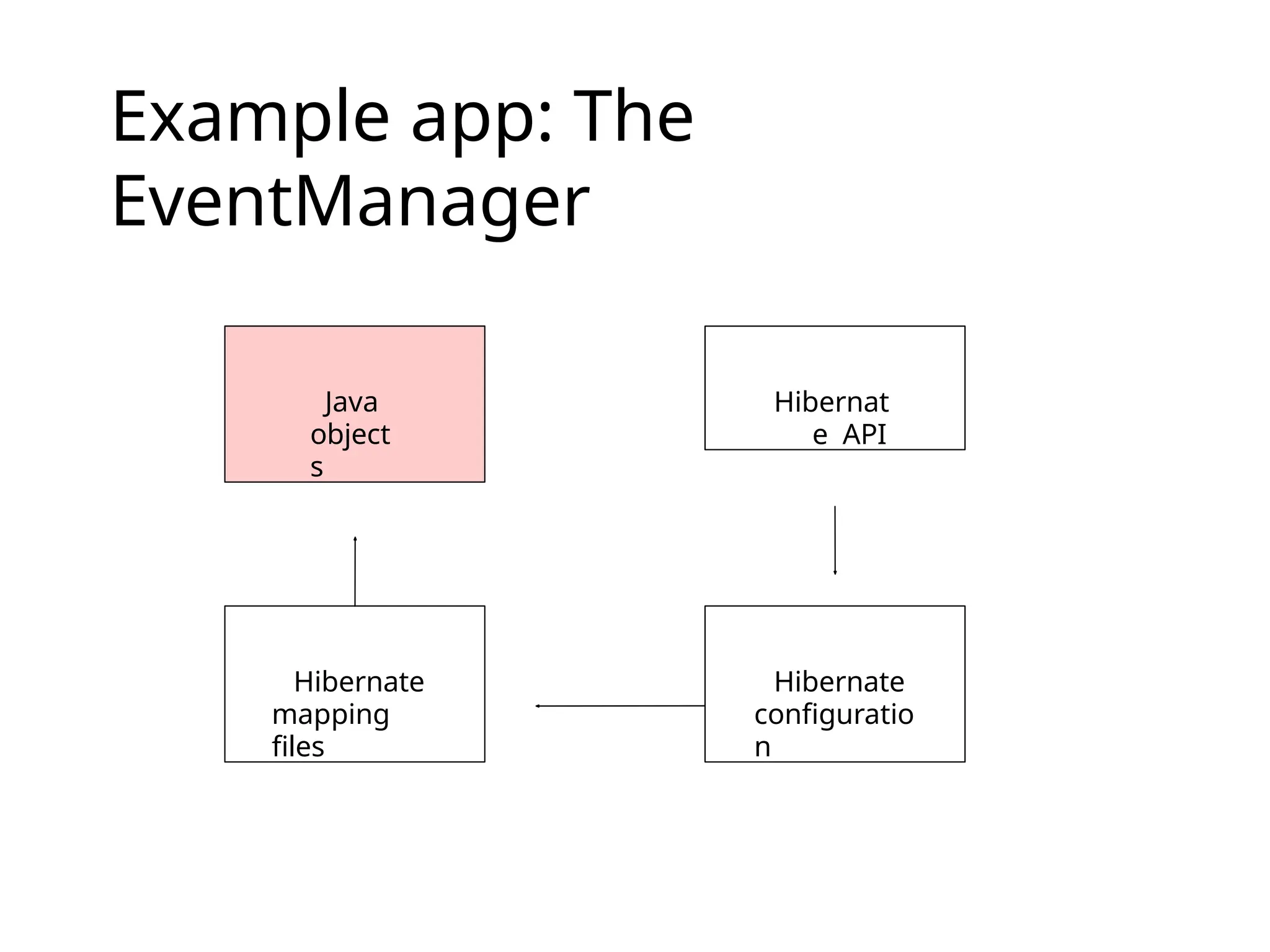
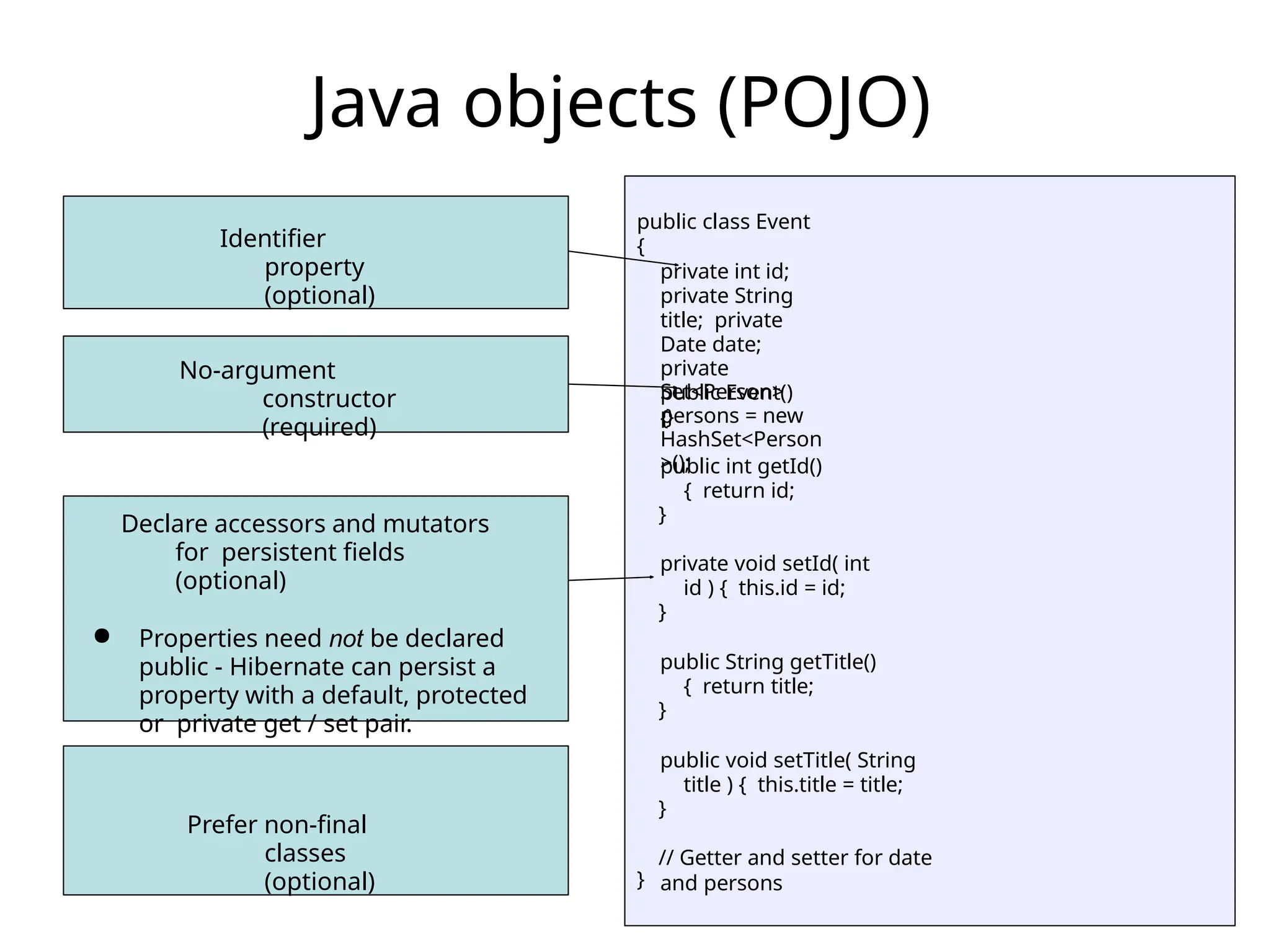
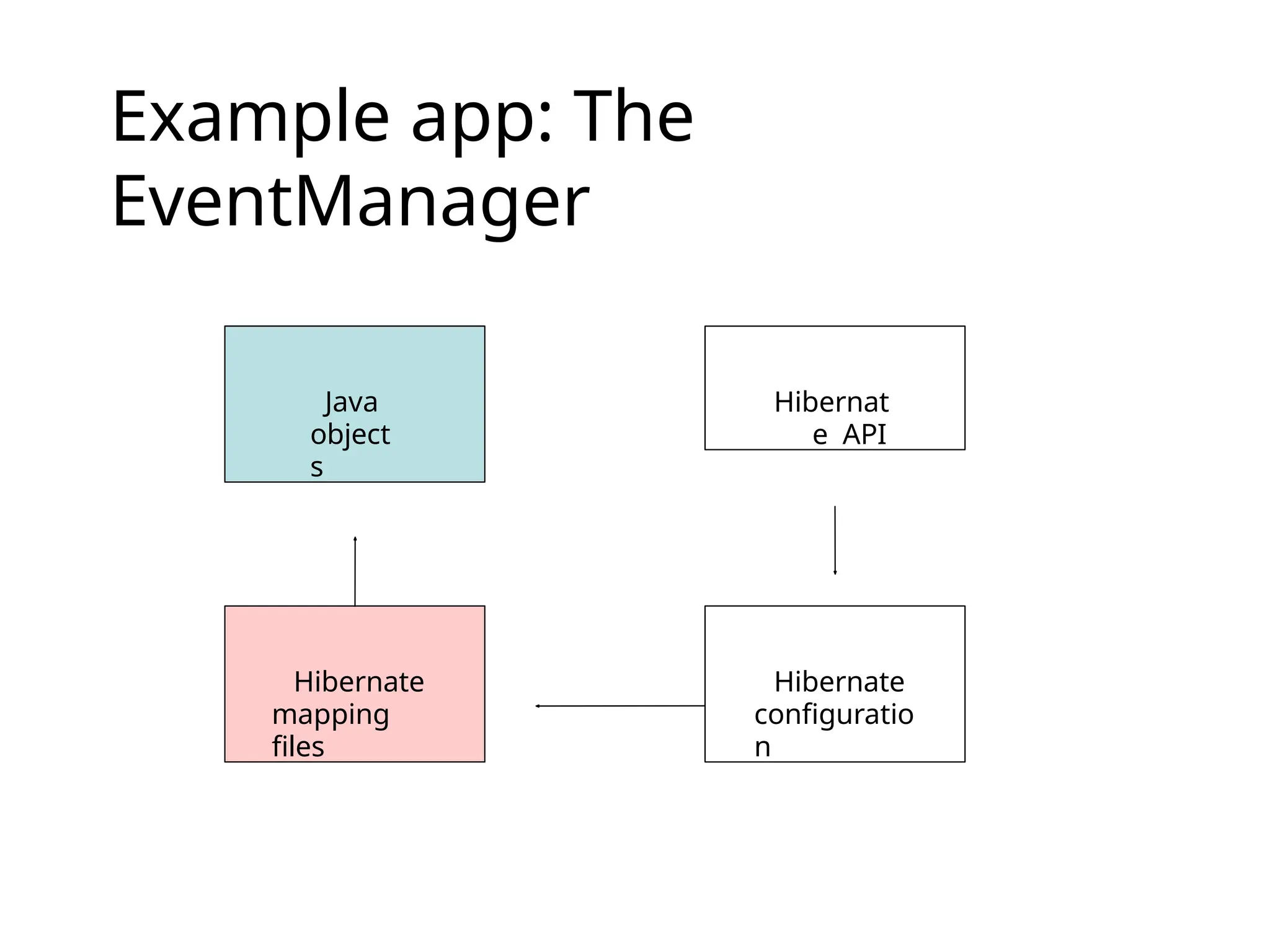
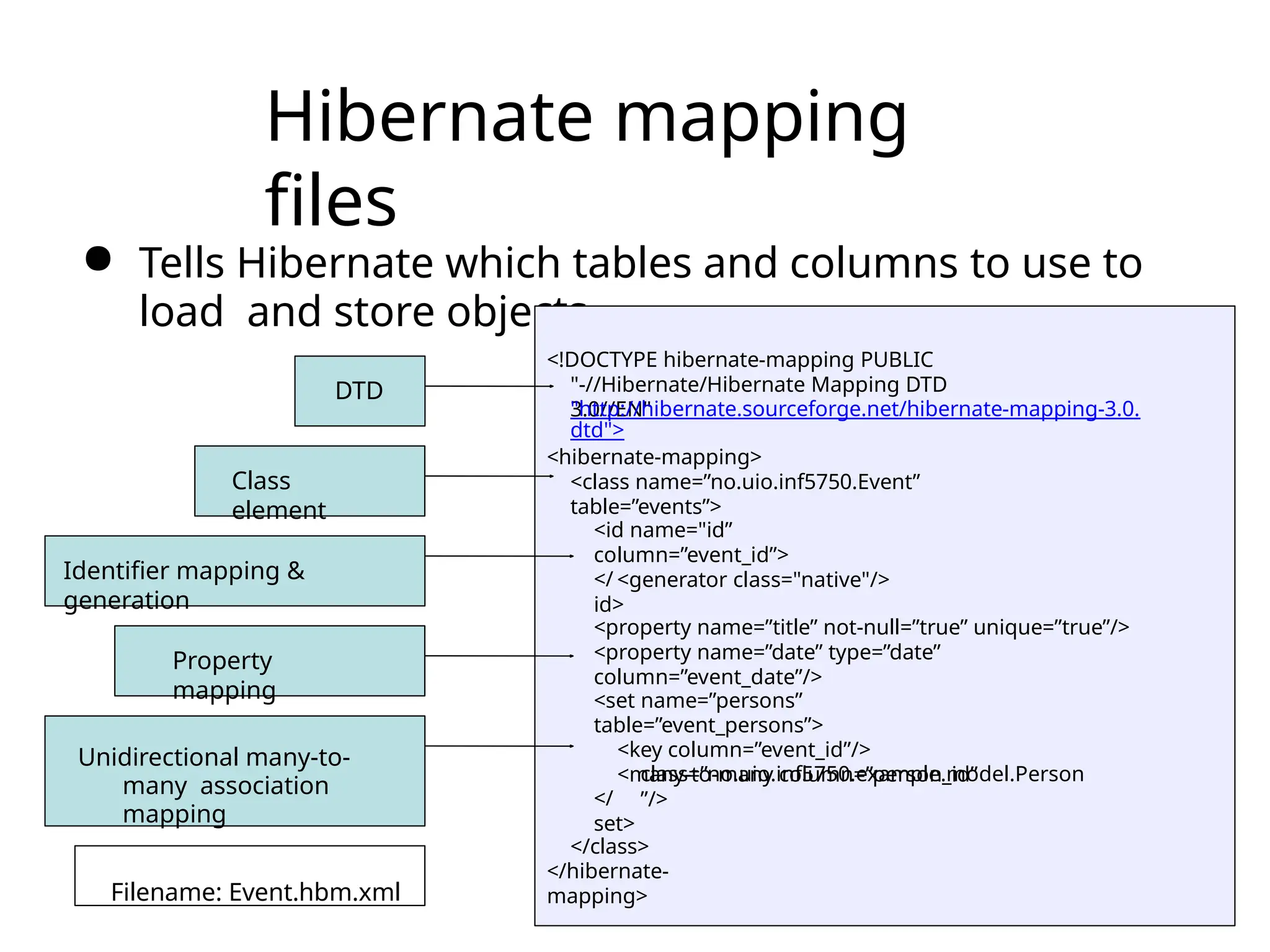
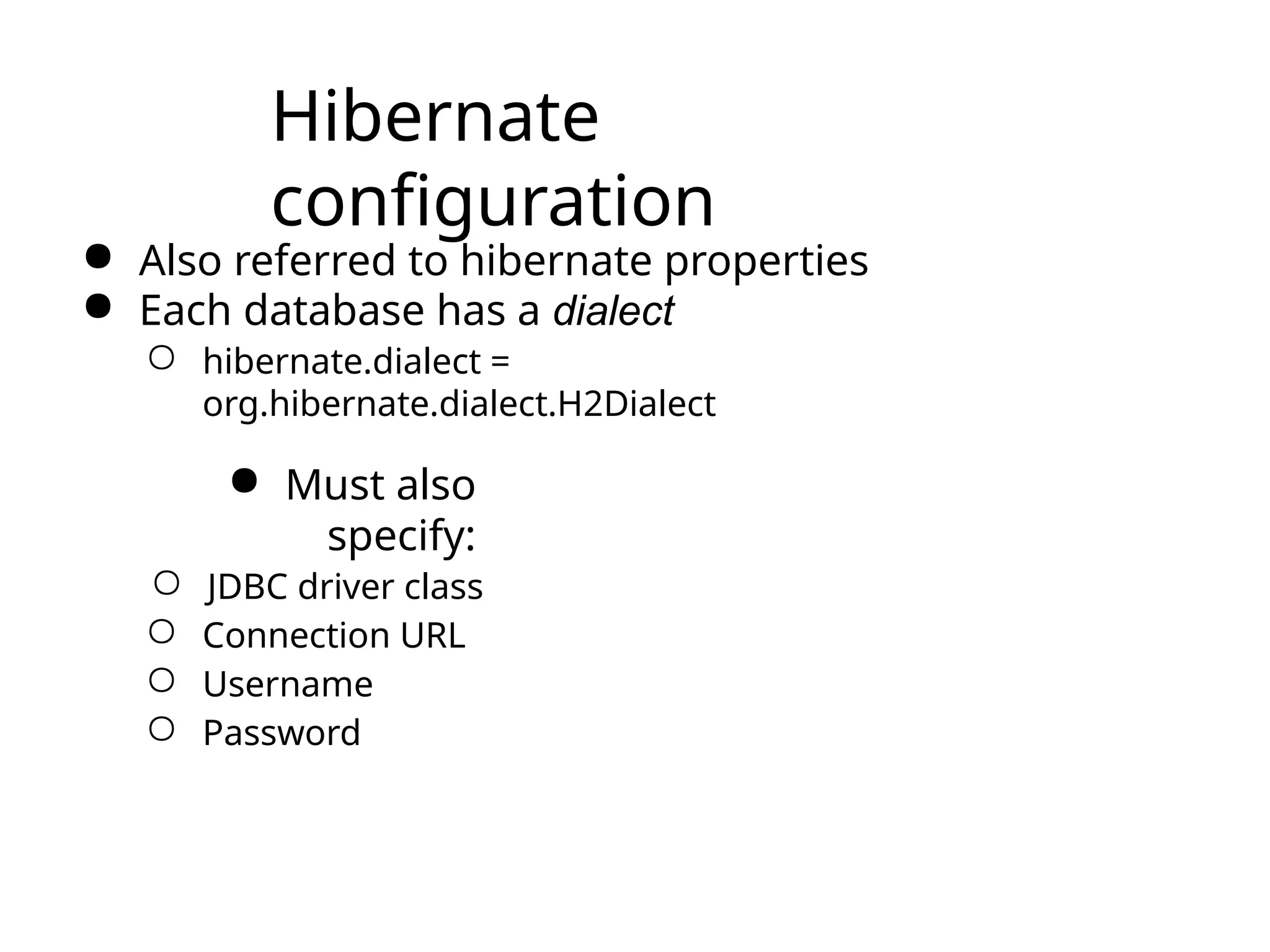
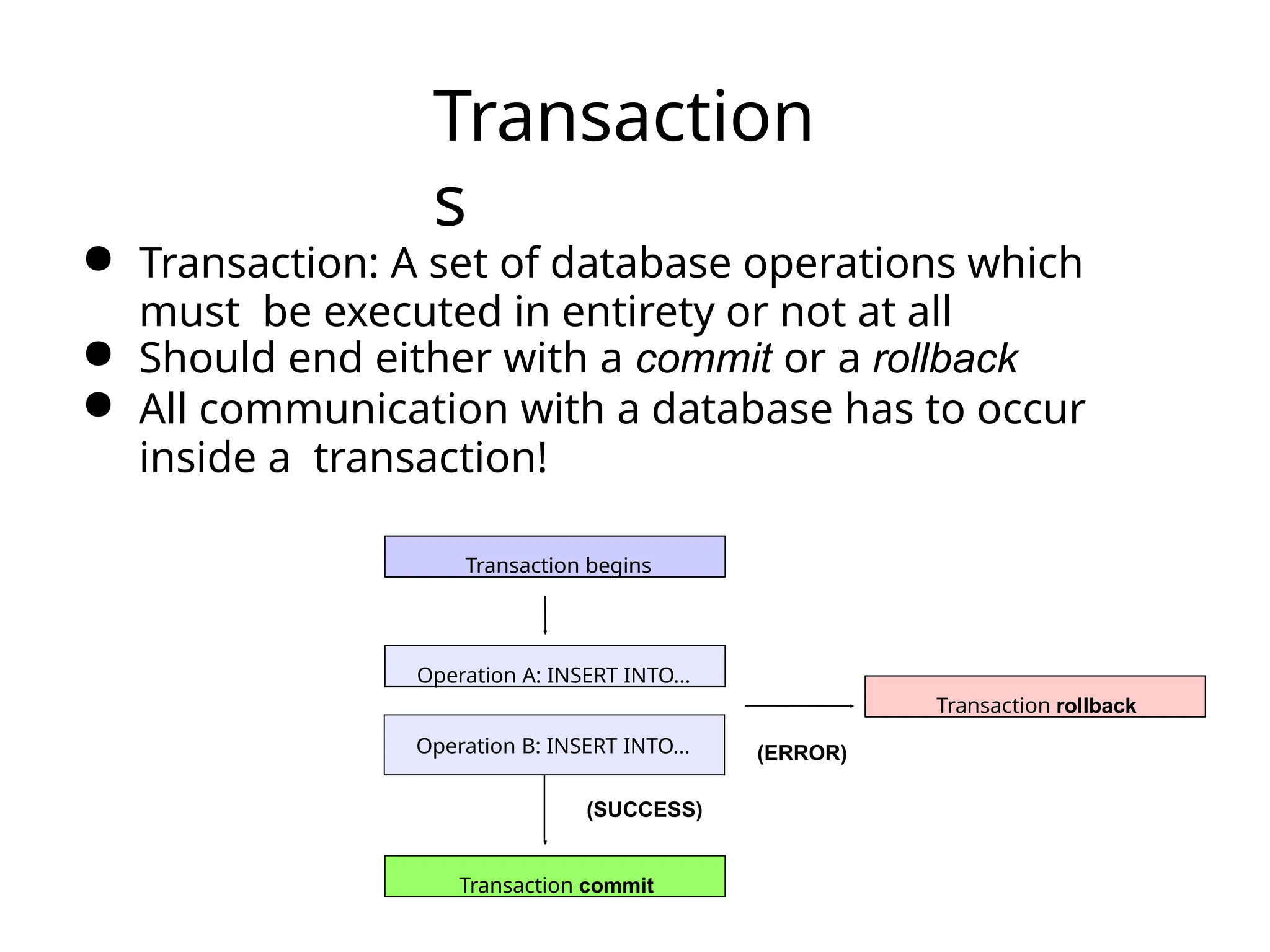
The document discusses the challenges of object-relational mapping (ORM) in Java, particularly the mismatch between object models and relational databases, and highlights Hibernate as the preferred solution for simplifying this process. It outlines how Hibernate allows for the direct storage and retrieval of Java objects without the need for extensive SQL coding. The document also explains some key concepts of Hibernate, including mapping files, configuration settings, and the importance of transactions in database operations.