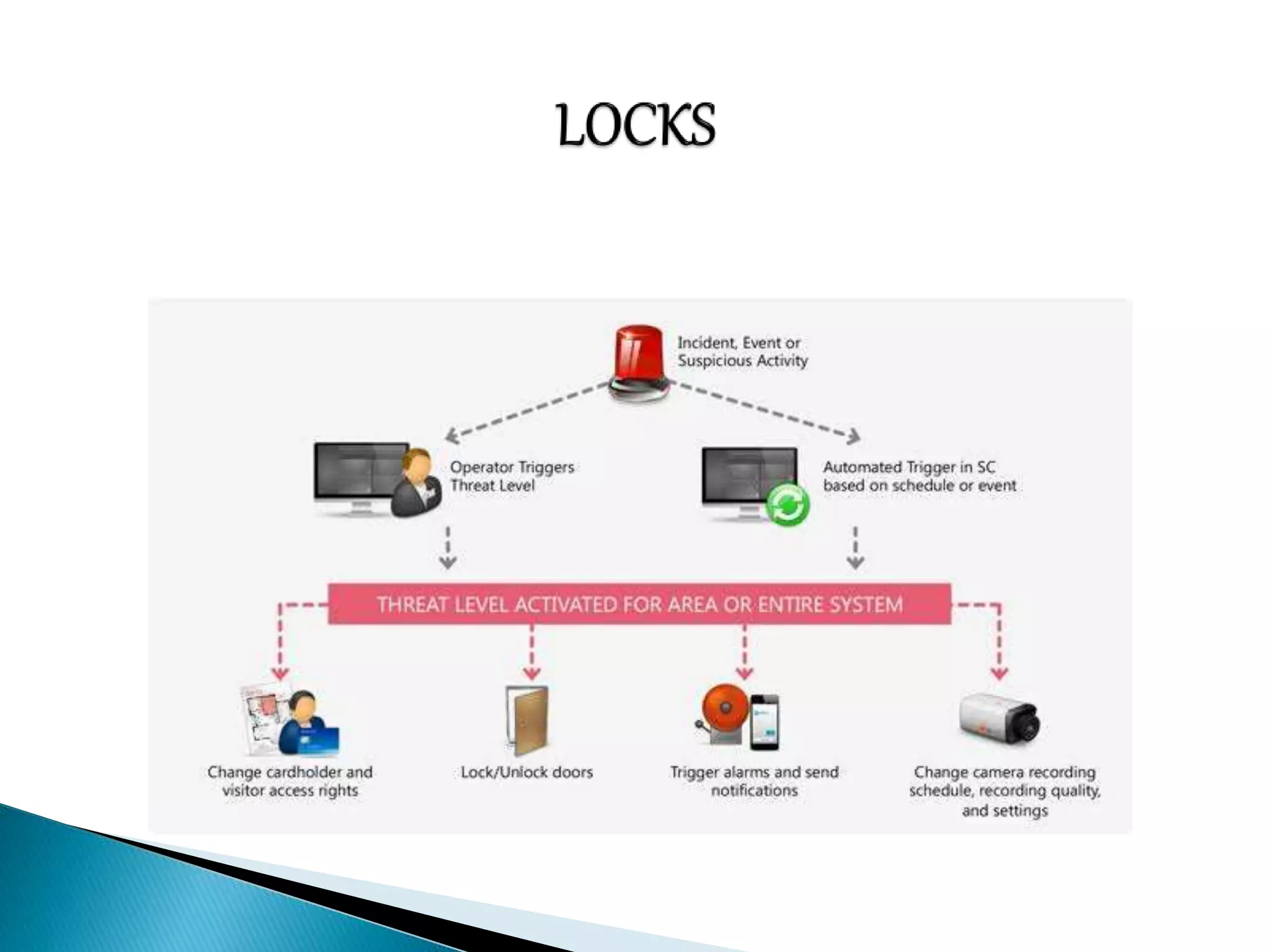
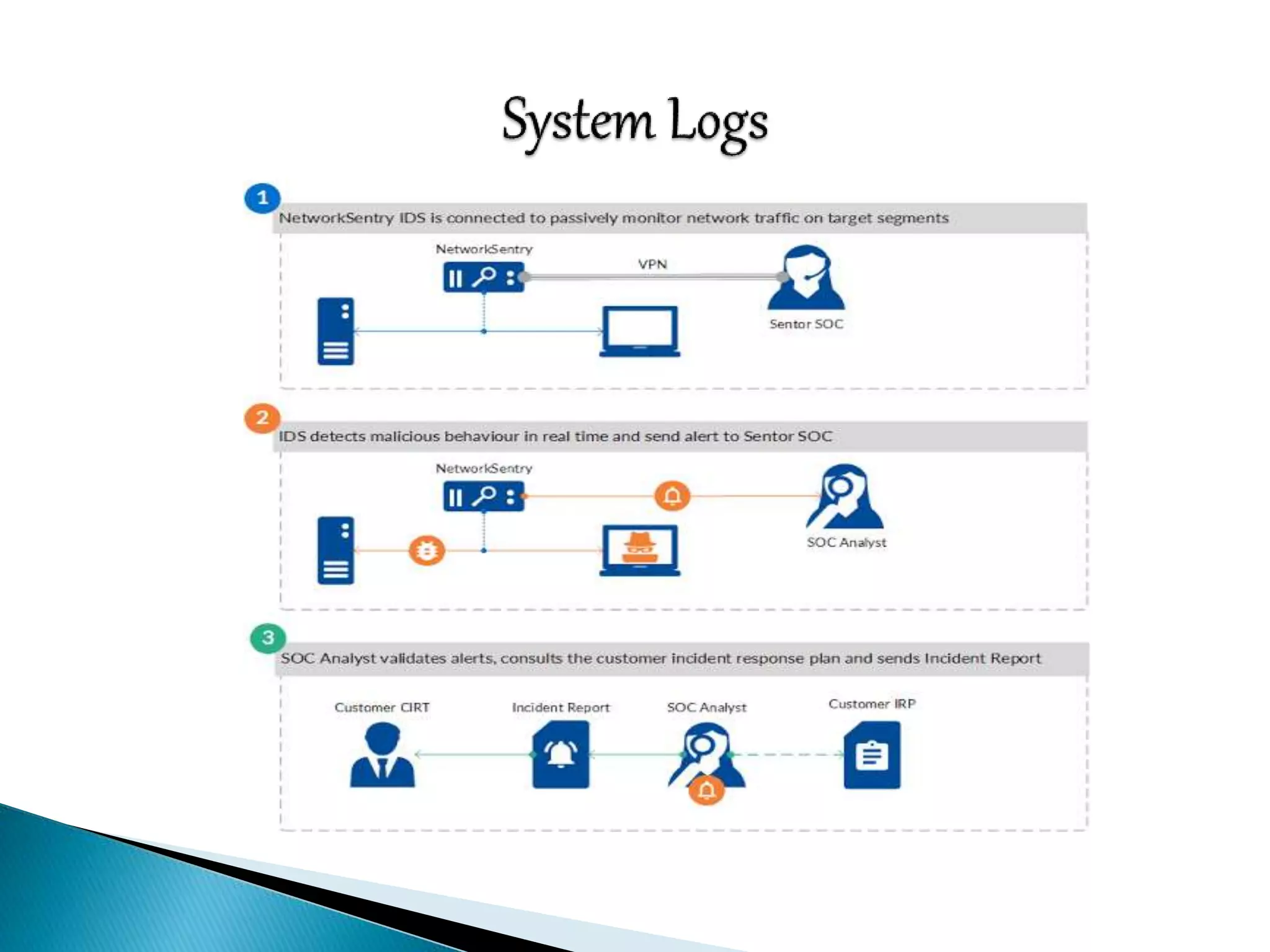
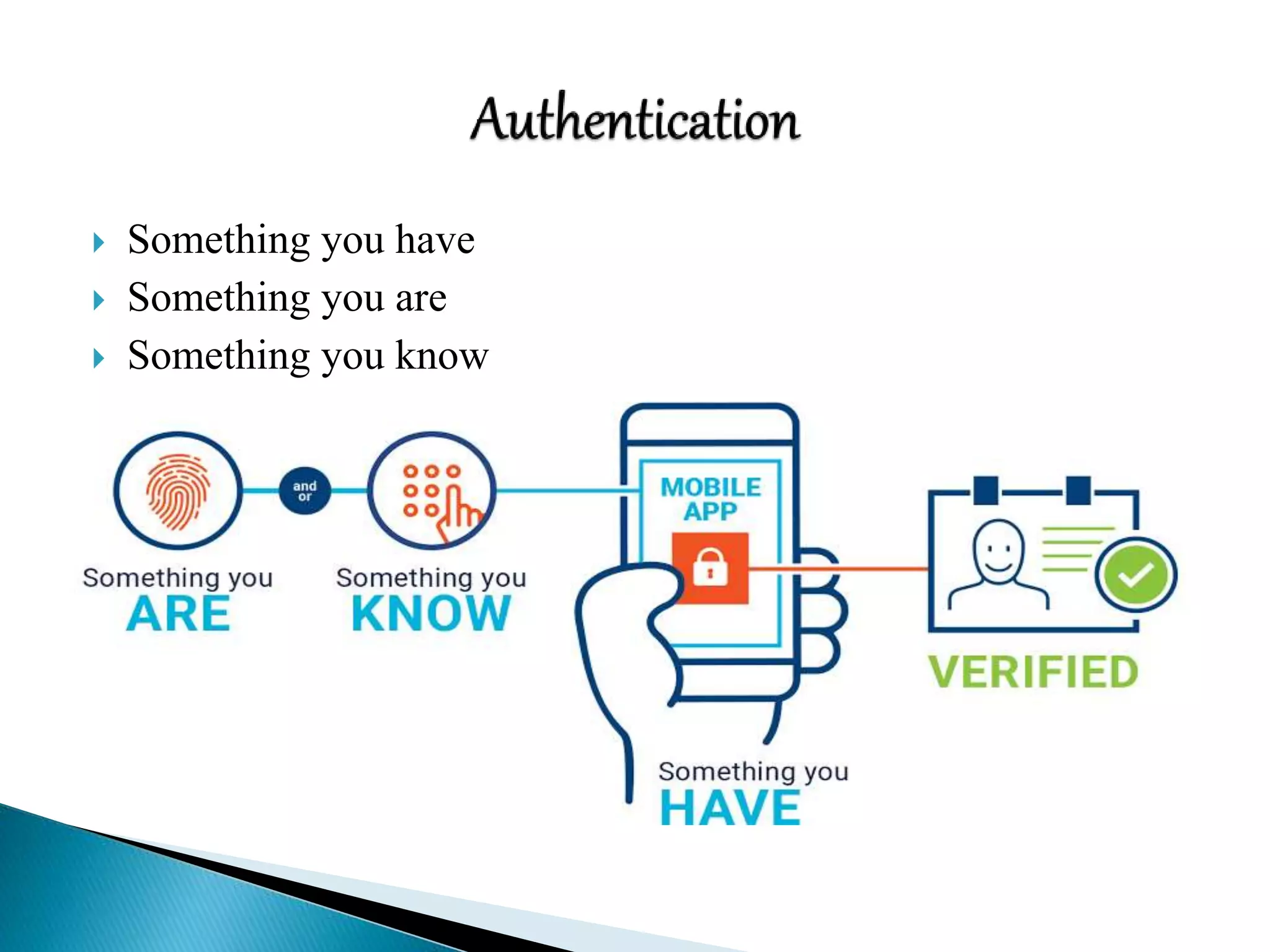
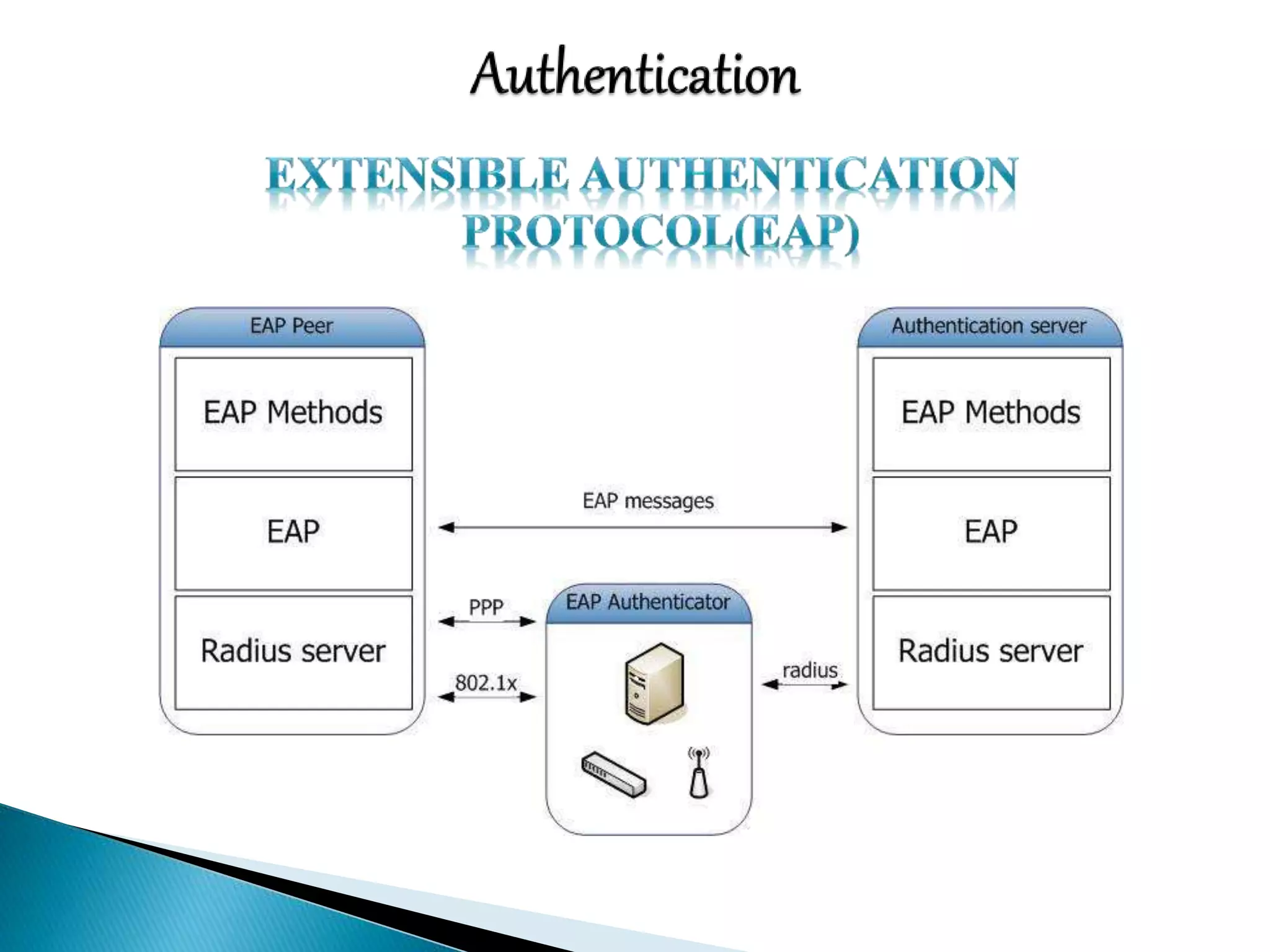
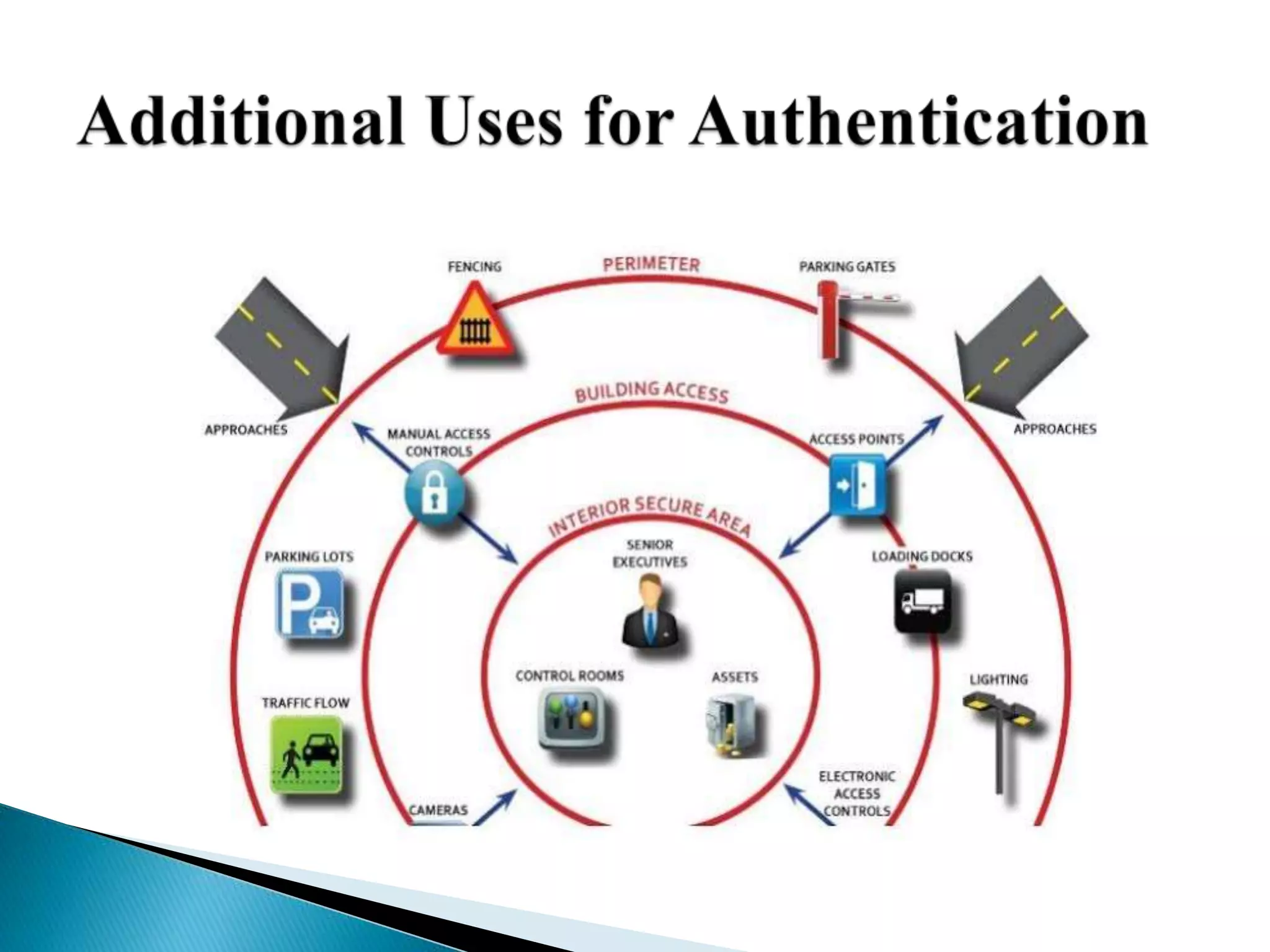
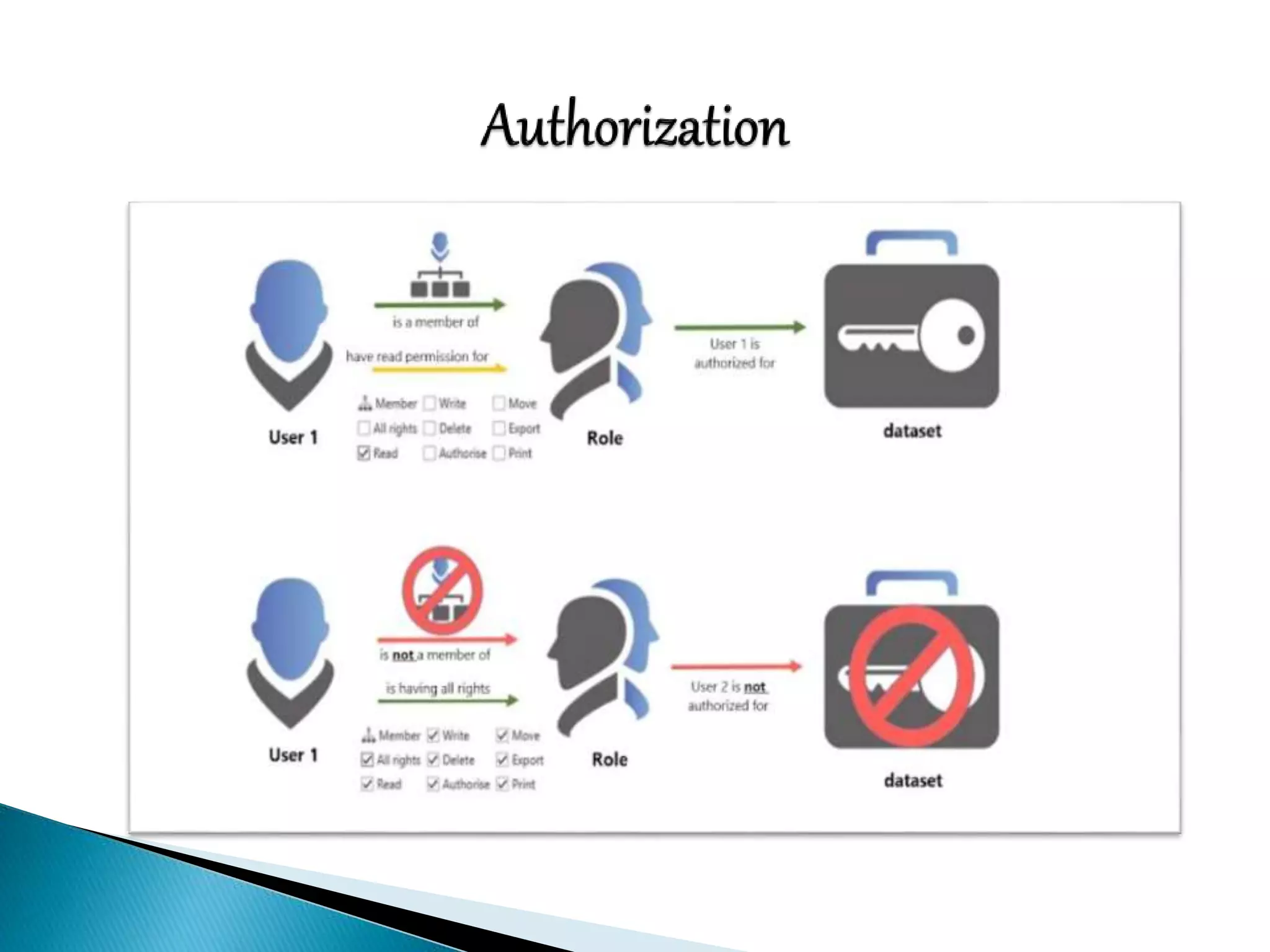
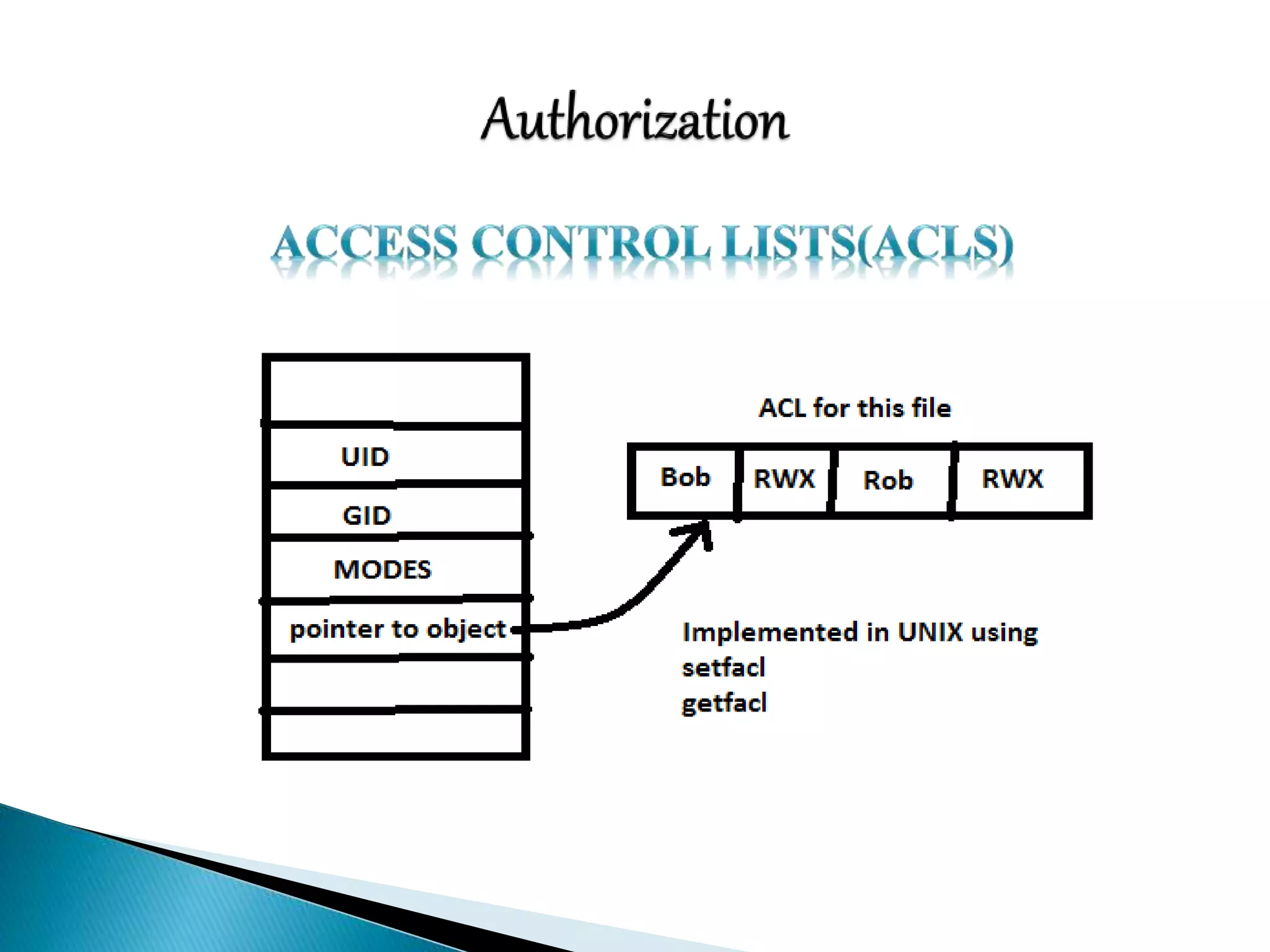
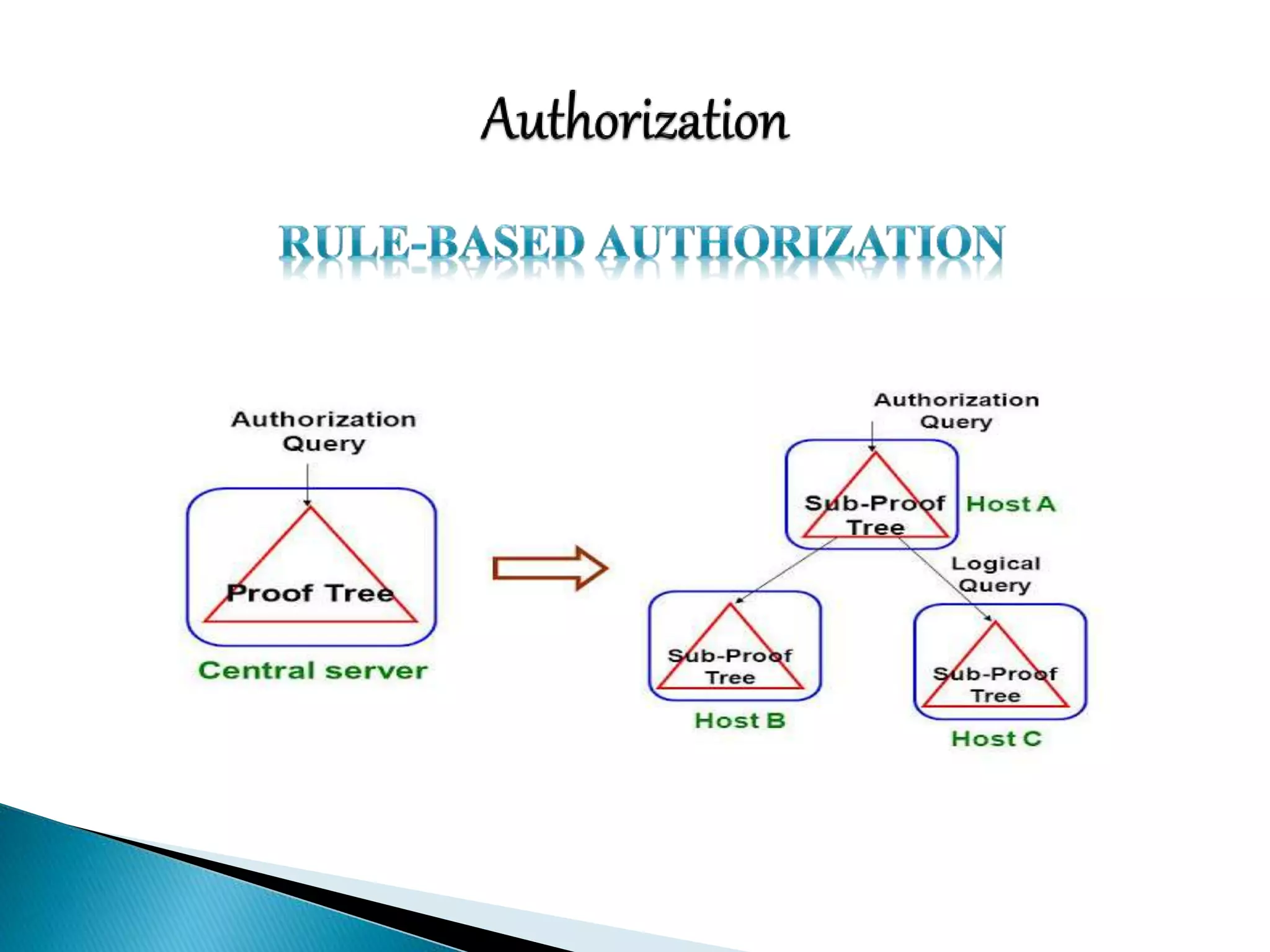
This document discusses various aspects of physical security for assets. It covers classifying physical assets, conducting physical vulnerability assessments, choosing secure site locations, securing assets with physical controls like locks and entry systems, implementing physical intrusion detection methods like CCTV, alarms, and mantraps, and the importance of authentication and authorization controls.