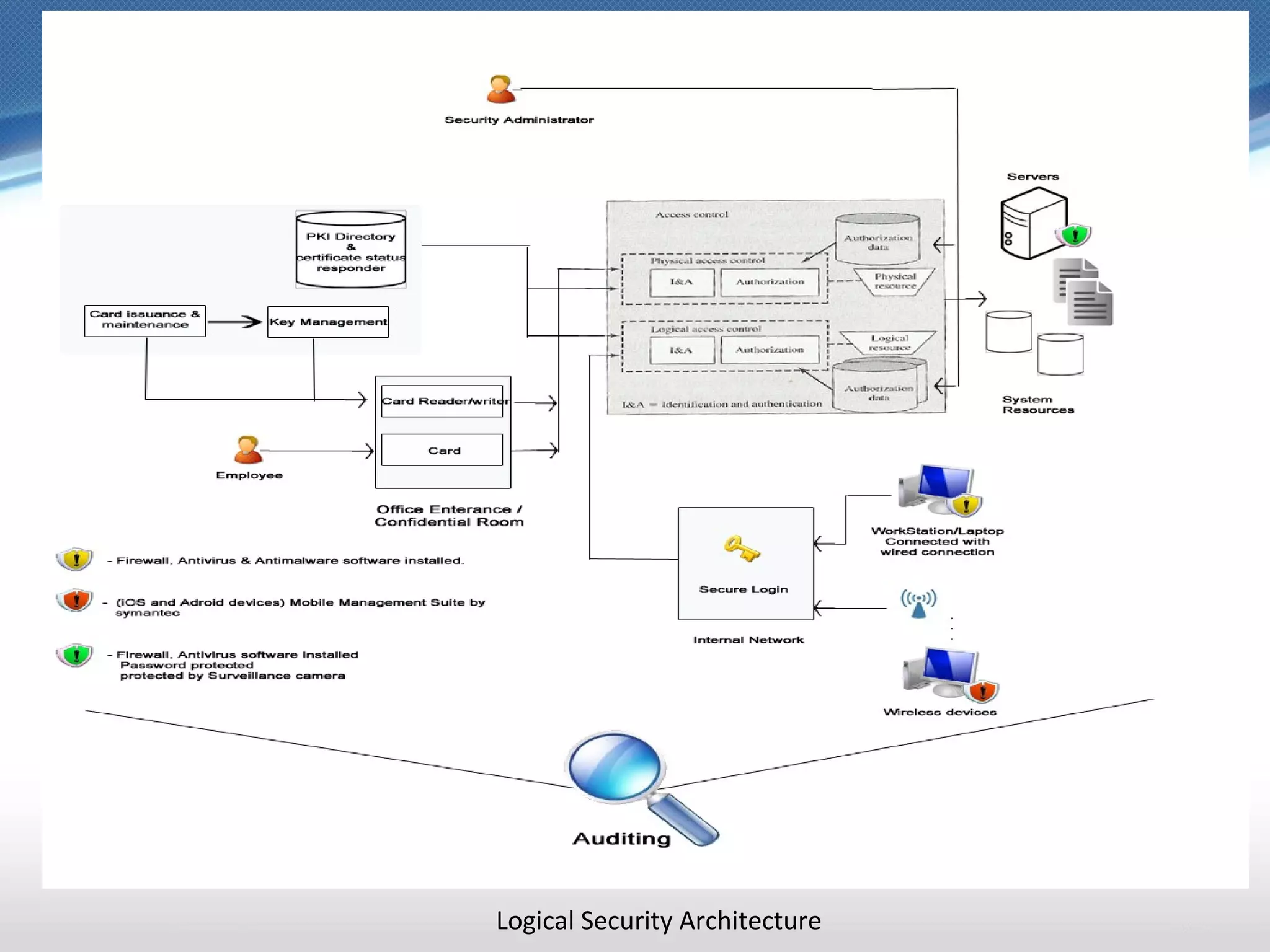
The document discusses security architecture, including security policies, logical security architecture, and physical security architecture. Some key points include establishing policies for password selection, software installations, and email use. The logical security architecture recommends appointing a security administrator, using role-based access controls, auditing user actions, and malware protection. The physical security architecture suggests securing server hardware, installing intrusion detection systems, and restricting access to critical resources and the facility.