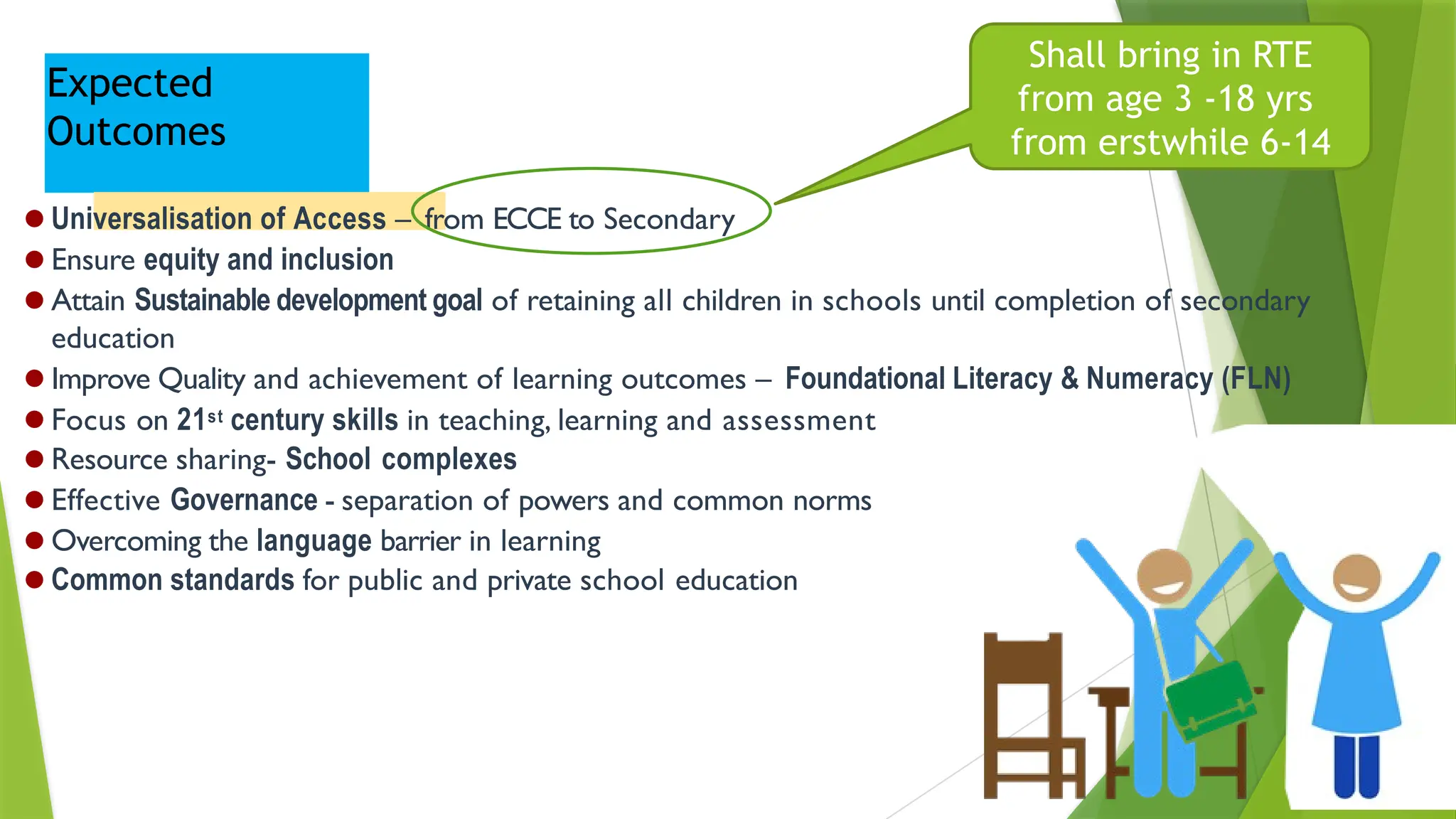
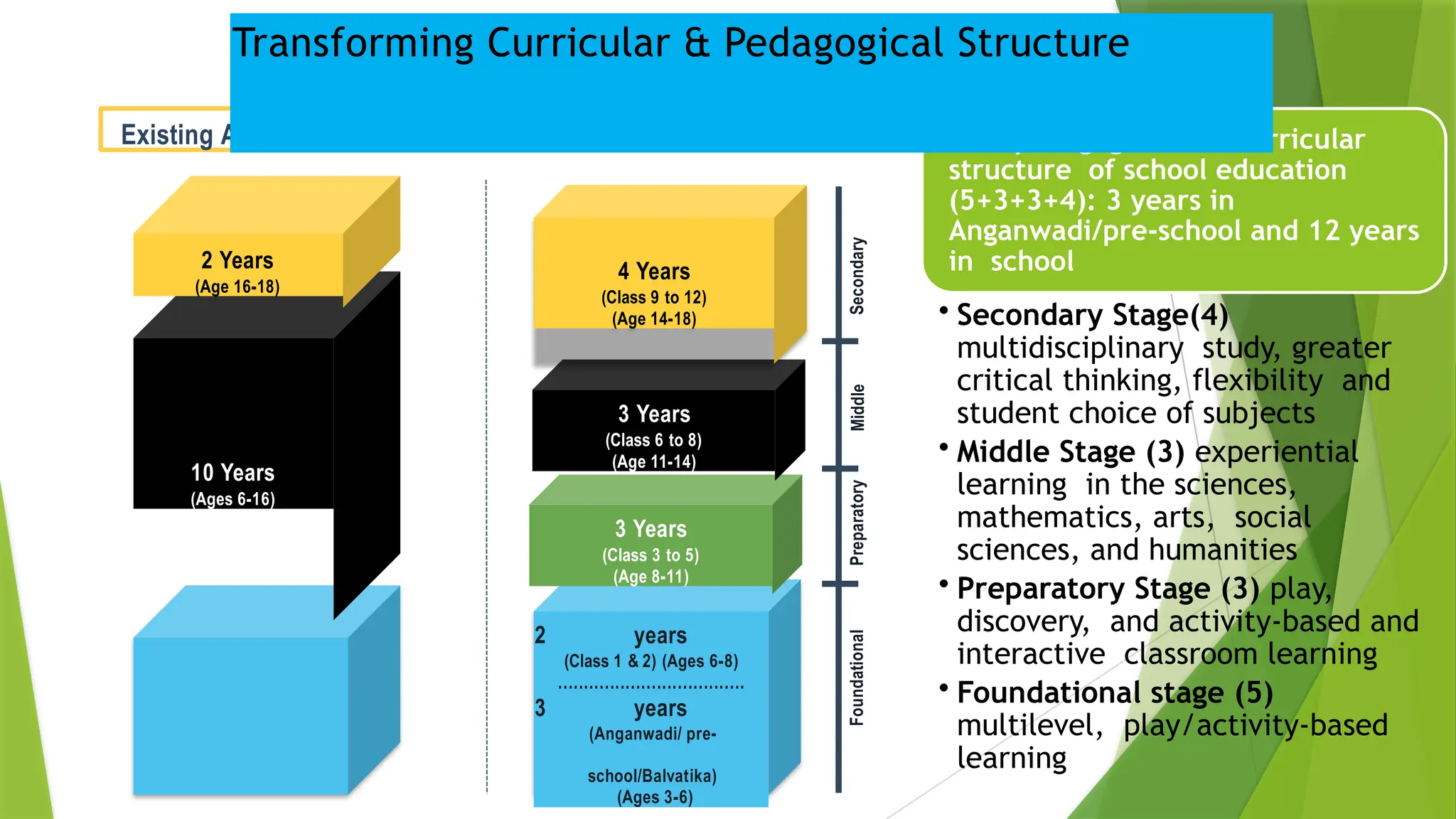
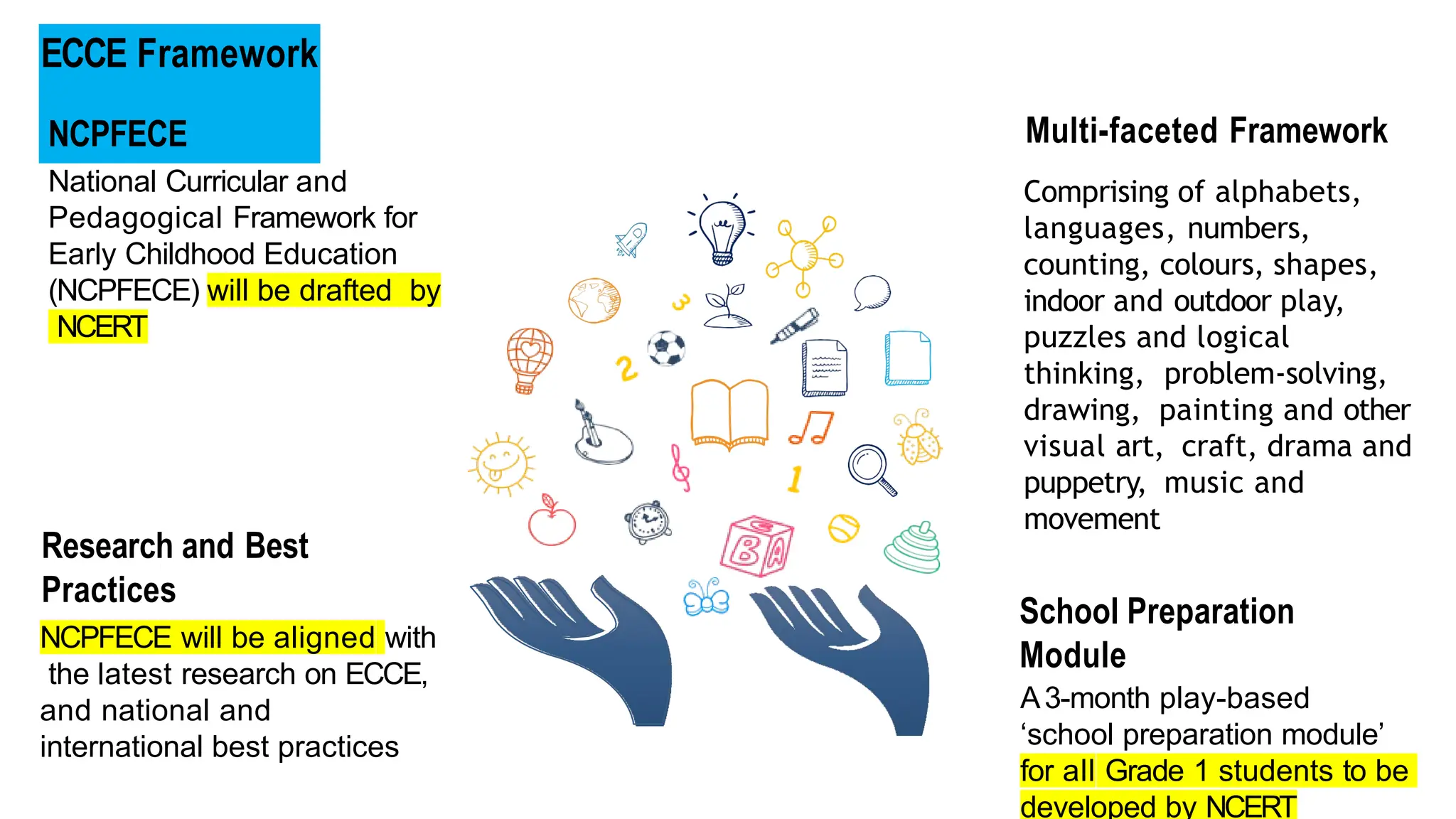
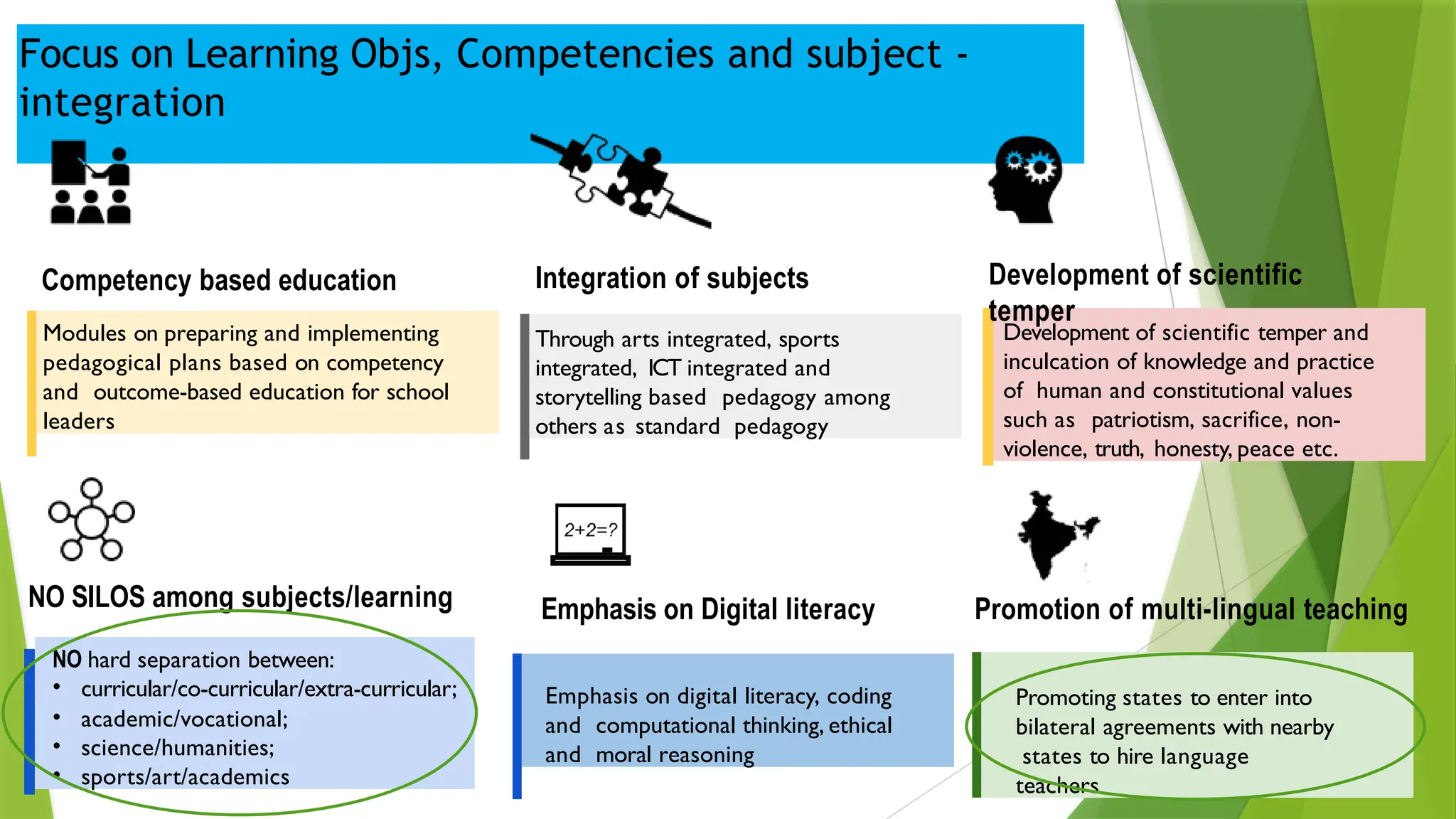
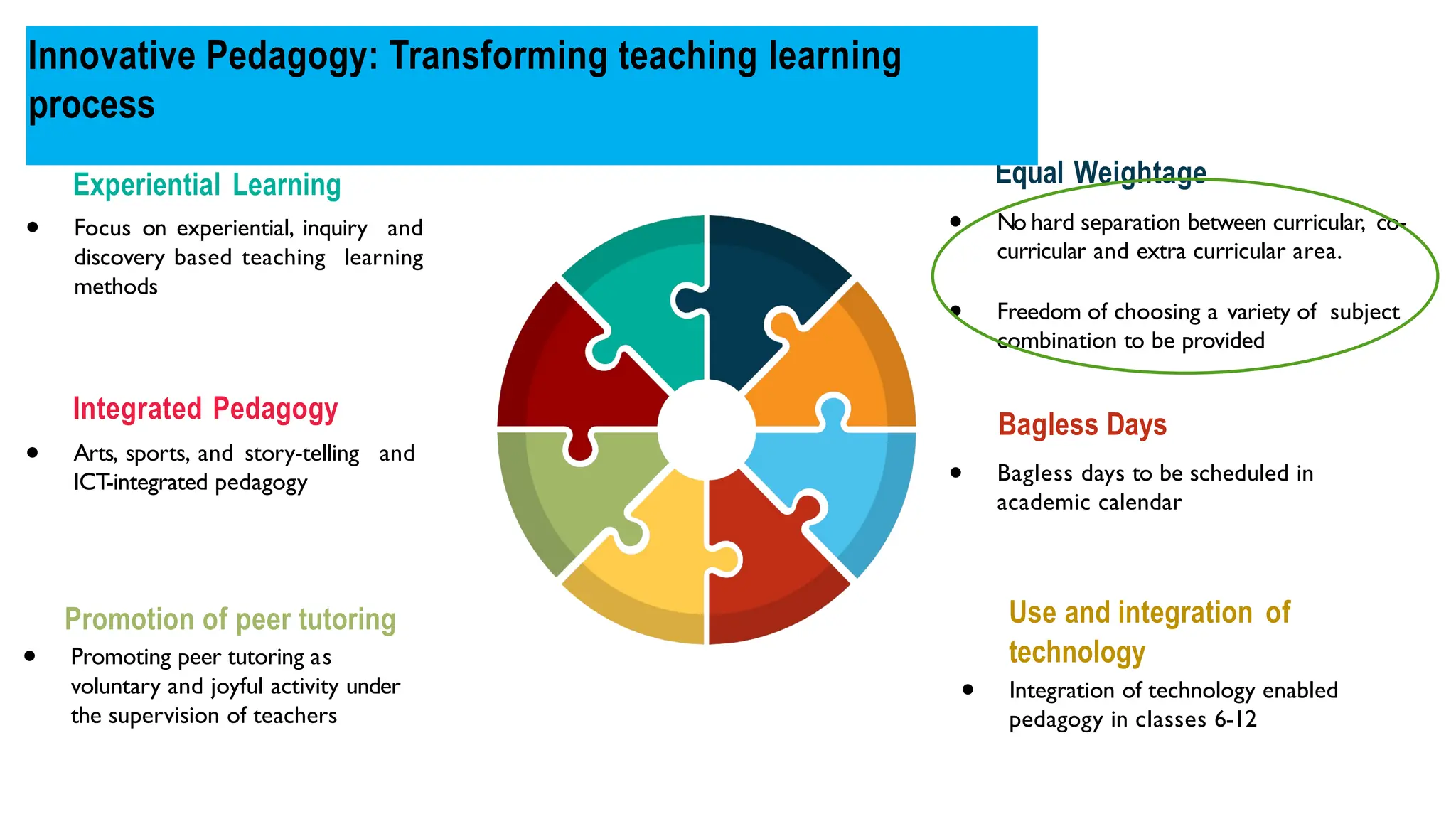
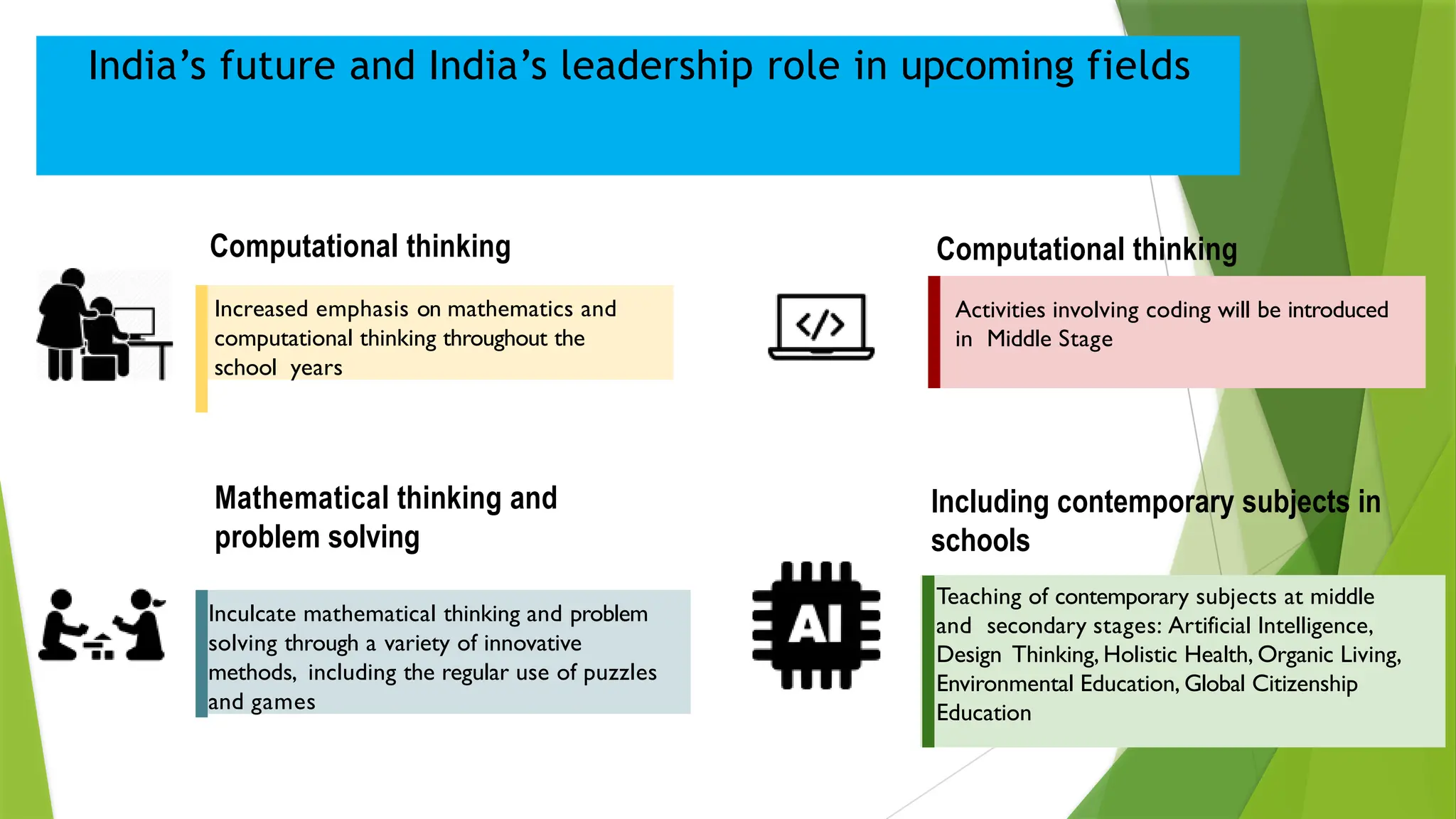
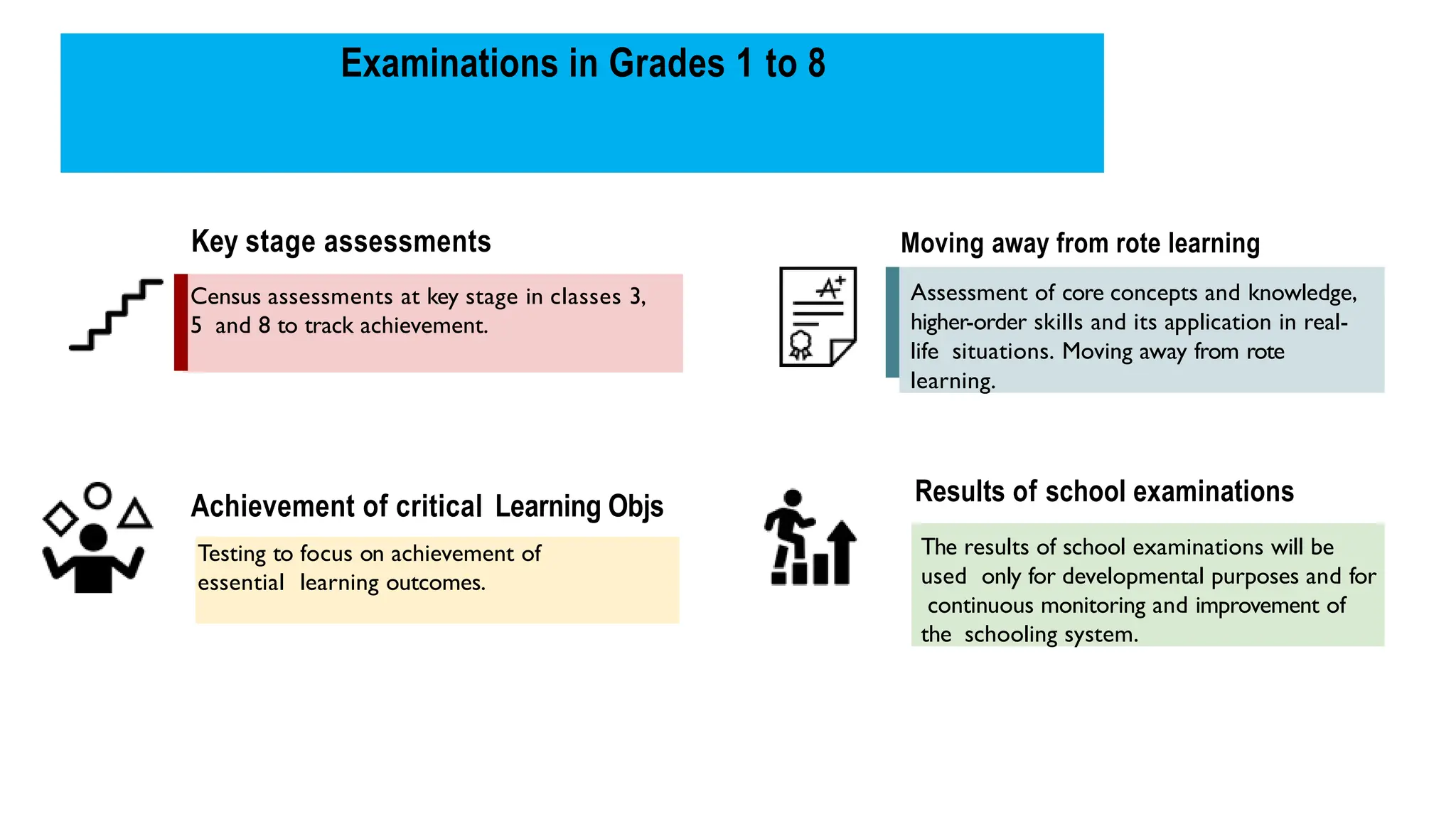
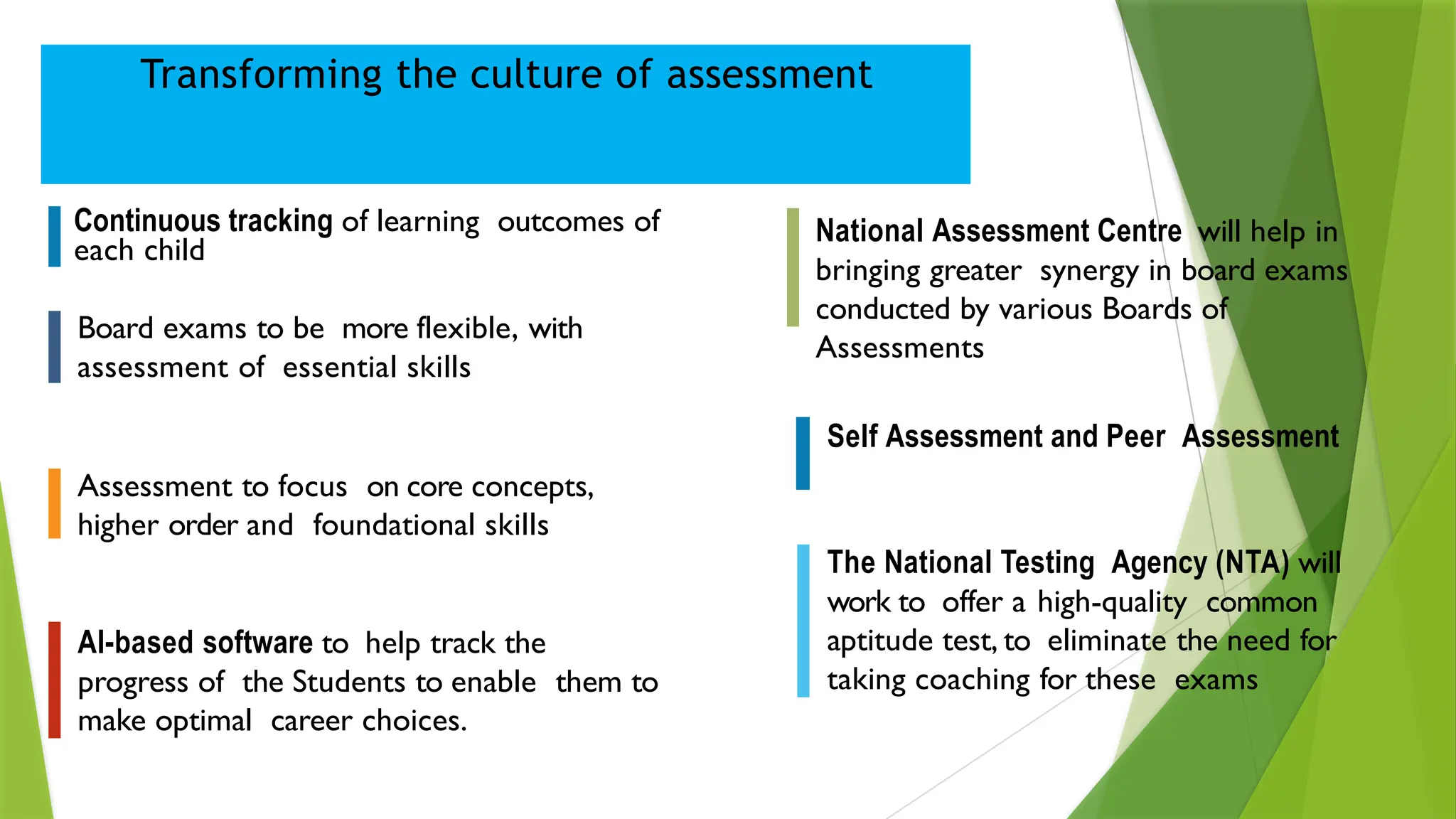
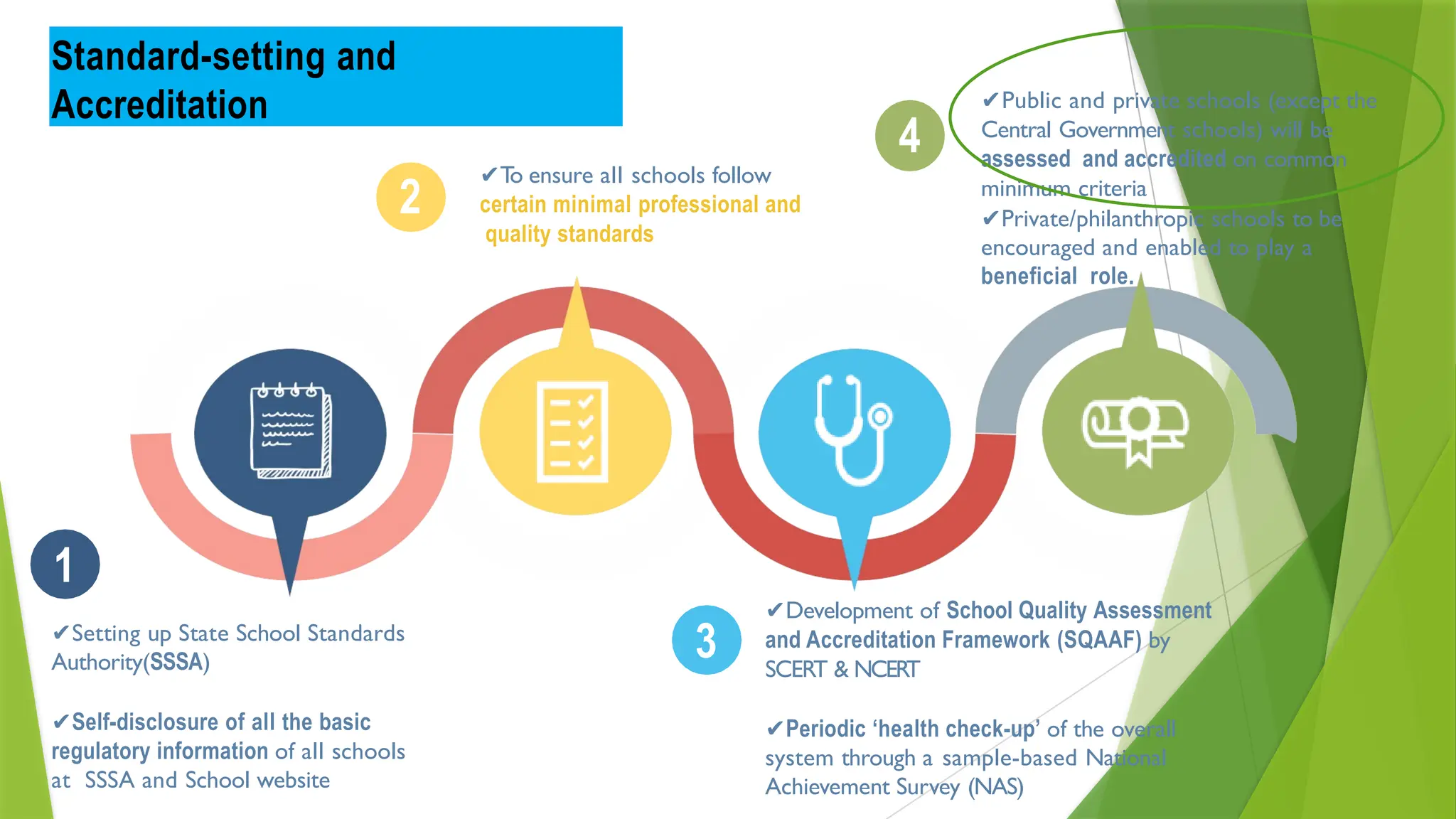
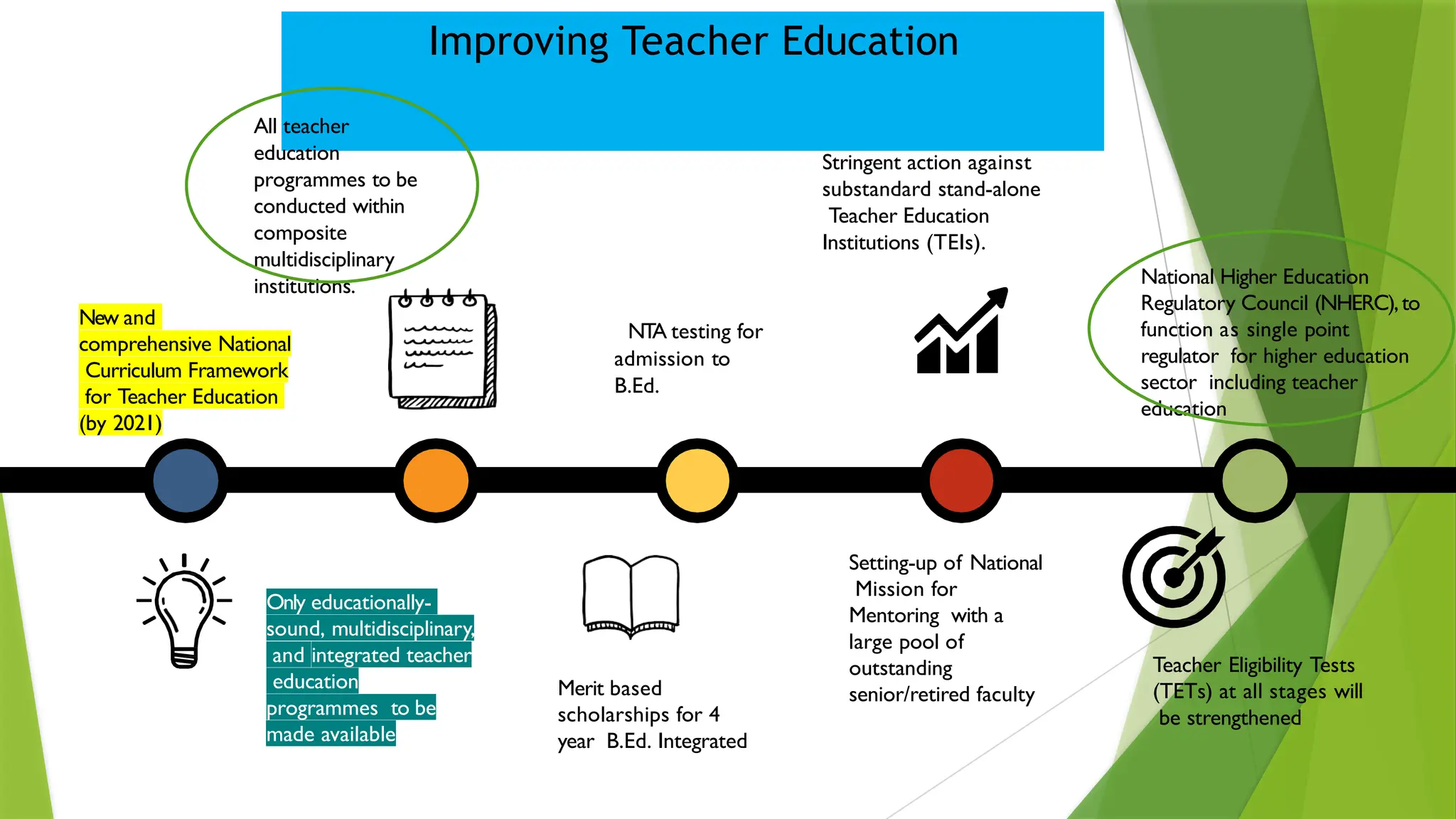
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 aims to transform India's education system by making it more holistic, inclusive, and equitable, focusing on critical thinking, creativity, and foundational skills. It introduces a new curricular structure, emphasizing experiential learning and multilingualism while promoting teacher empowerment and accountability. Key goals include universal access to early childhood education, improving learning outcomes, and integrating technology across educational practices.