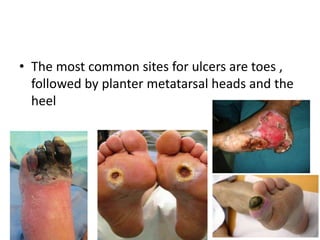
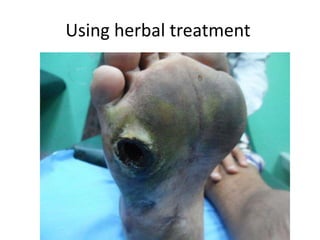
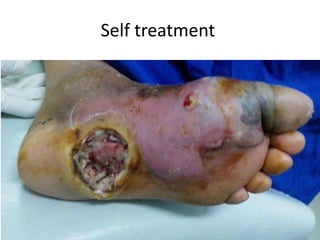
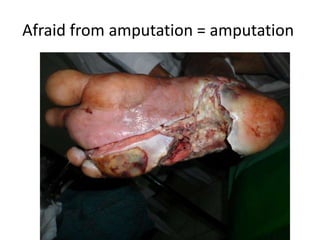
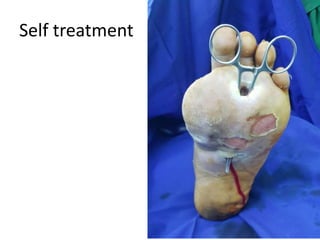
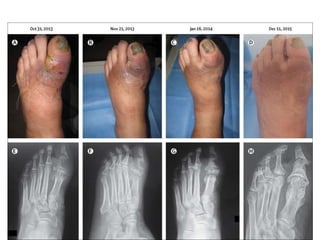
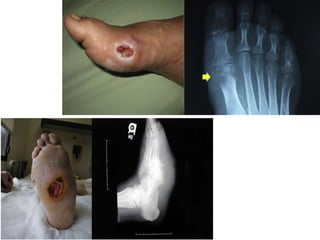
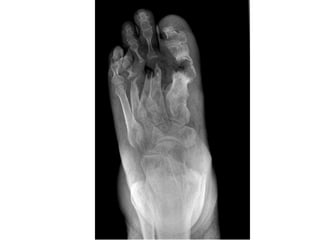
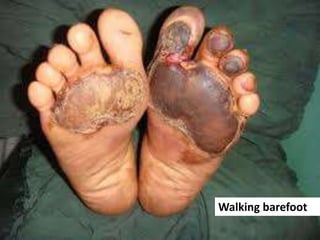
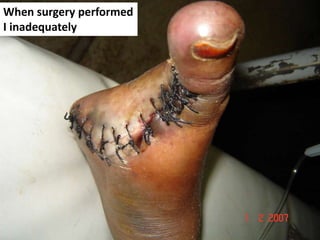
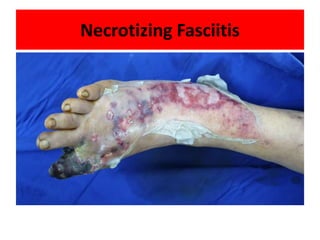
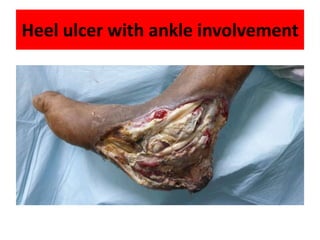
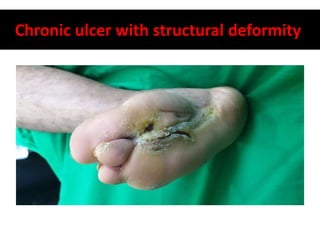
Diabetes mellitus is leading to increasing cases of diabetic foot ulcers, which can complicate the condition in over 15% of affected individuals and precede many non-traumatic lower limb amputations. Factors such as peripheral neuropathy and health care negligence contribute to this issue, with solutions including better screening, education, and multidisciplinary support. Effective prevention and management are essential to reduce the risks associated with diabetic foot complications.