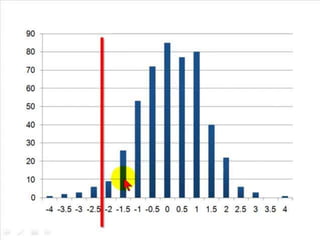
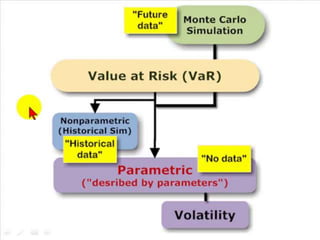
The document discusses risk management strategies for banks. It covers value at risk (VAR) which predicts maximum potential losses, and substitutes for VAR like sensitivity analysis. It also discusses liquidity risk, the potential for loss from inability to meet obligations. Early warning signs of liquidity risk include deteriorating credit quality or earnings. The board and senior management oversee risk management strategies and monitor performance. Responsibilities include implementing risk procedures and maintaining management information systems to identify, measure, monitor and control risks.