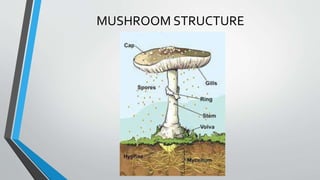
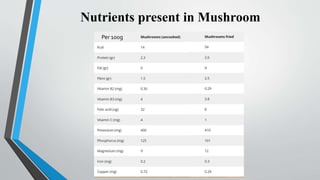
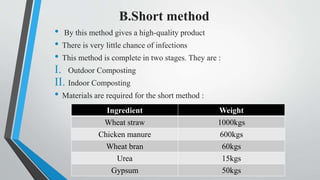
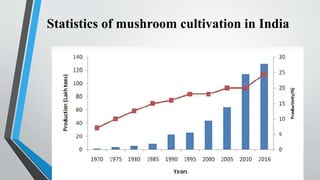
The document summarizes the process of mushroom cultivation. It discusses the structure of mushrooms and the nutrients they contain. The main steps of cultivation are described as: 1) Using mushroom spawn, 2) Preparing compost by longer or shorter methods, 3) Spawning the compost, 4) Applying a casing layer, and 5) Cropping mushrooms over 50-60 days. Common mushrooms grown are Agaricus bisporus due to their high worldwide production levels.