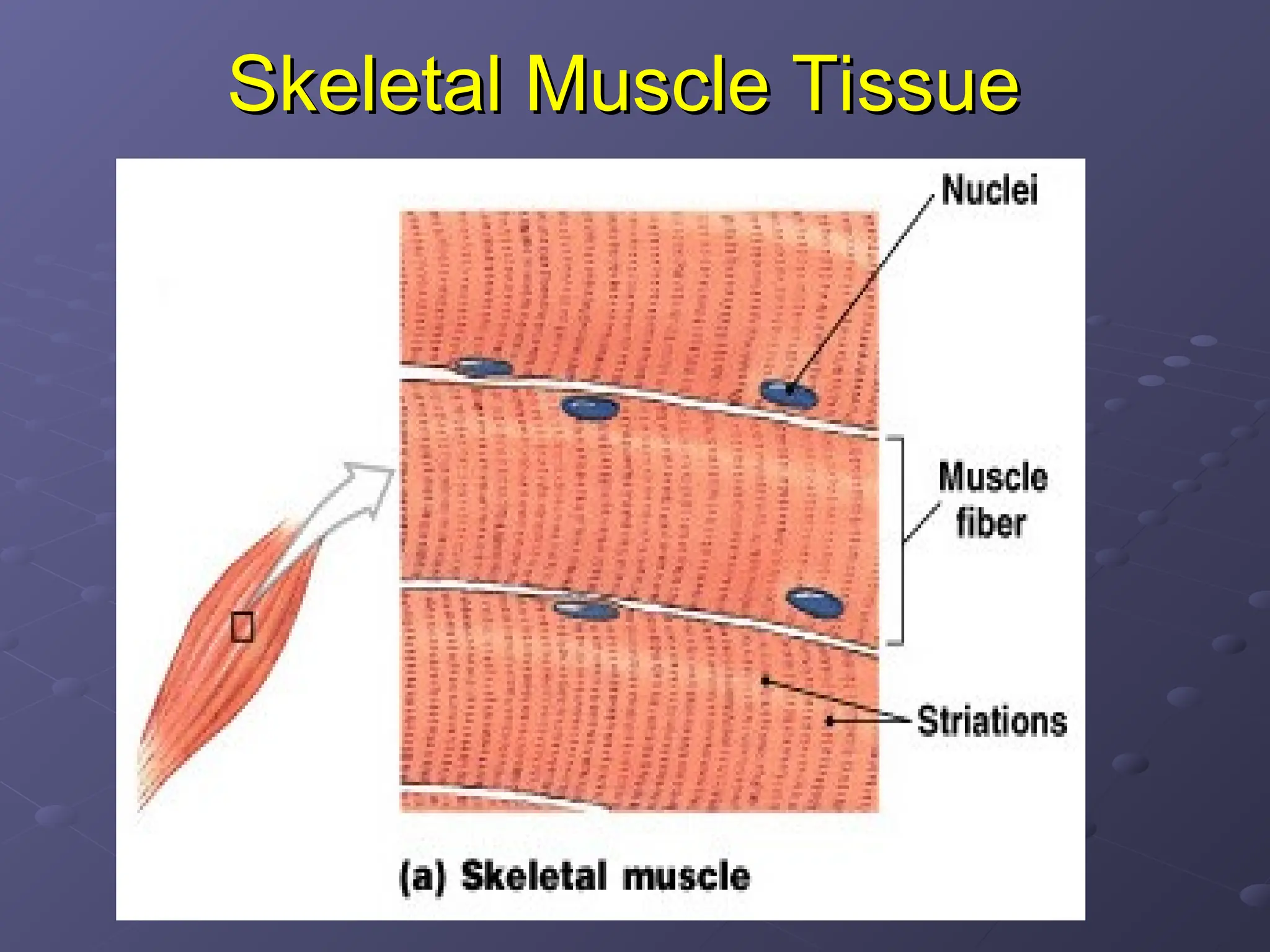
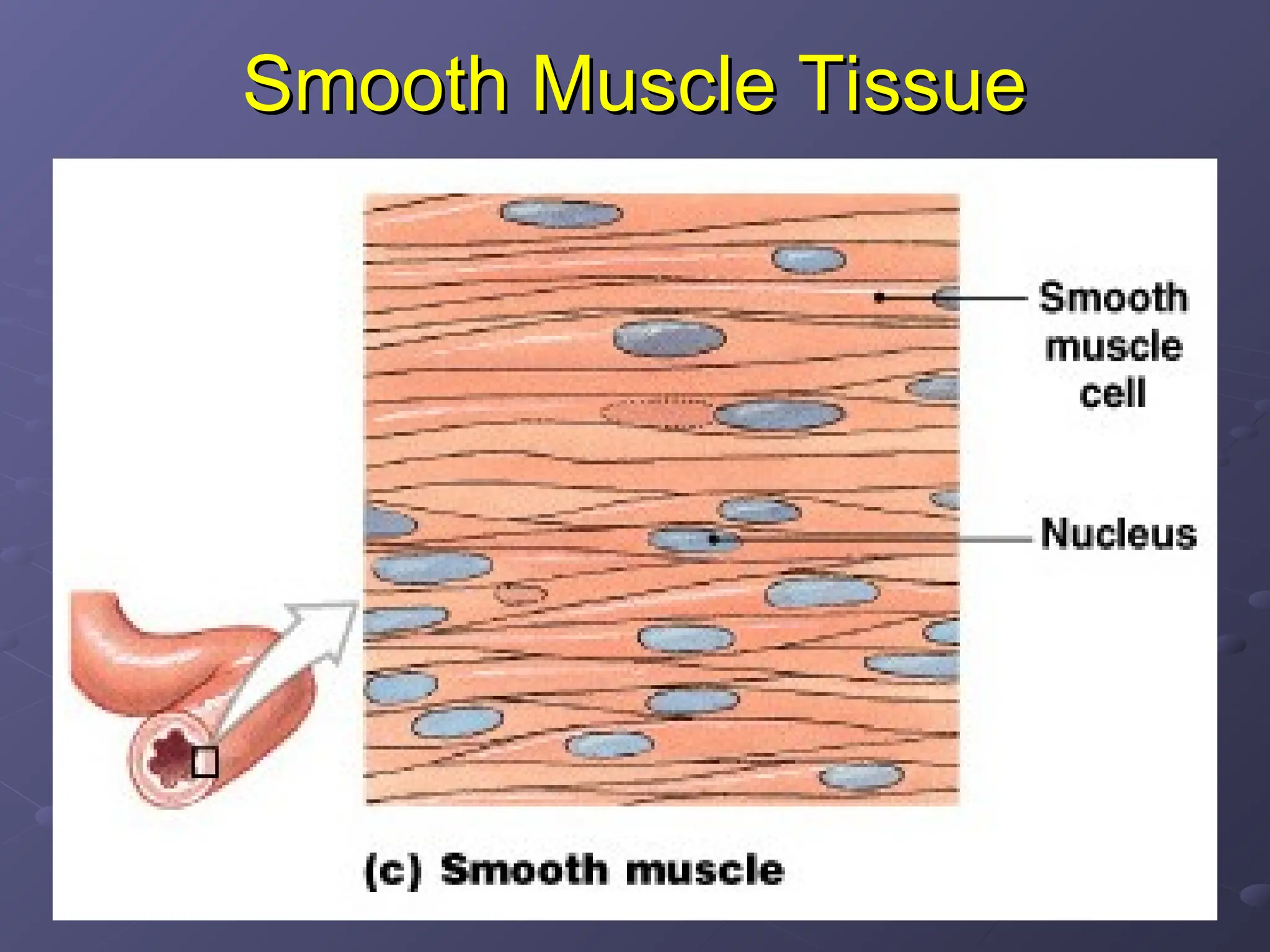
El tejido muscular se clasifica en tres tipos: esquelético, cardíaco y liso. Los músculos esqueléticos son estriados y voluntarios, mientras que los músculos cardíacos son estriados e involuntarios, y el tejido muscular liso es no estriado e involuntario. Cada tipo de músculo tiene características únicas en términos de estructura, control y ubicación en el cuerpo.