Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times



![Thank-you for watching :]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclecell-110310023645-phpapp01/85/Muscle-cell_Student-Presentation-6-320.jpg)
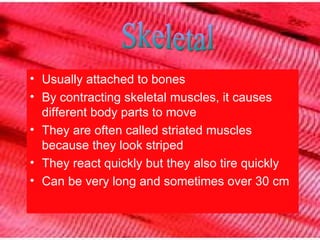
Muscle cells come in three main types - skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscle cells are found throughout the body, attach to bones, and allow for movement by contracting. They are striated and look striped but tire quickly. Cardiac muscle cells are only found in the heart walls and help power heartbeats. Smooth muscle cells are involuntary and found throughout systems like breathing and digestion, reacting slowly but enduringly.




![Thank-you for watching :]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musclecell-110310023645-phpapp01/85/Muscle-cell_Student-Presentation-6-320.jpg)