Embed presentation
Download to read offline
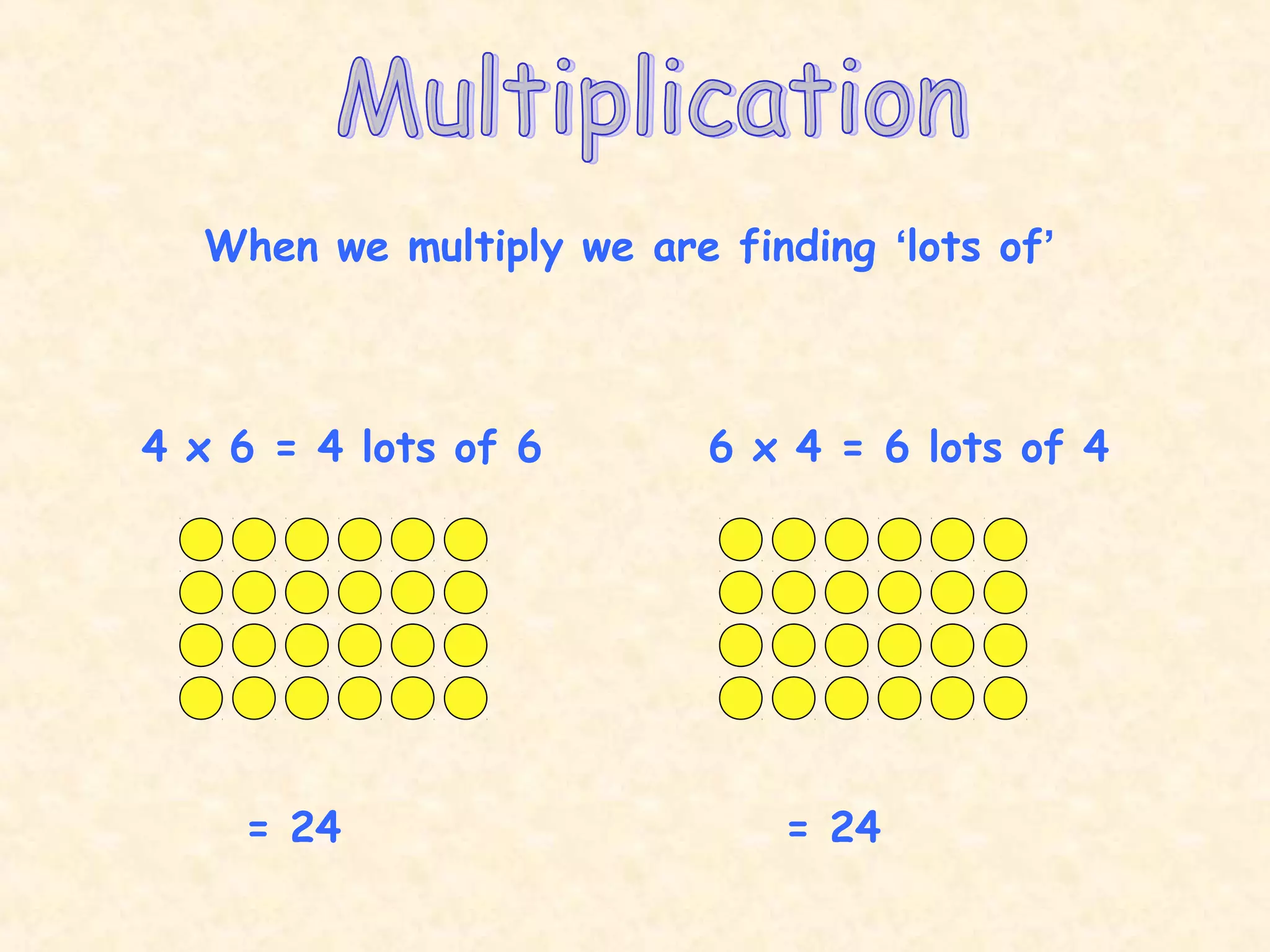
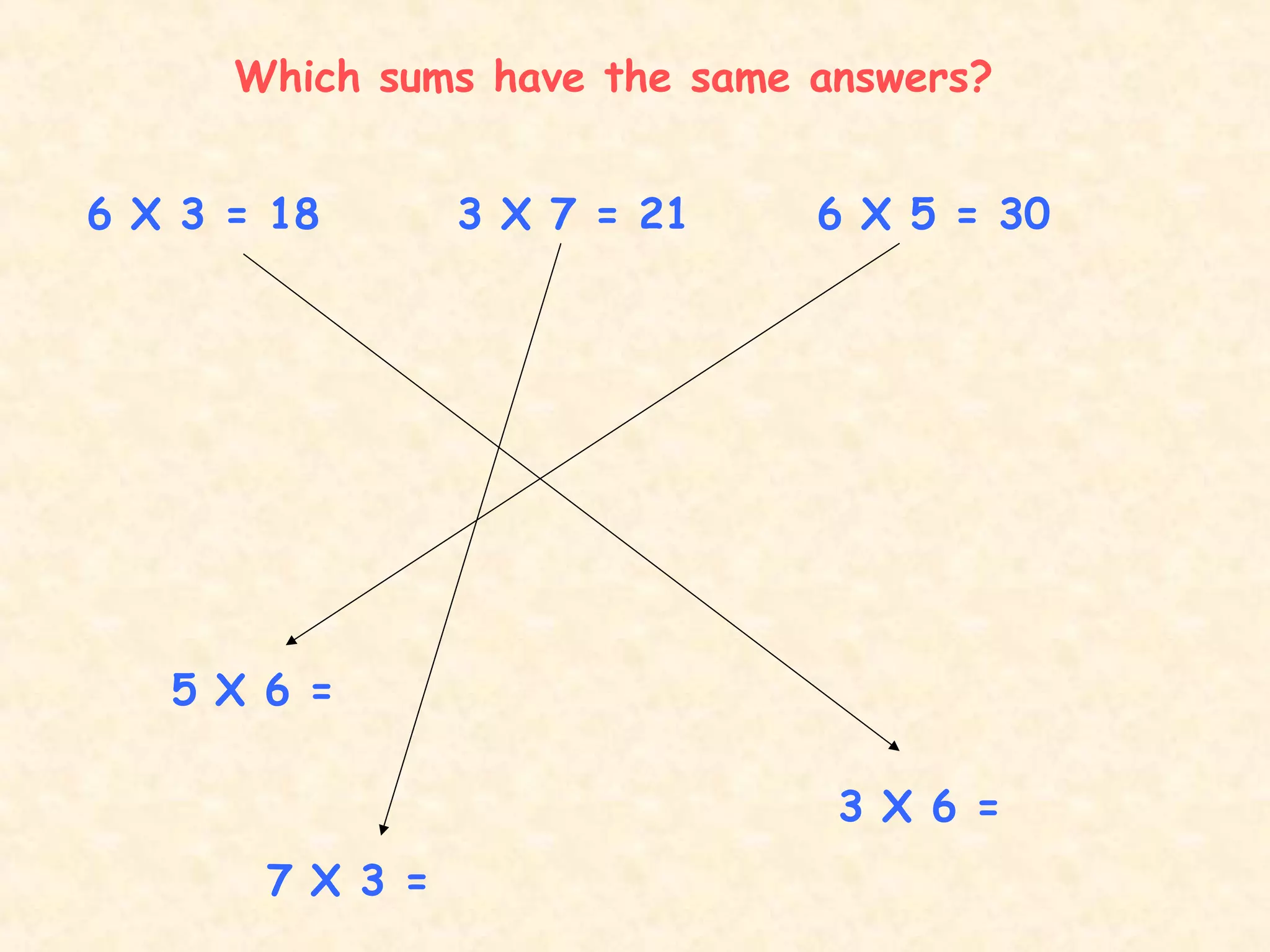
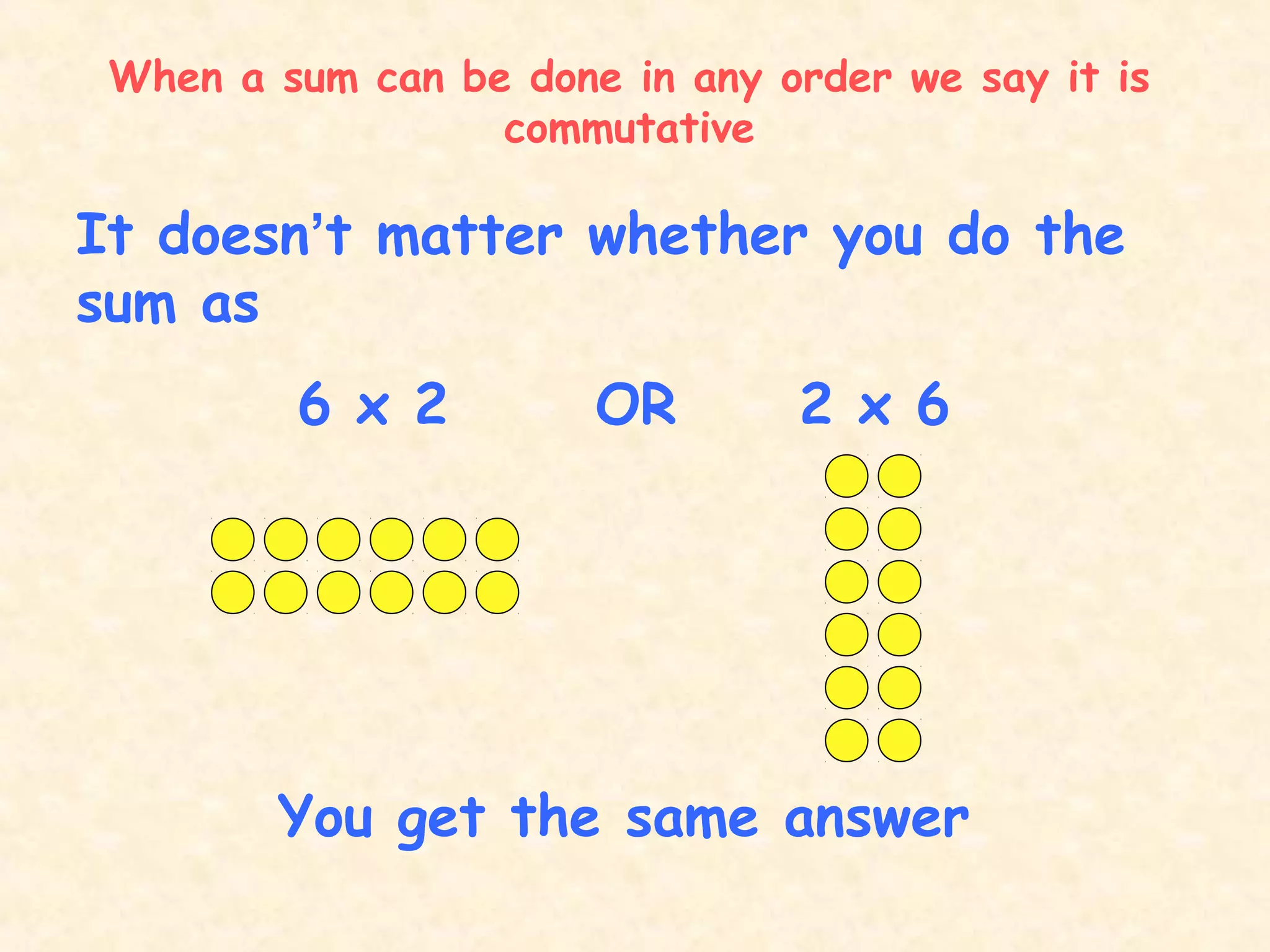
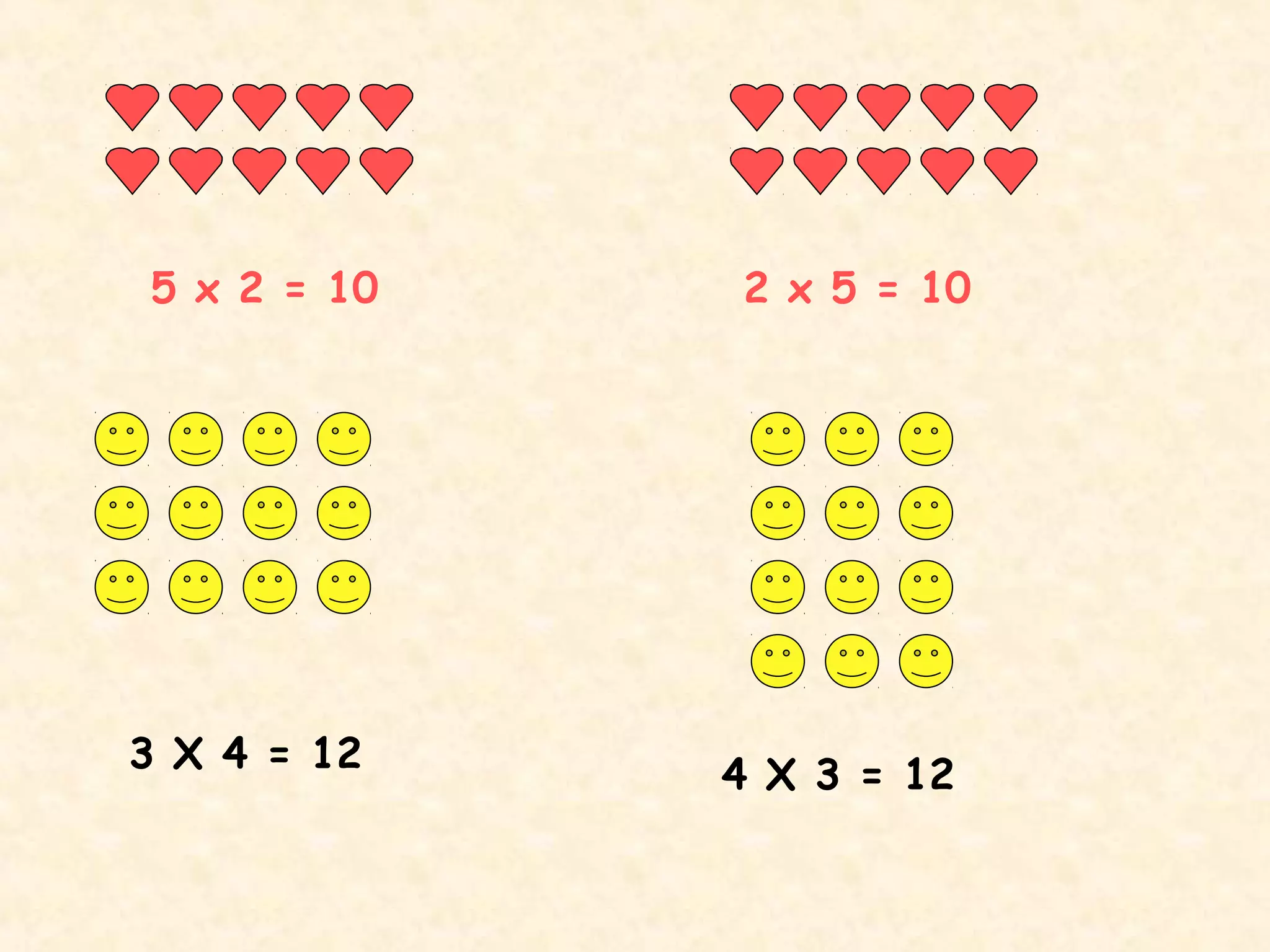
This document discusses commutative properties in multiplication. It provides examples of multiplication problems that have the same answer regardless of the order the numbers are multiplied, such as 4 x 6 equals 6 x 4 and both equal 24. The document explains that when a sum can be done in any order, it is considered commutative, as the order does not change the final answer. It provides additional examples of commutative multiplication problems like 5 x 2 equaling 10, which is the same as 2 x 5.



