Embed presentation



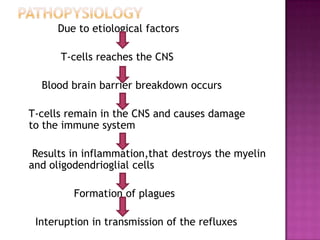




Multiple sclerosis is a progressive degenerative disease that affects the myelin sheath of neurons in the central nervous system, most commonly occurring in people aged 20 to 40. While the specific etiology is unknown, genetic and environmental factors like childhood viral infections may contribute to increased risk. The disease results from an autoimmune response where T-cells activated by an unknown trigger damage myelin and oligodendrocytes through inflammation, forming lesions that interrupt nerve signal transmission. Diagnosis involves assessing medical history, conducting physical exams and scans like MRI and CT, and blood tests. Treatment includes therapies to aid functioning as well as medications like antibiotics, painkillers, and corticosteroids.






