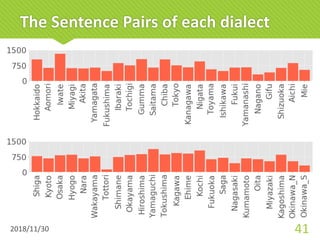
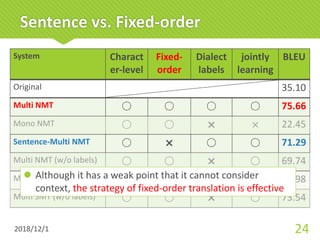
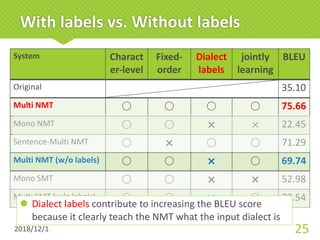
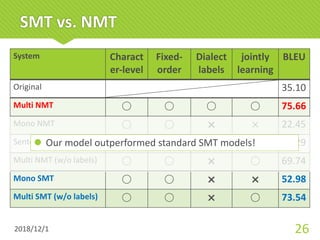
The document discusses a multi-dialect neural machine translation (NMT) system aimed at enabling smart speakers to understand various Japanese dialects. It highlights the challenges posed by the limited corpus of dialect data and the importance of leveraging similarities among dialects to improve translation accuracy. The study concludes that the proposed model achieves better performance compared to traditional methods by utilizing character-level, fixed-order, and multilingual approaches.














![Approach (Multilingual NMT)
šA multilingual NMT[Johnson+, 2017] utilizes shared
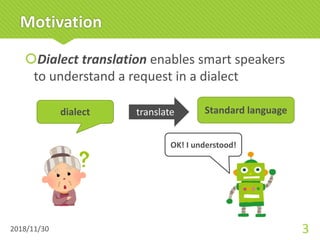
properties between dialects by way of a unified model
that learns multiple languages jointly
2018/11/30 17
Multilingual
NMT
hiyai
syakkoiHokkaido
Kochi
tsumetai
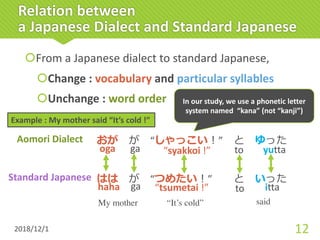
(cold)
Standard
Japanese
hyakkoi
Yamagata
Automatically
learning similarity
between
languages](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paclic32abe-190103130422/85/Multi-dialect-Neural-Machine-Translation-and-Dialectometry-17-320.jpg)







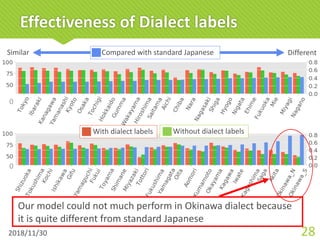





![Japanese dialectal typology
šDialectological researcher said that dialects spread
from an ancient capital city to remote areas
concentrically [Yanagida, 1980]
2018/12/1 34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paclic32abe-190103130422/85/Multi-dialect-Neural-Machine-Translation-and-Dialectometry-34-320.jpg)


![References
š[Johnson+, 2017] Google’s Multilingual Neural
Machine Translation System: Enabling Zero-Shot
Translation, ACL2017
š[Yanagida, 1980] Kunio Yanagida. 1980. “Kagyuko”.
Iwanami Shoten, Publishers.
2018/12/1 37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paclic32abe-190103130422/85/Multi-dialect-Neural-Machine-Translation-and-Dialectometry-37-320.jpg)