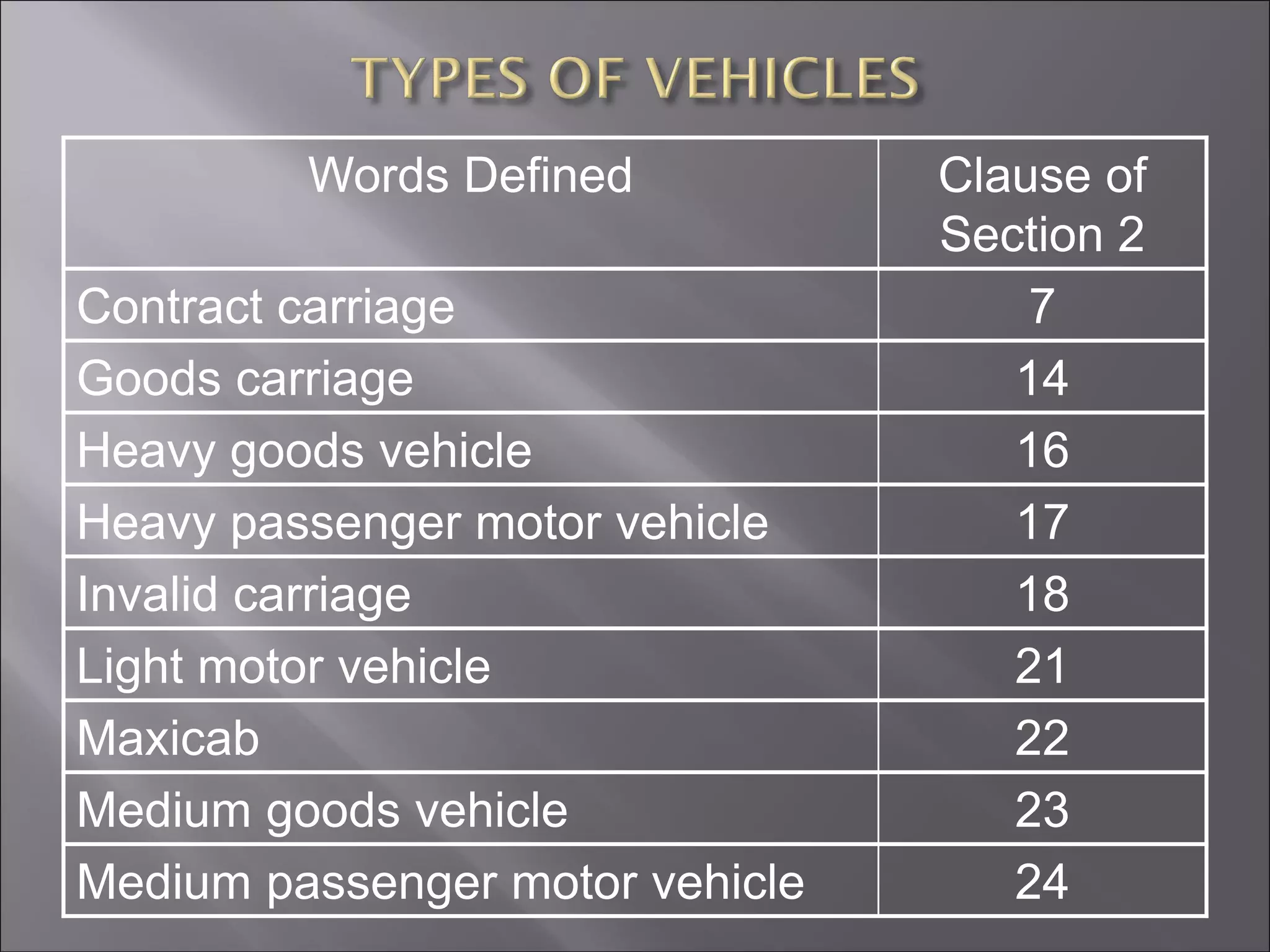
This document summarizes key aspects of the Motor Vehicles Act of 1988 in India. It defines important terms like motor vehicle, motor cab, goods carriage, and contract carriage. It outlines the 14 chapters and 217 sections of the Act. It discusses provisions around licensing of drivers and conductors, vehicle registration, regulation of transport vehicles, and insurance requirements. The Act grants powers to central and state governments to regulate road traffic and transport and make rules. It also specifies various vehicle-related and traffic offenses and associated penalties. In summary, the Motor Vehicles Act of 1988 is the primary law governing road transport by vehicles in India.