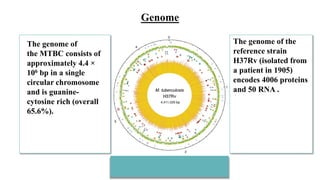
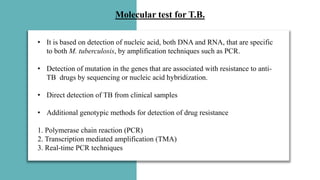
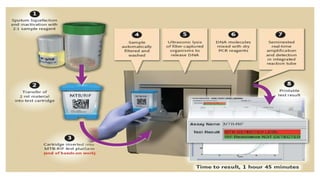
This document discusses molecular biology tests for tuberculosis (TB), specifically the Xpert MTB/RIF assay. The assay uses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to amplify TB bacterial DNA and detect resistance to the drug rifampicin. It has advantages of being rapid, requiring minimal training, and having a closed cartridge system that minimizes contamination. The assay directly detects TB and rifampicin resistance from sputum samples in under two hours.