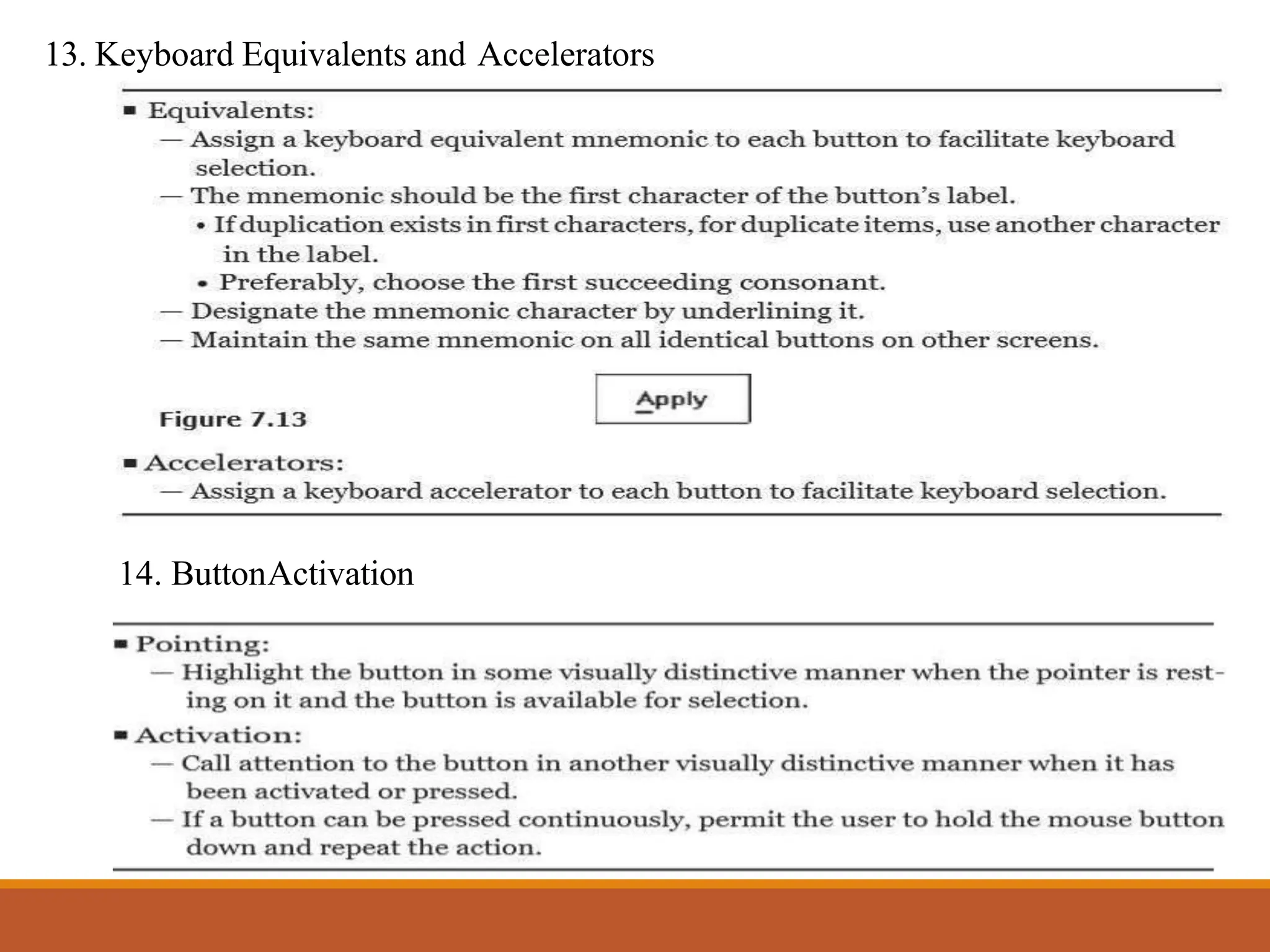
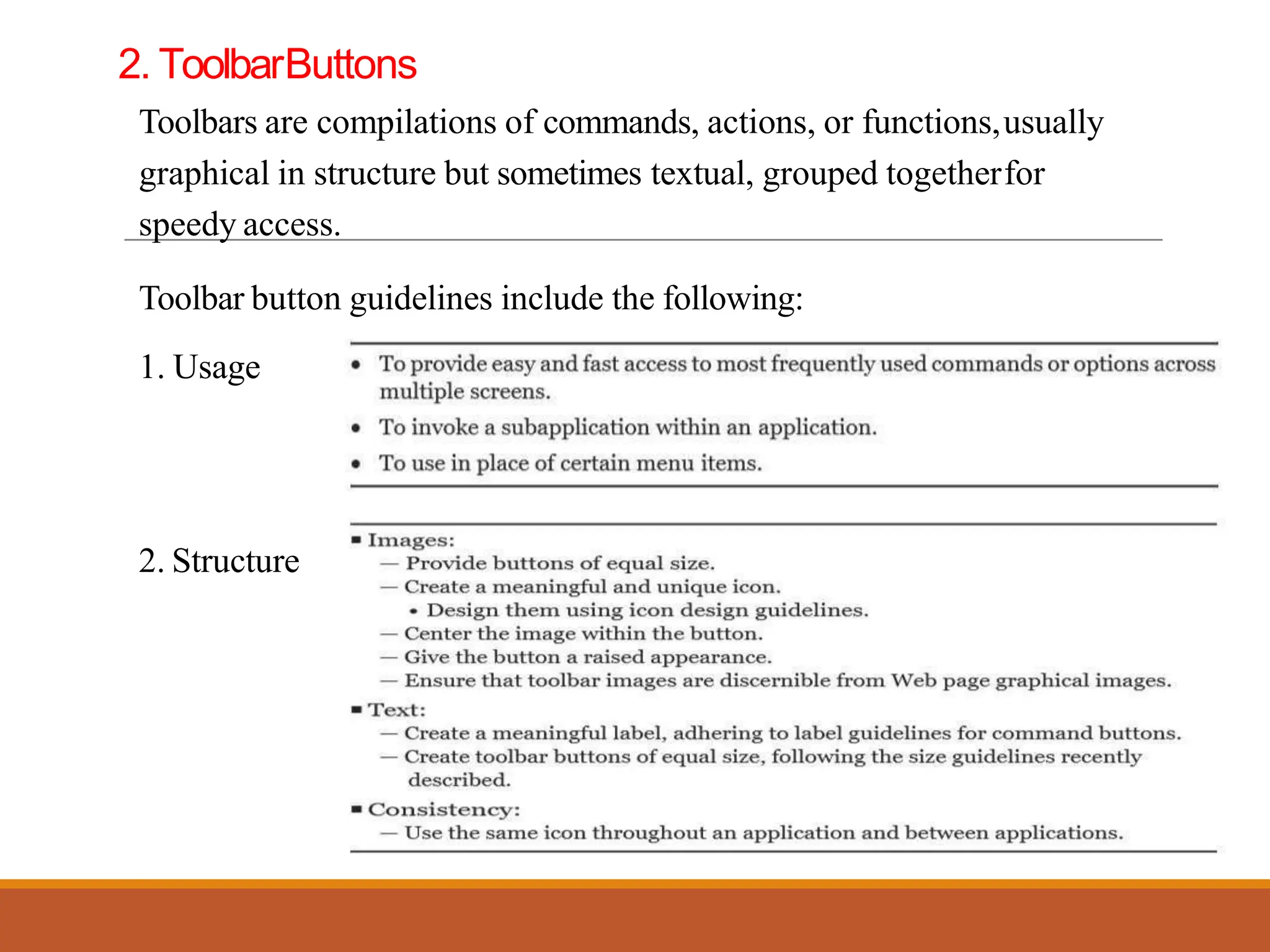
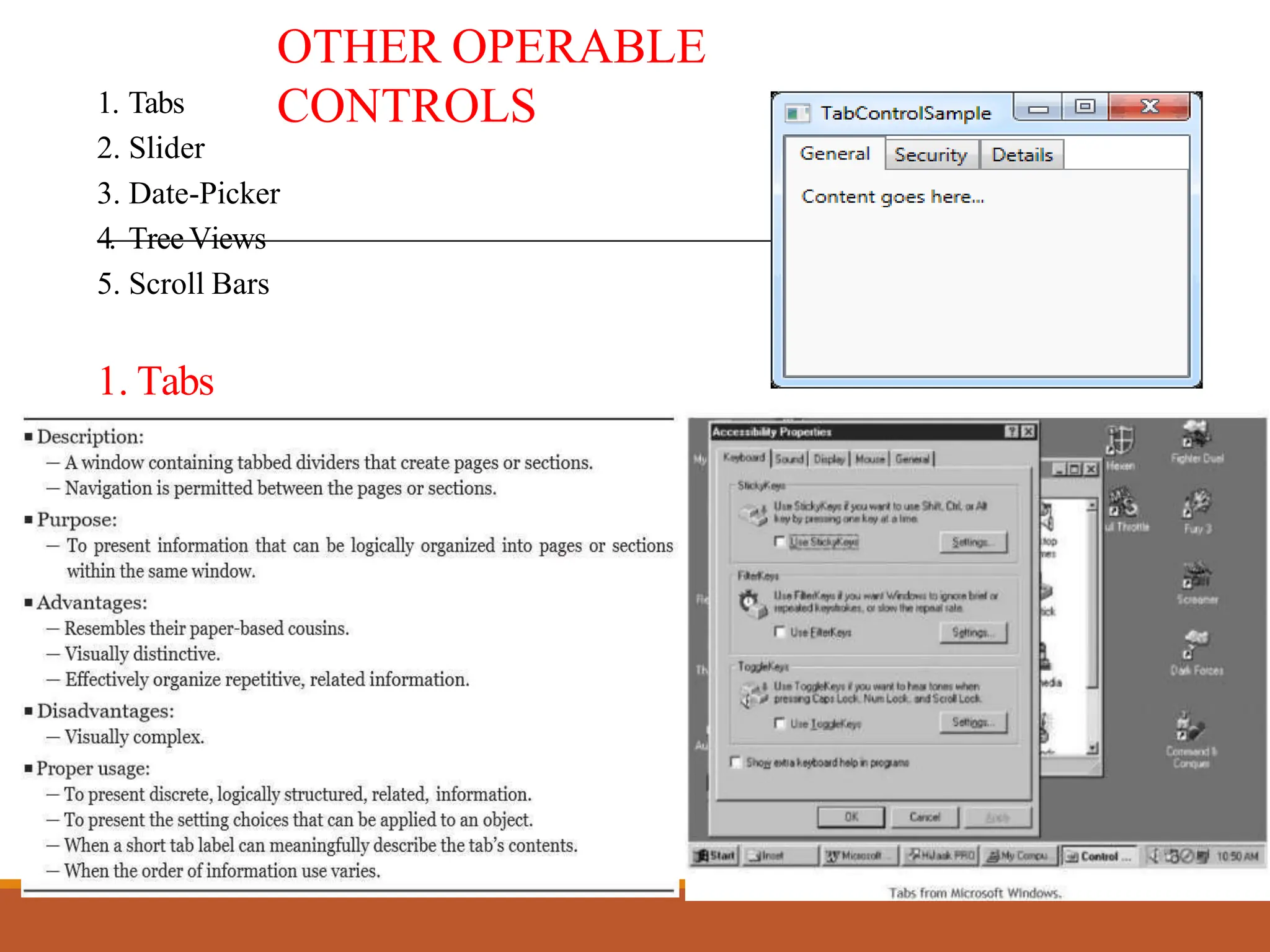
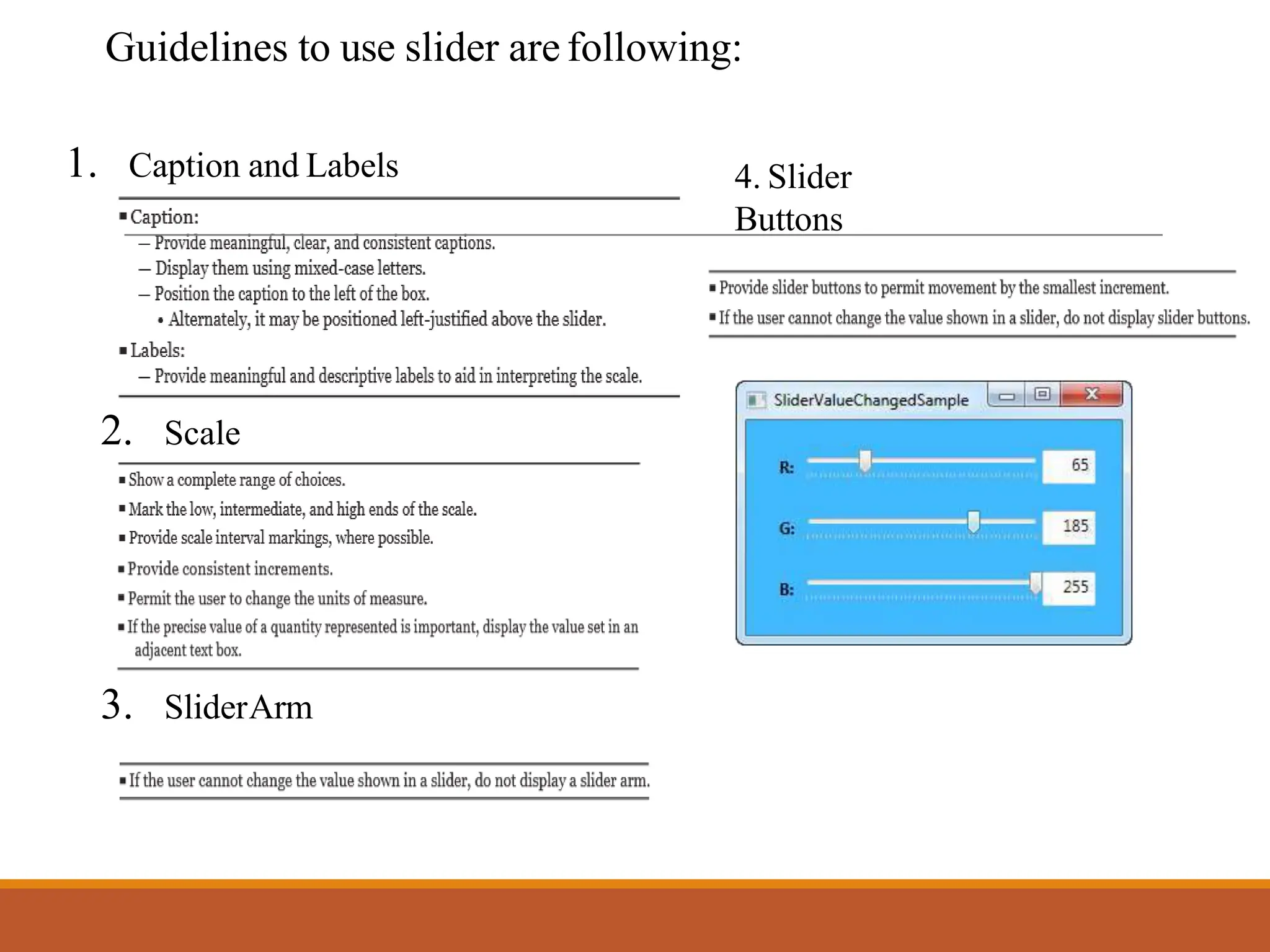
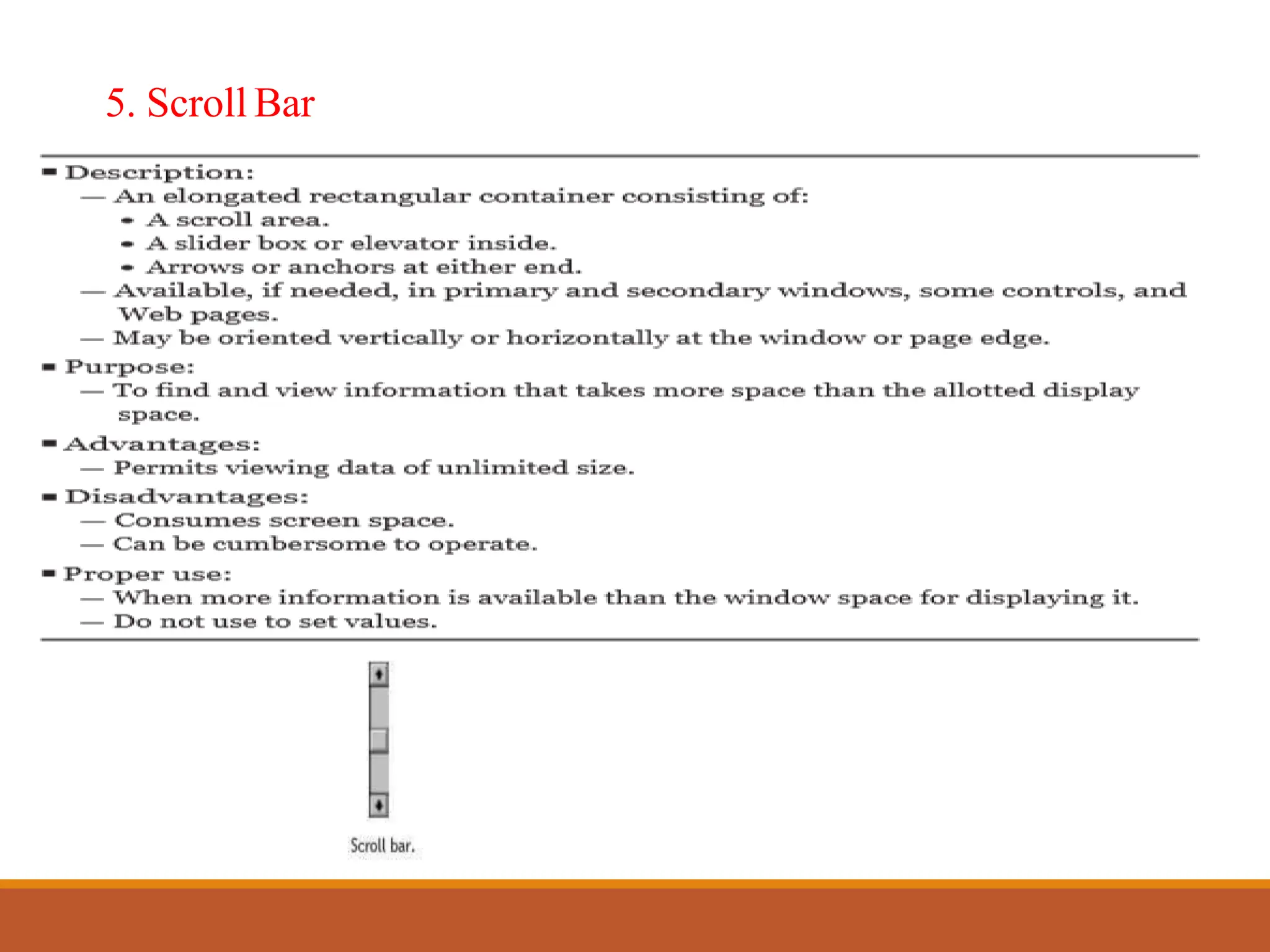
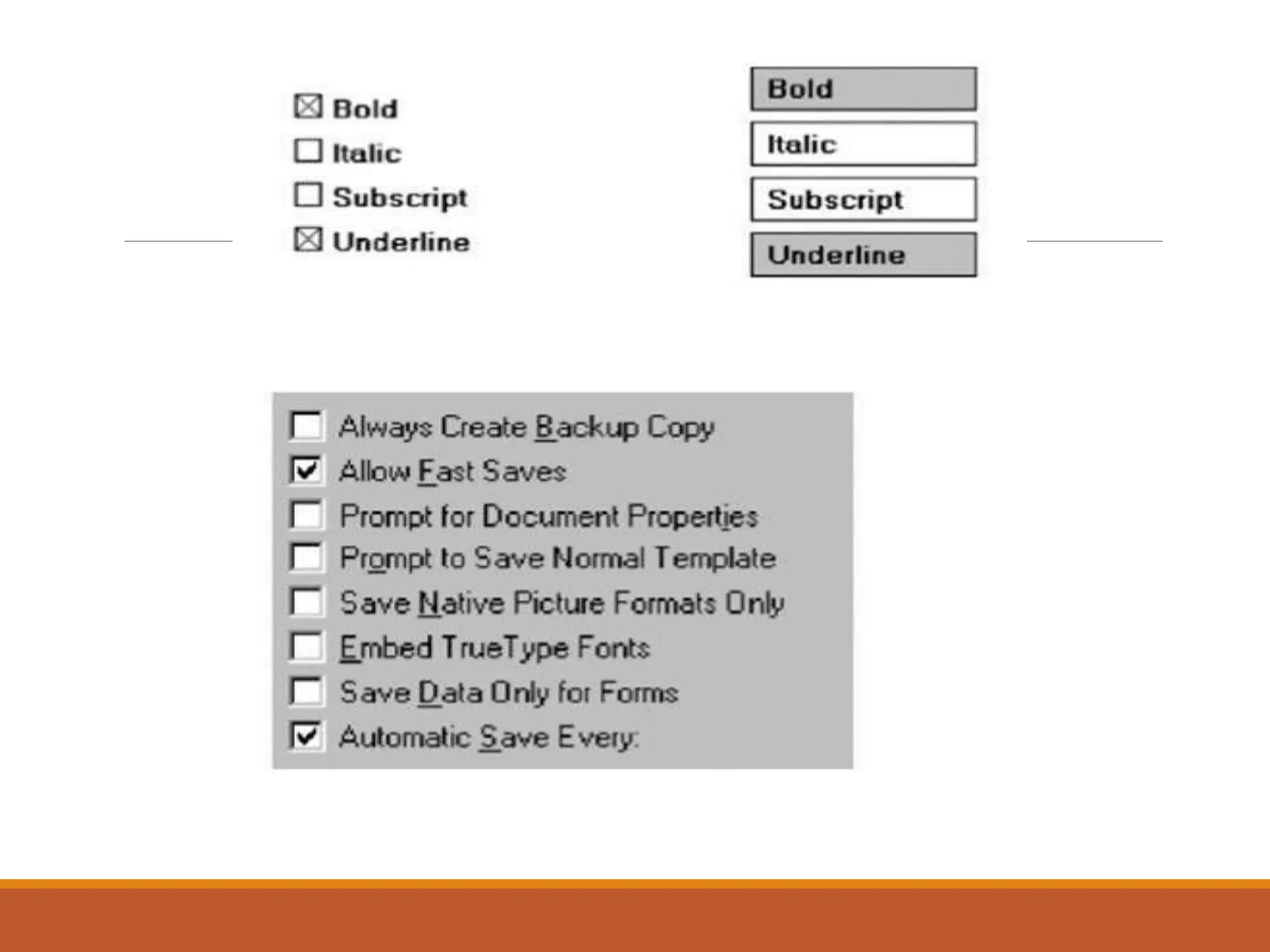
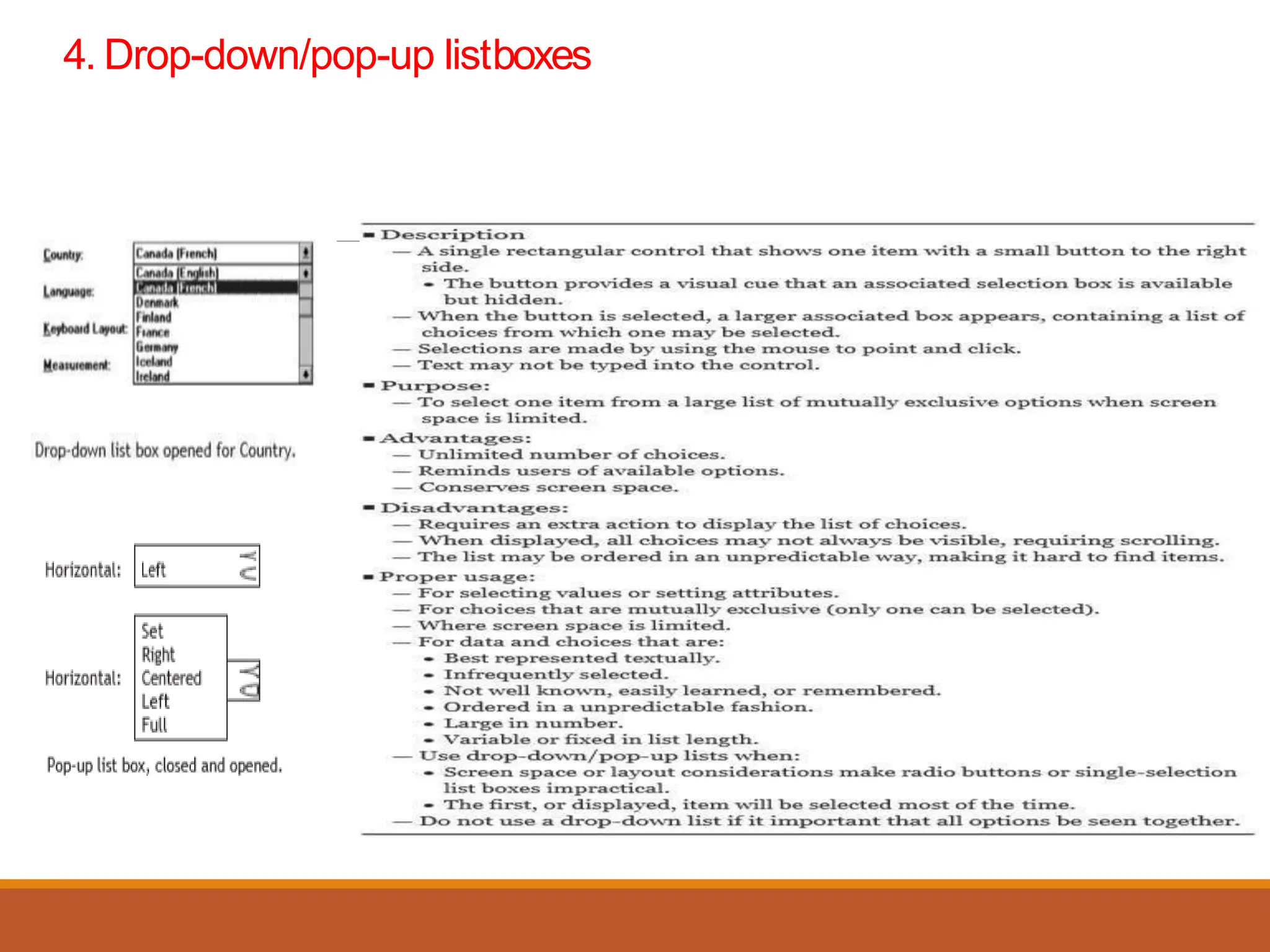
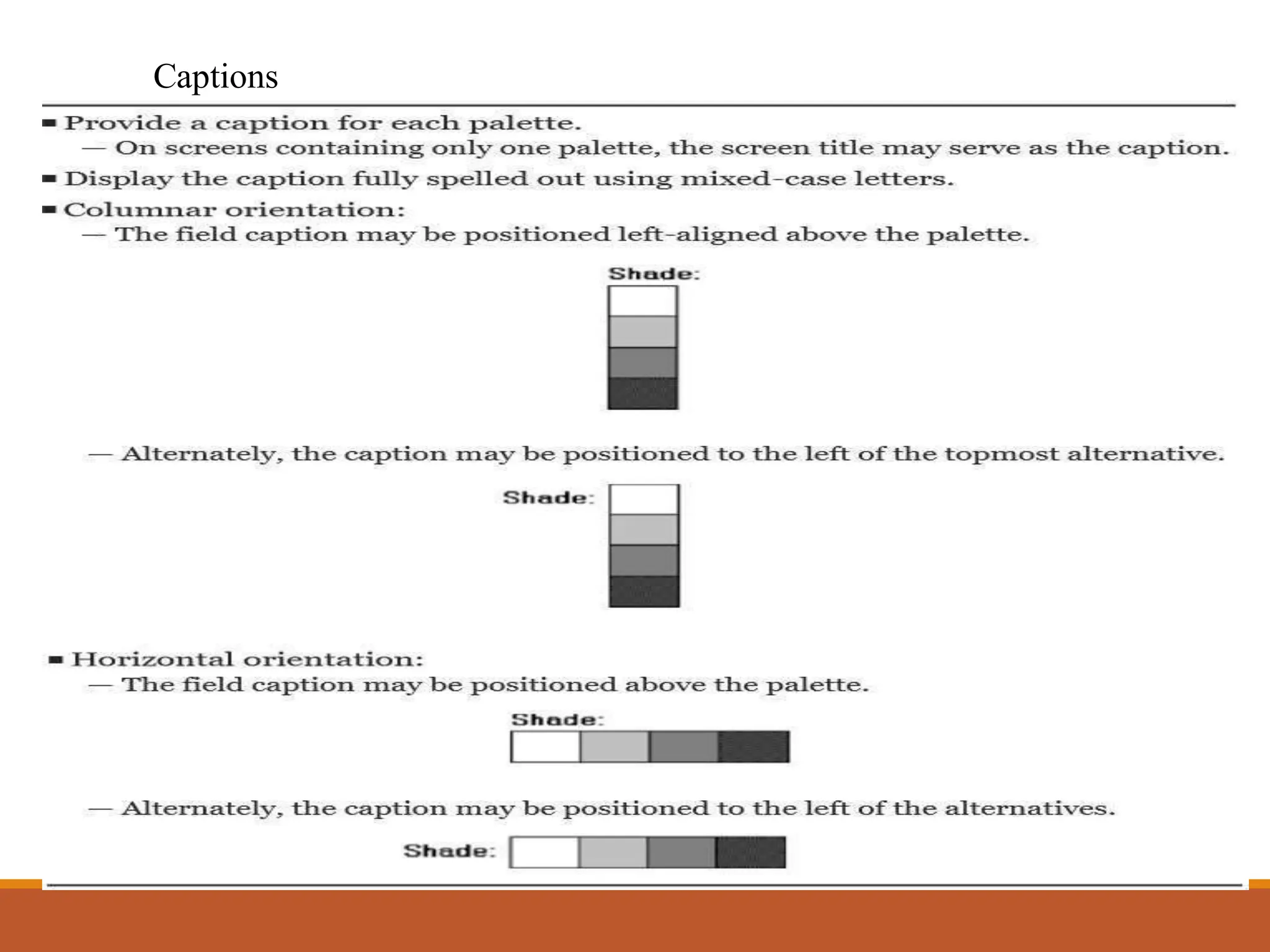
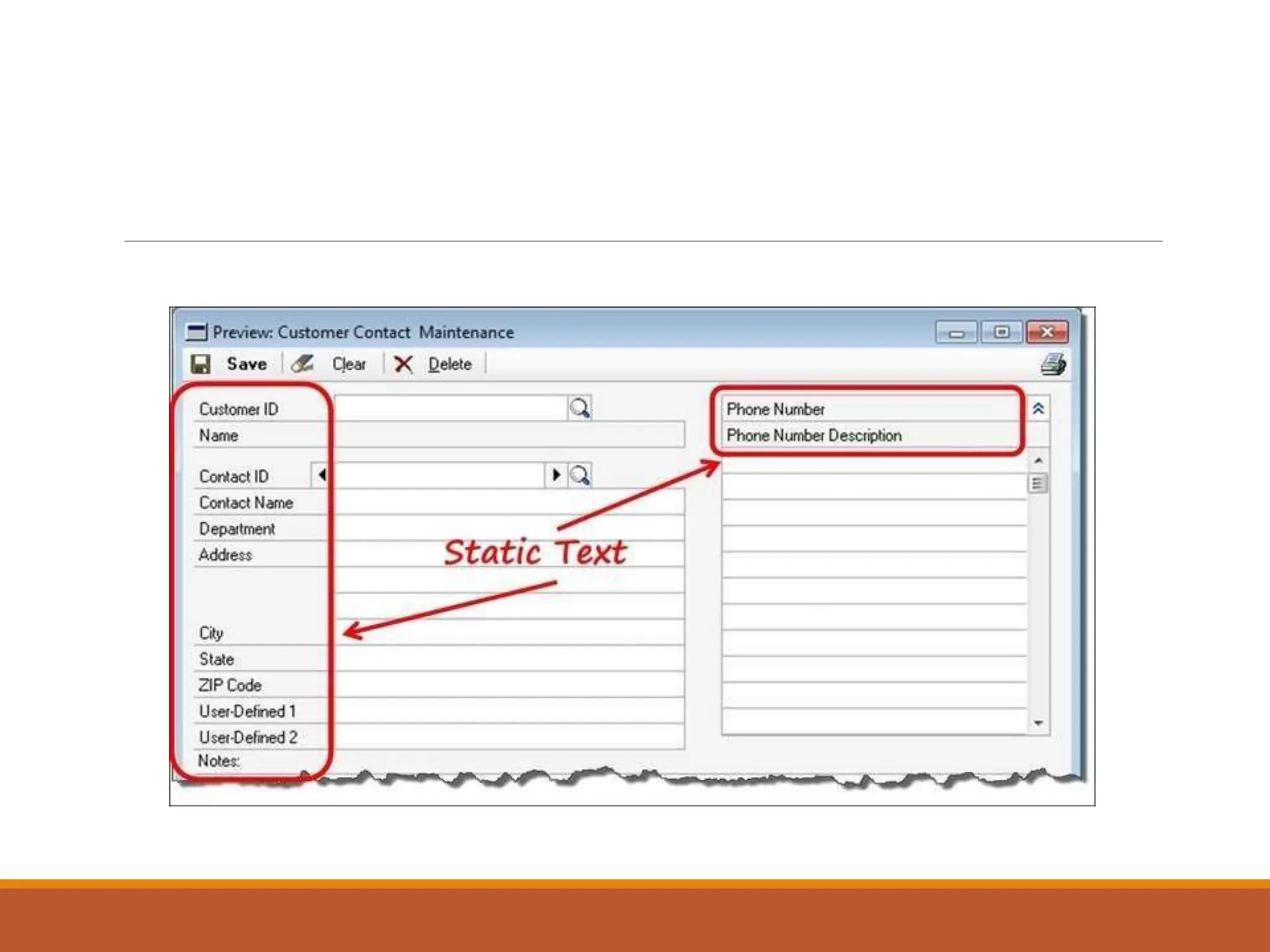
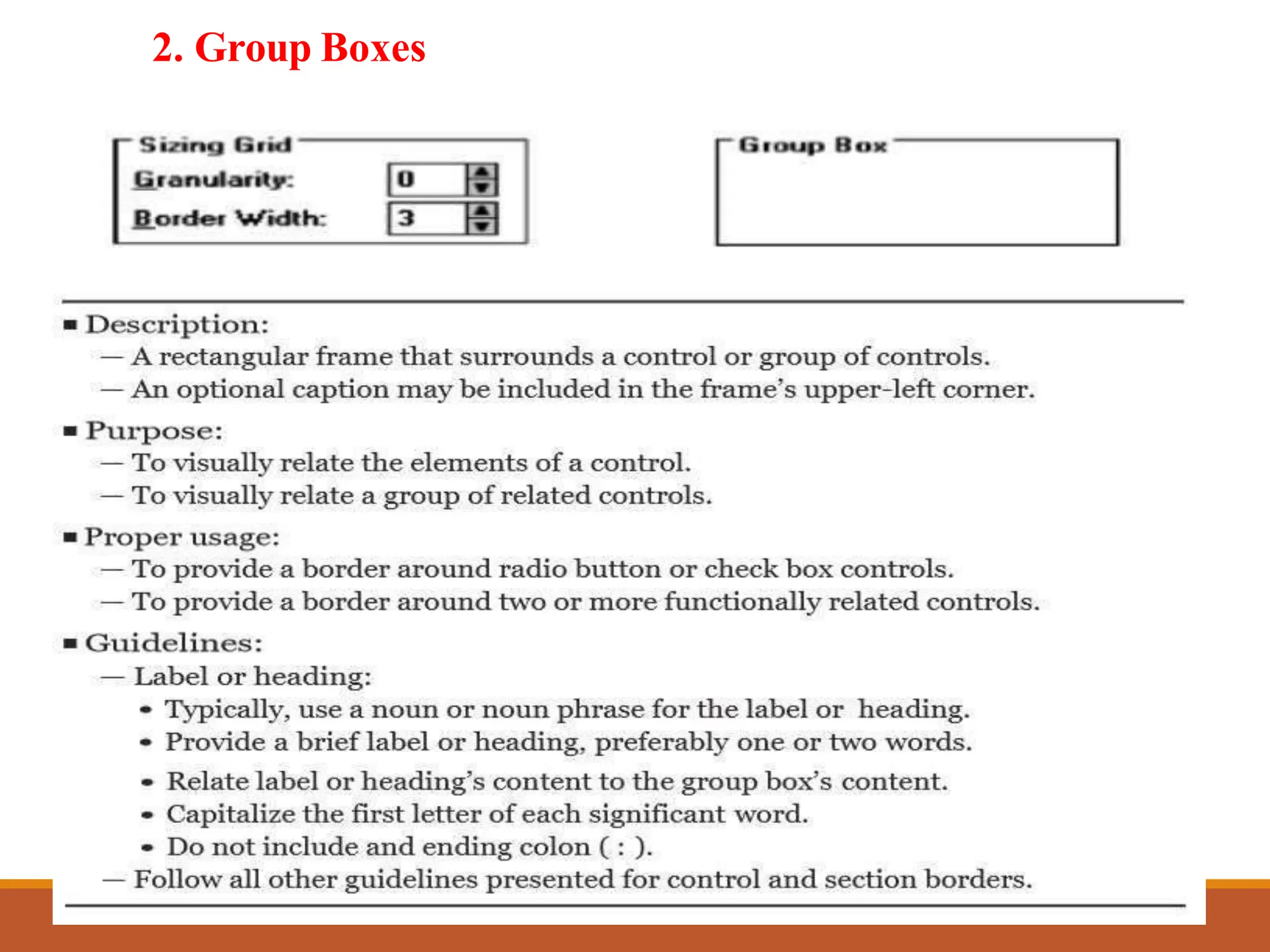
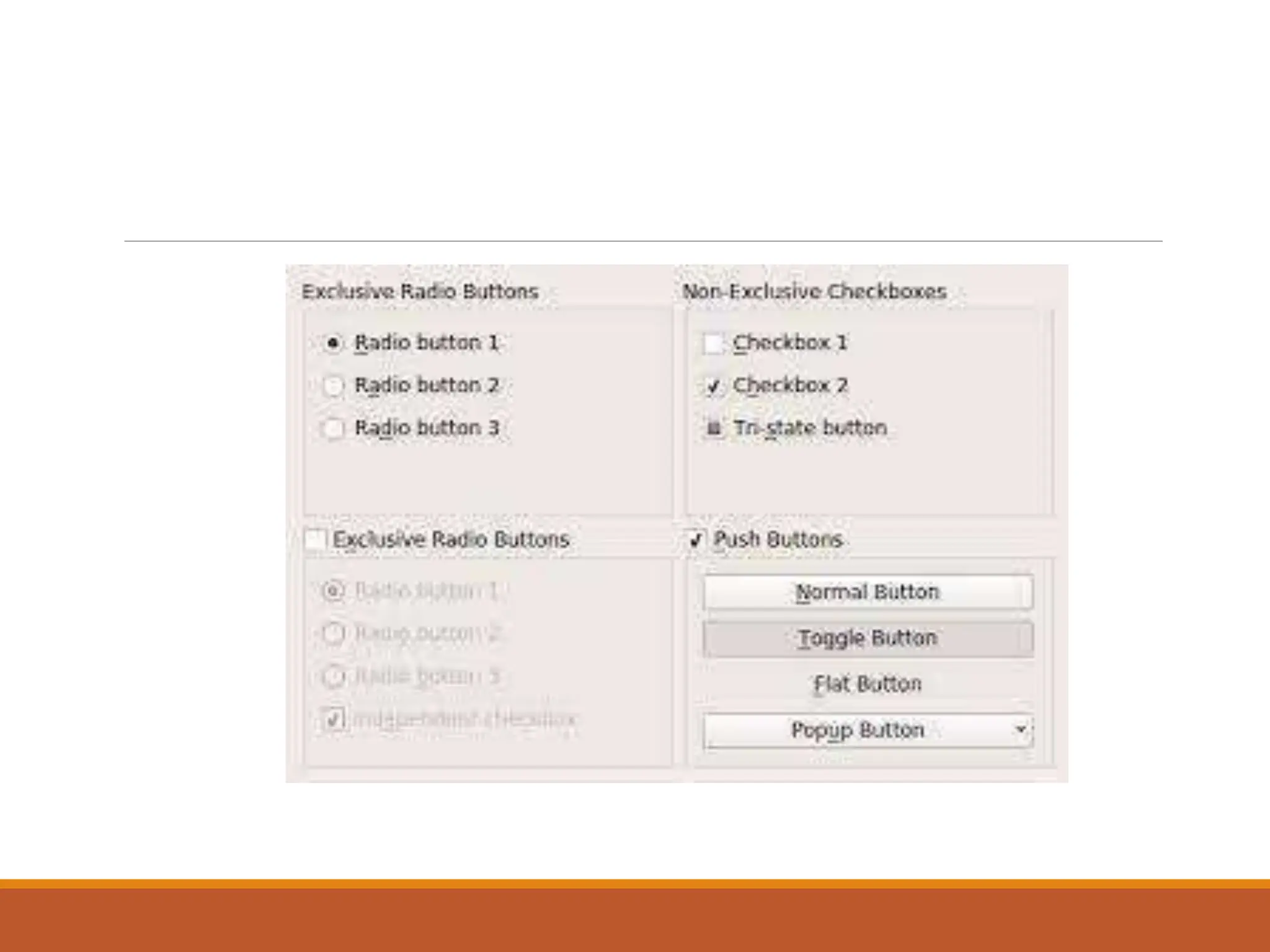
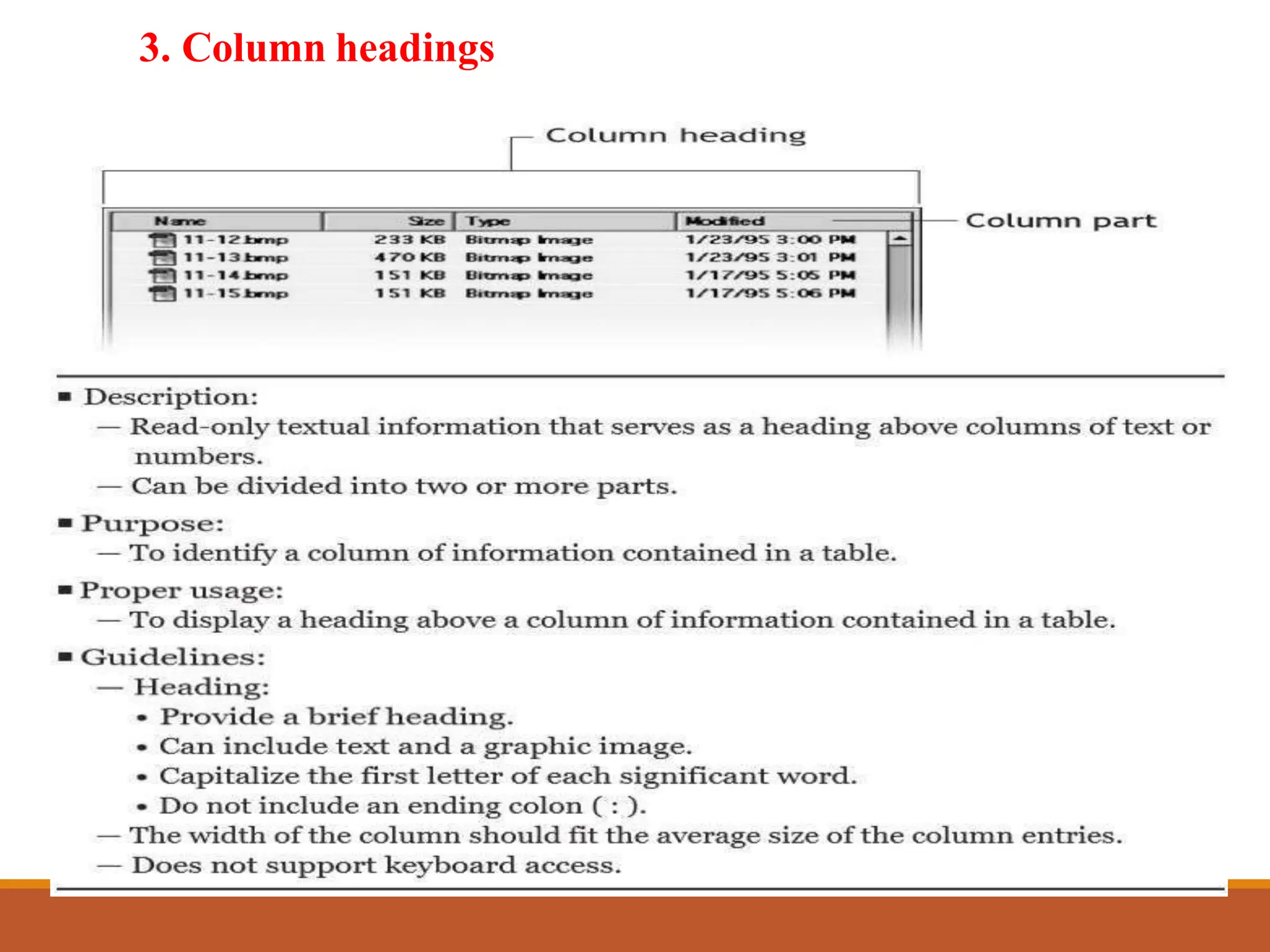
This document discusses different types of screen-based controls including operable controls like buttons, text entry/read-only controls, selection controls, presentation controls, custom controls, and prototypes. It provides guidelines for using various controls like command buttons, text boxes, radio buttons, and drop-down lists. The document also covers different types of windows tests that can be used to evaluate a design like guidelines reviews, think-aloud evaluations, cognitive walkthroughs, heuristic evaluations, and usability tests.