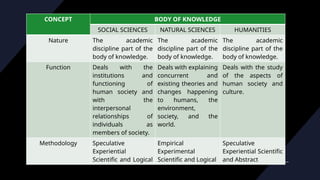
The document explores the nature and functions of social sciences and humanities, emphasizing their historical development and differentiation from natural sciences. It outlines various branches of humanities, including anthropology, archaeology, classics, and philosophy, and their roles in understanding human society and culture. Additionally, it discusses the interdisciplinary nature of social sciences, their methodologies, and how they address social relationships and societal functions.