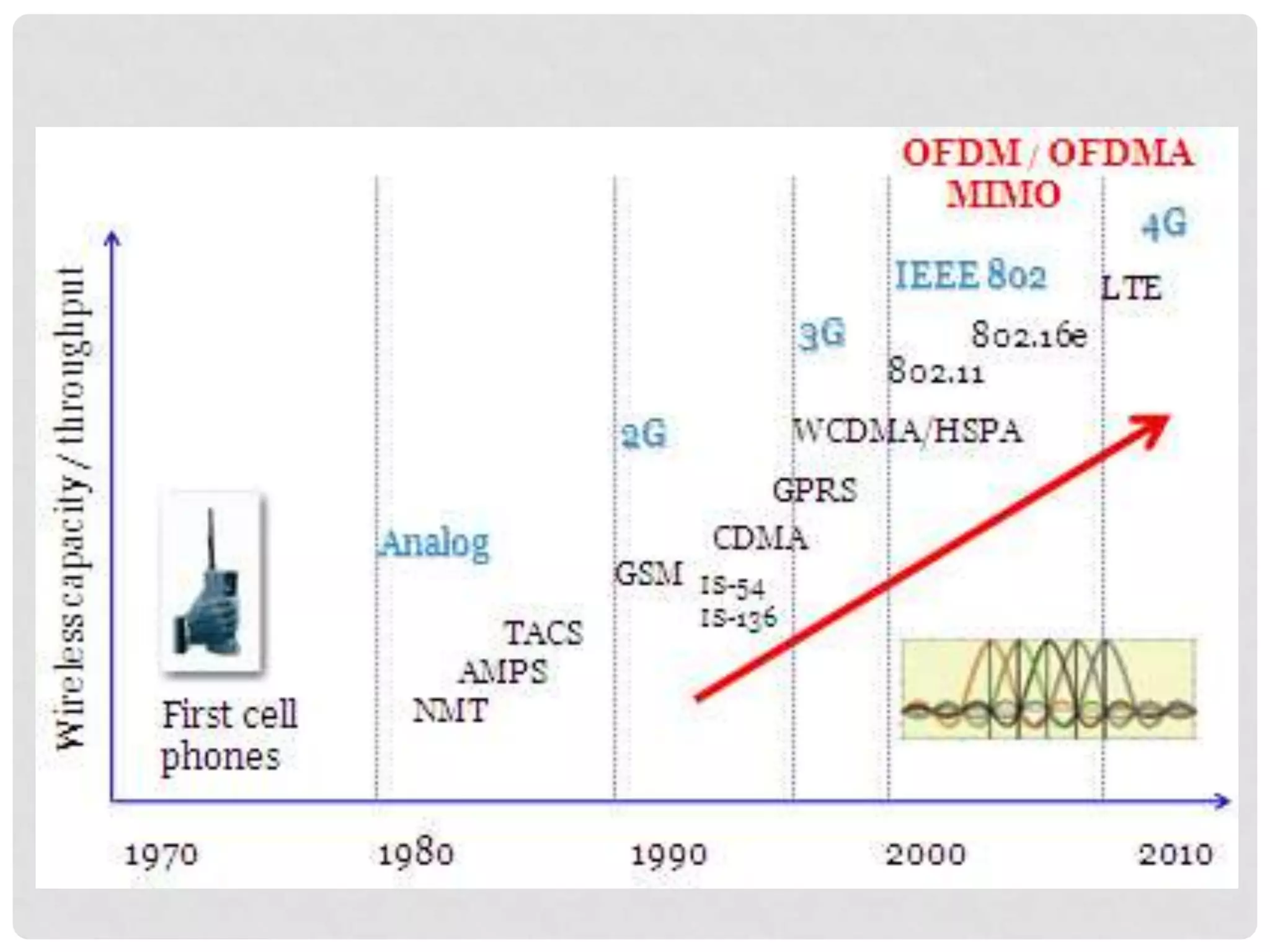
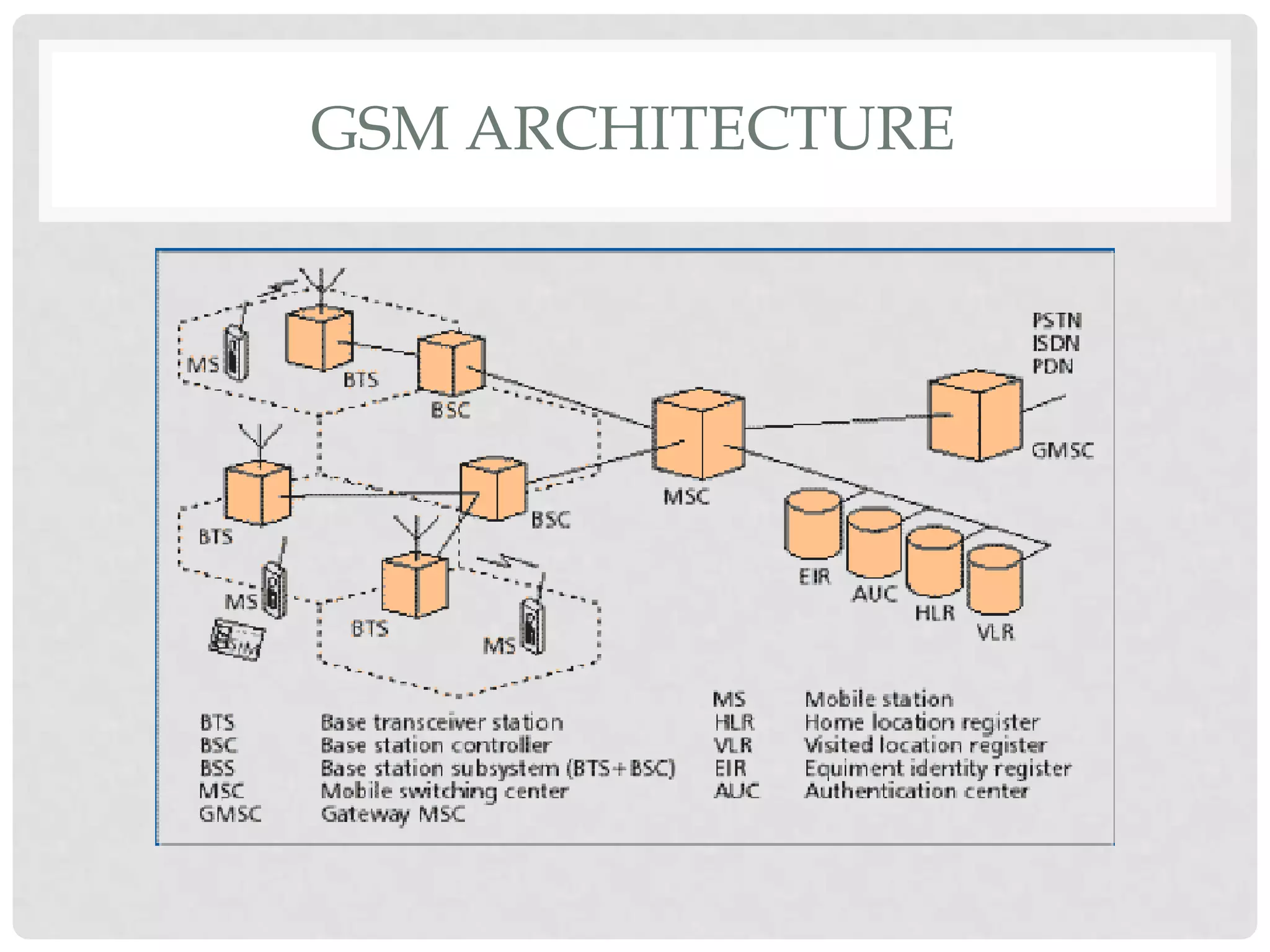
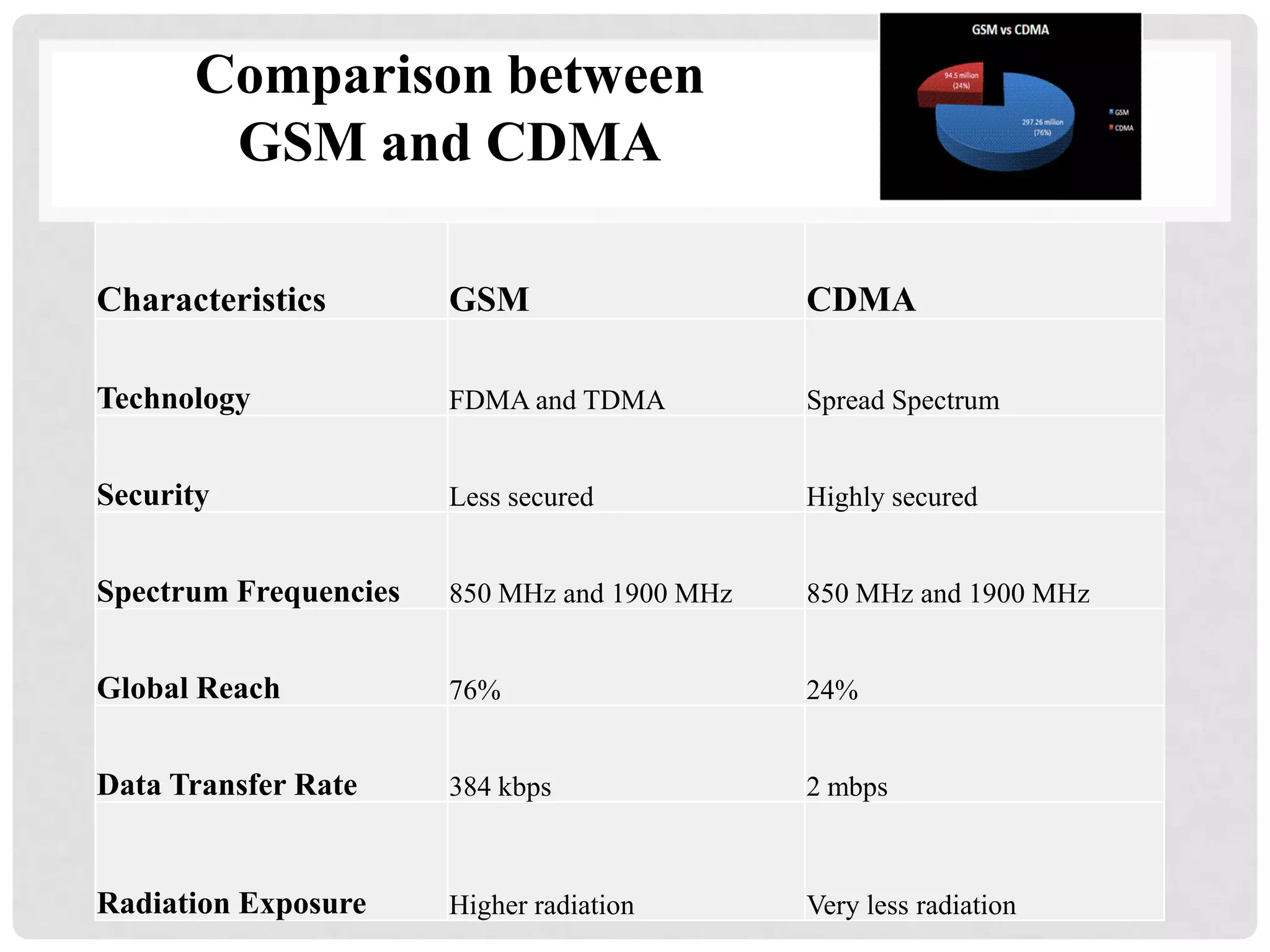
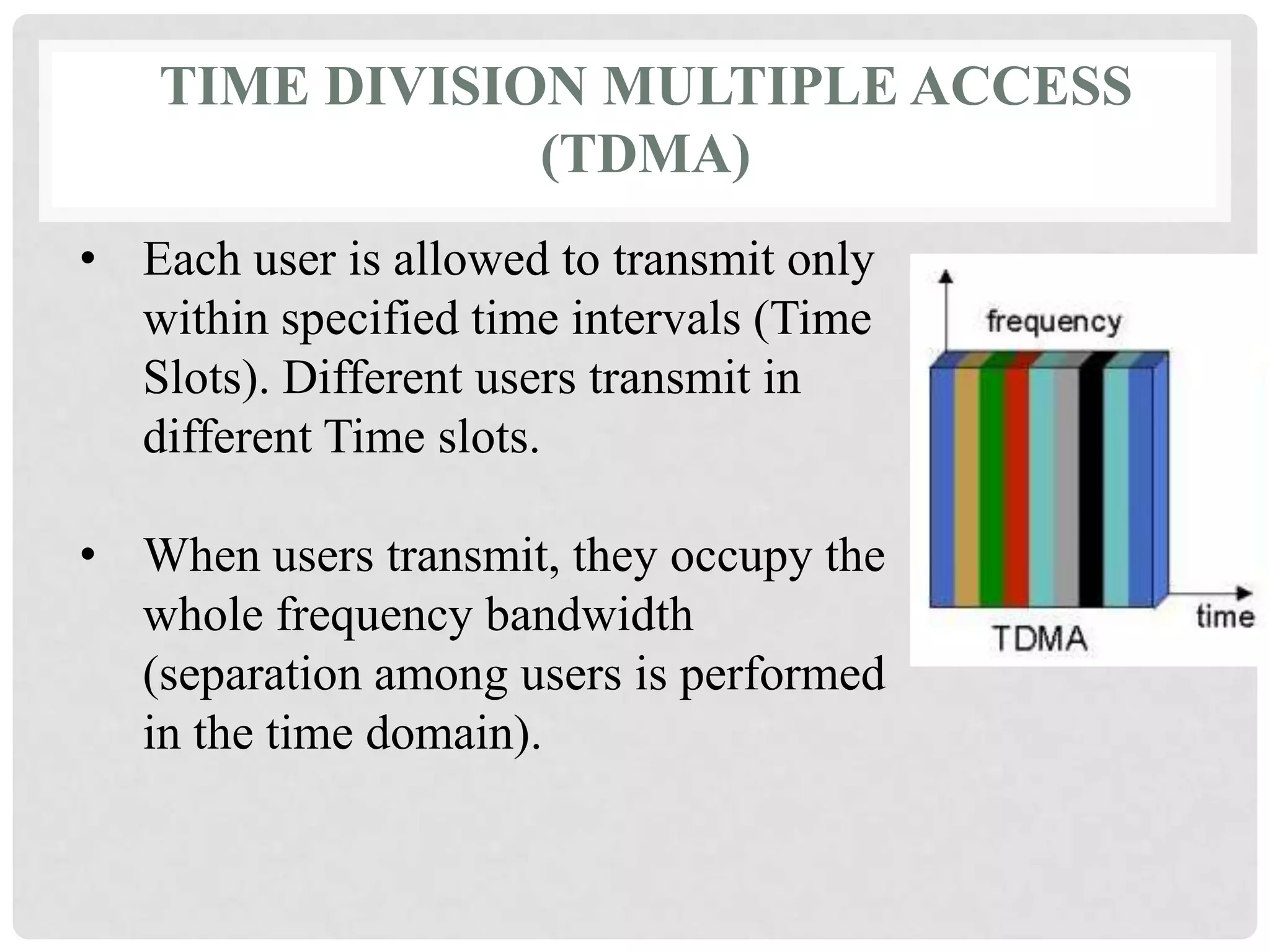
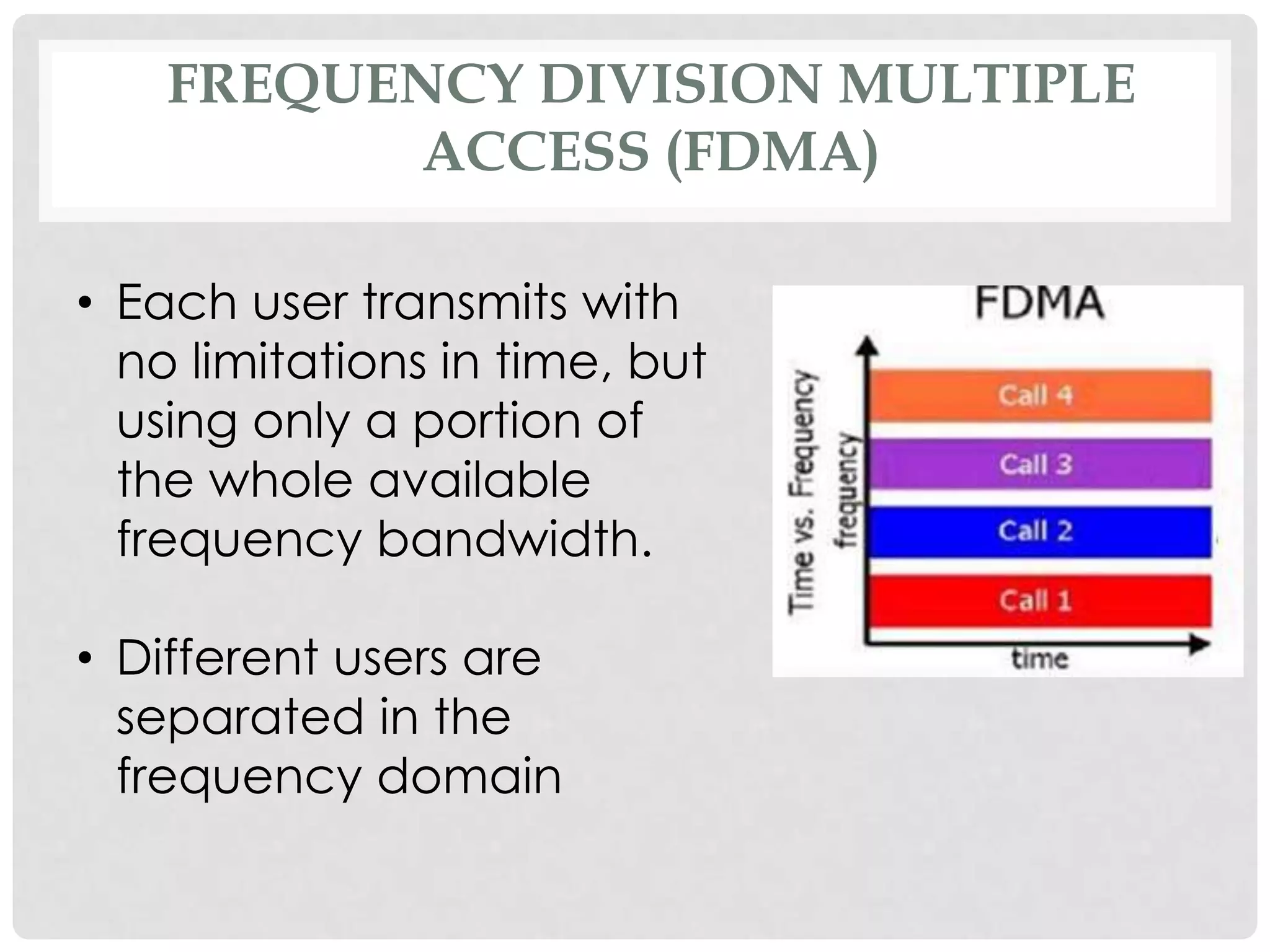
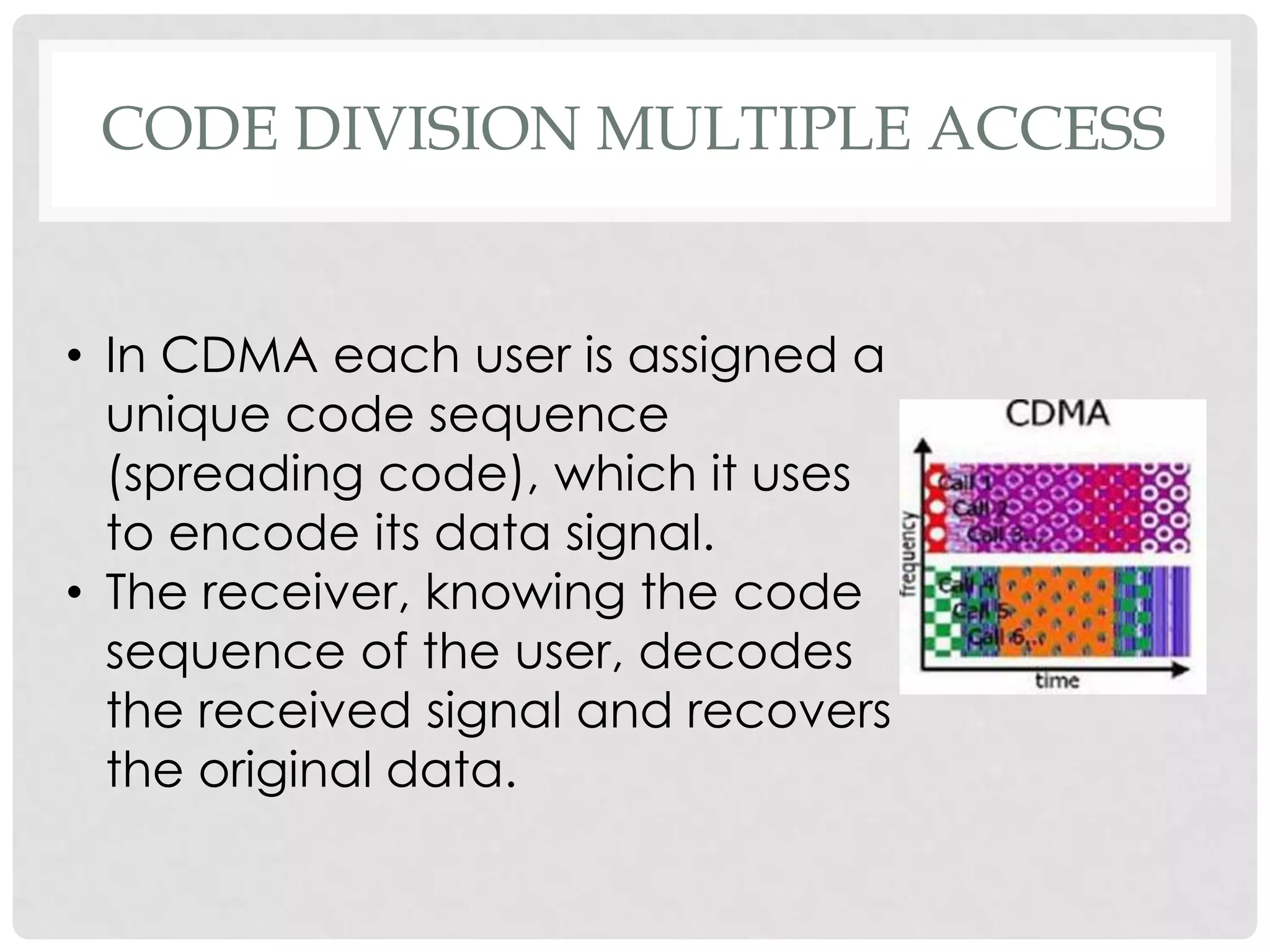
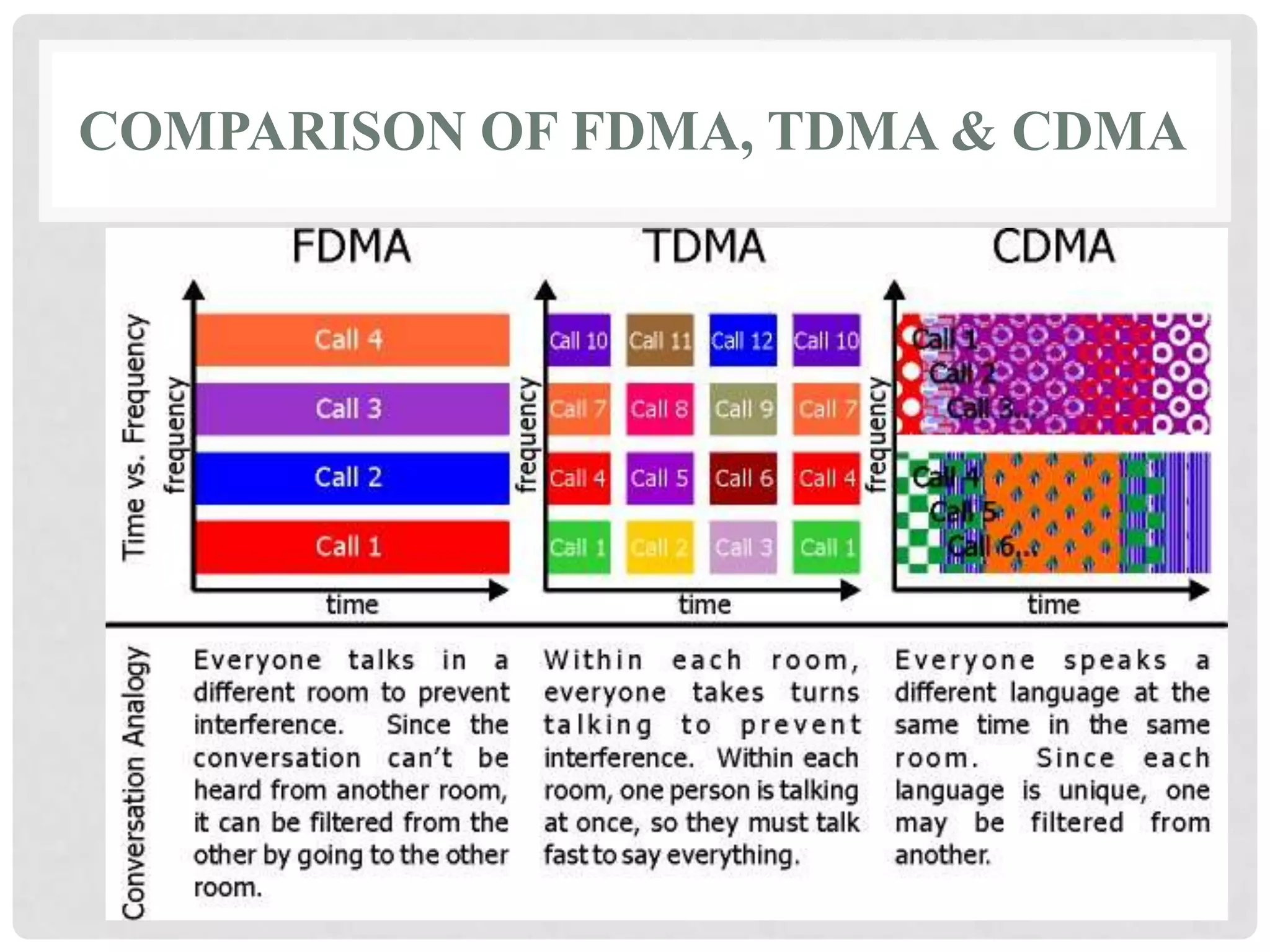
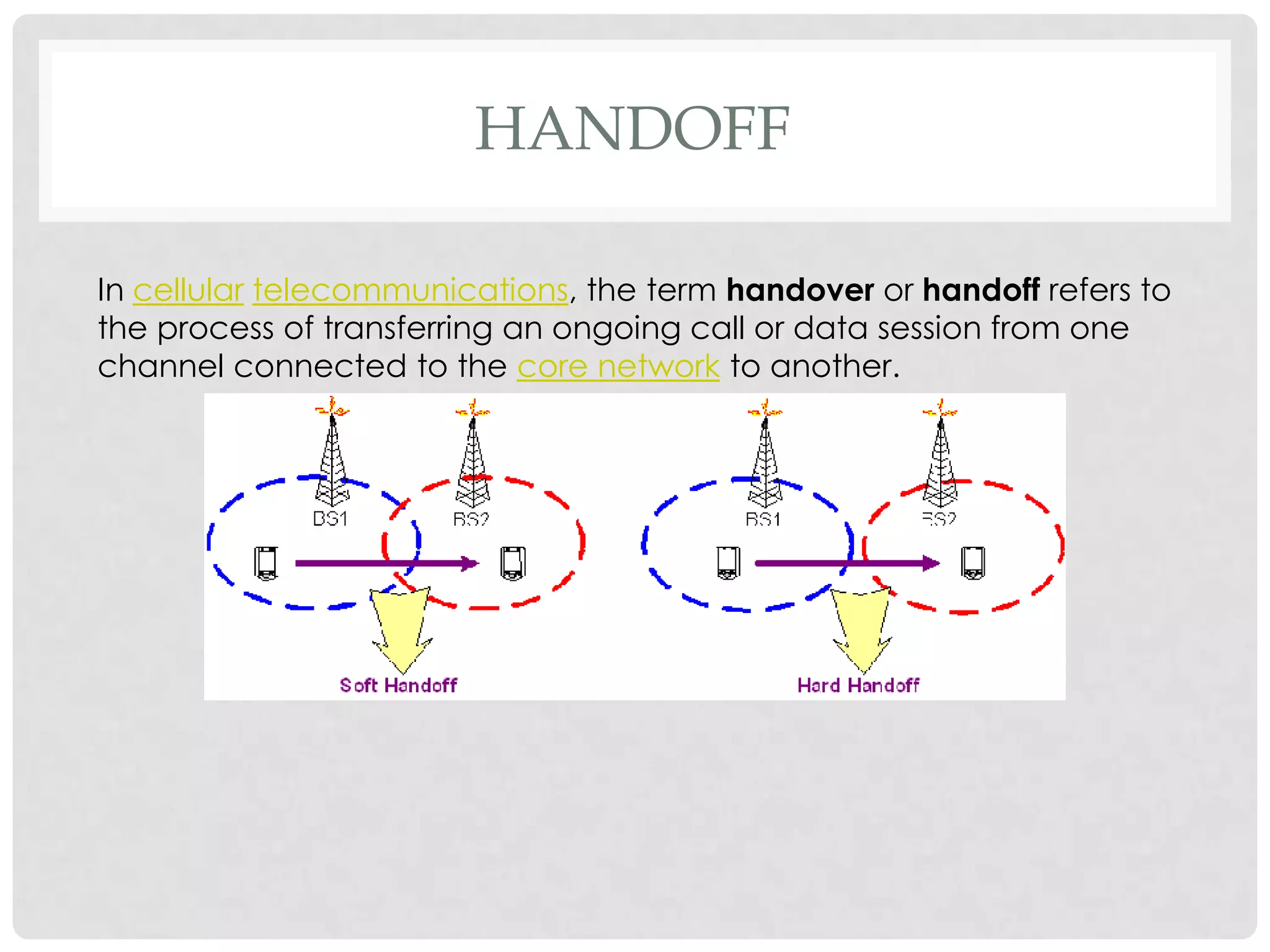
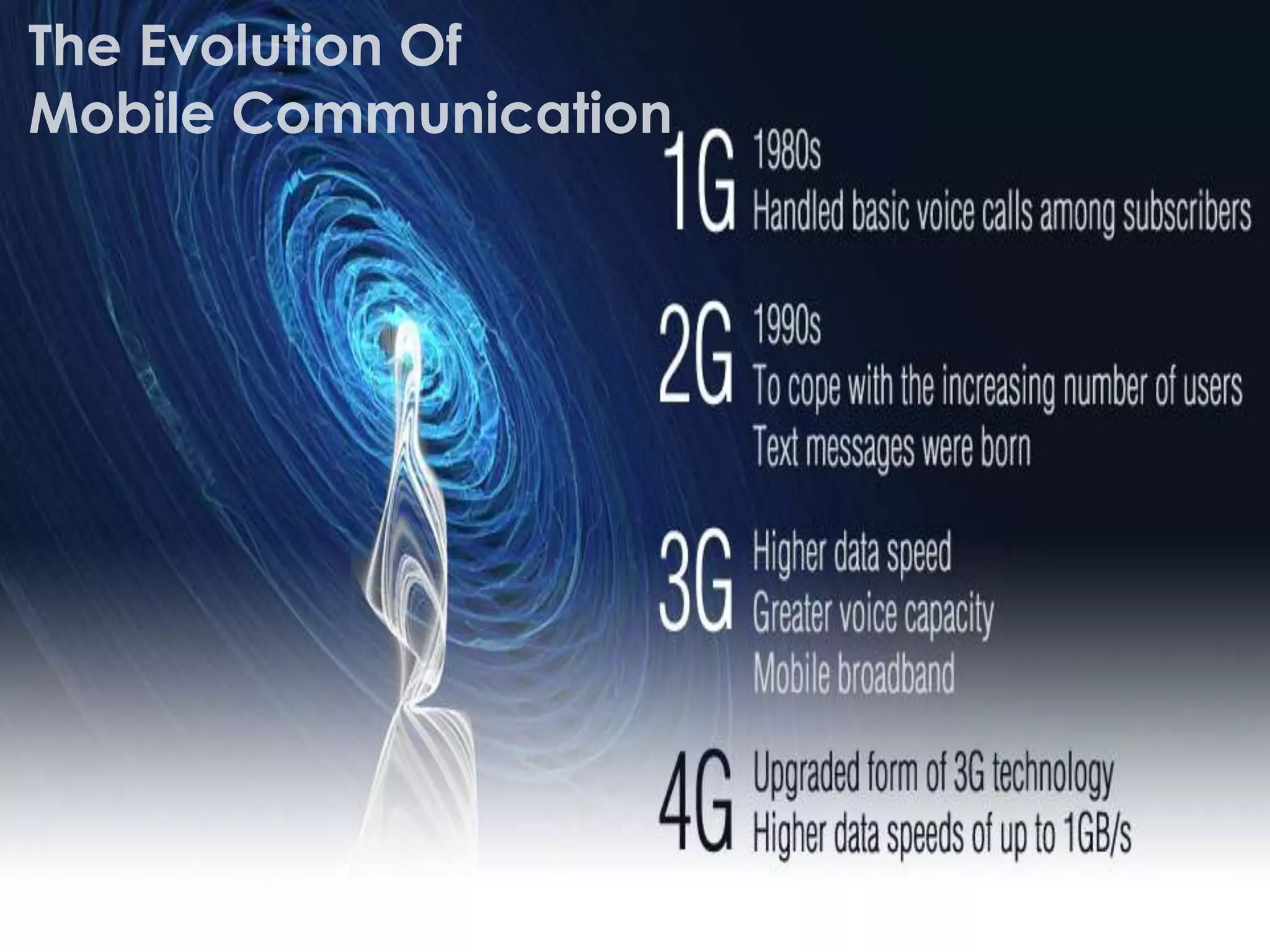
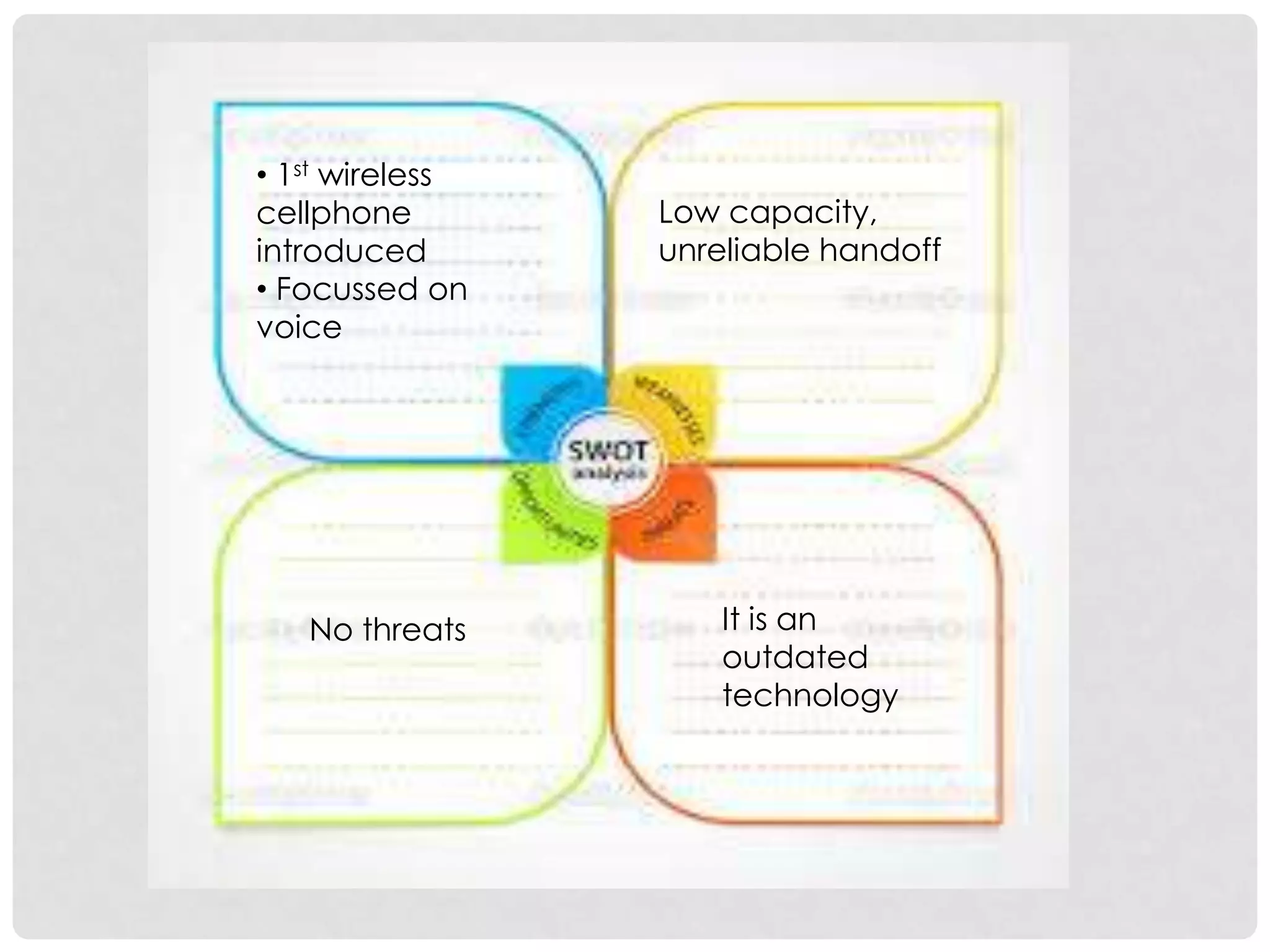
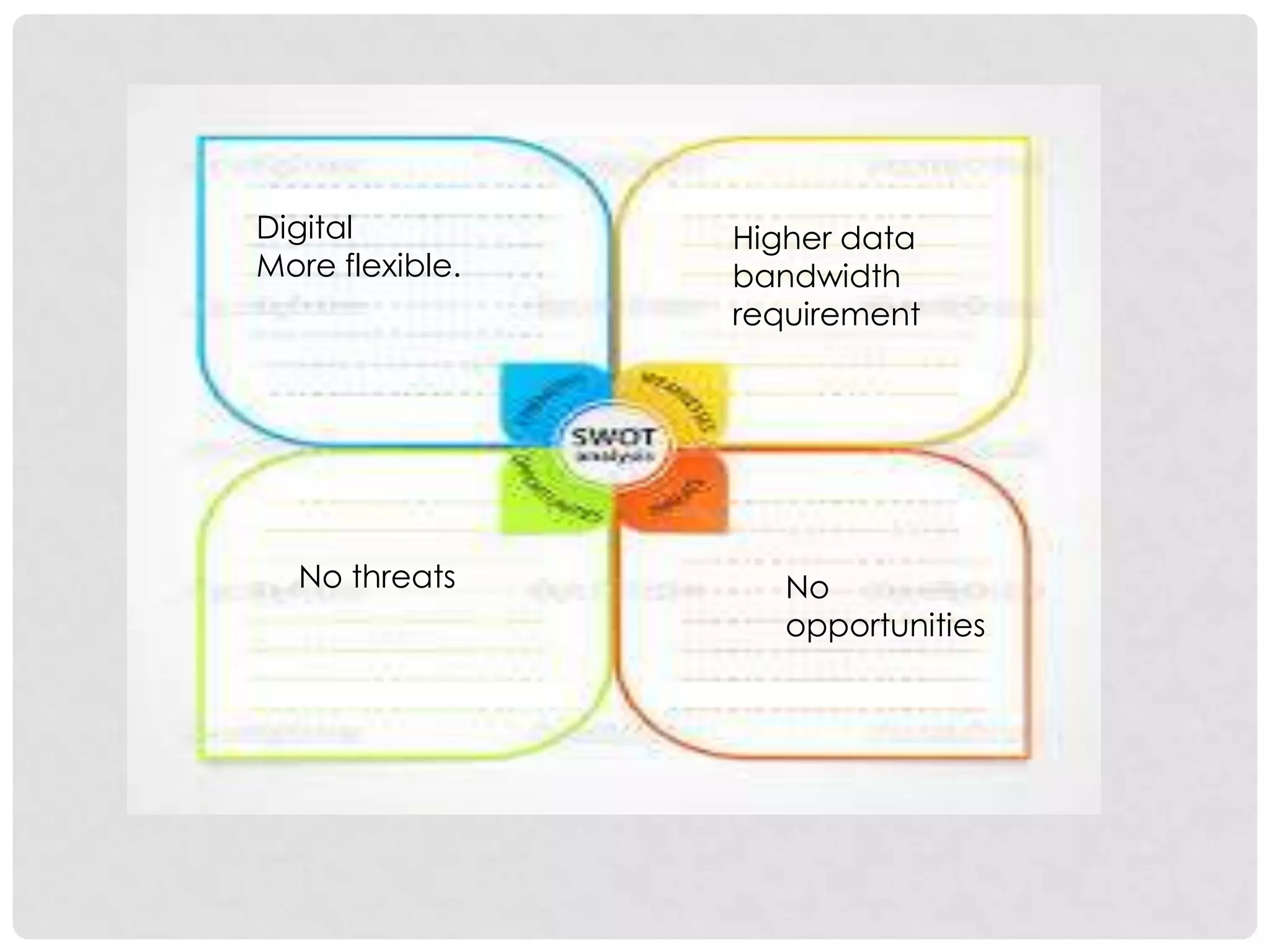
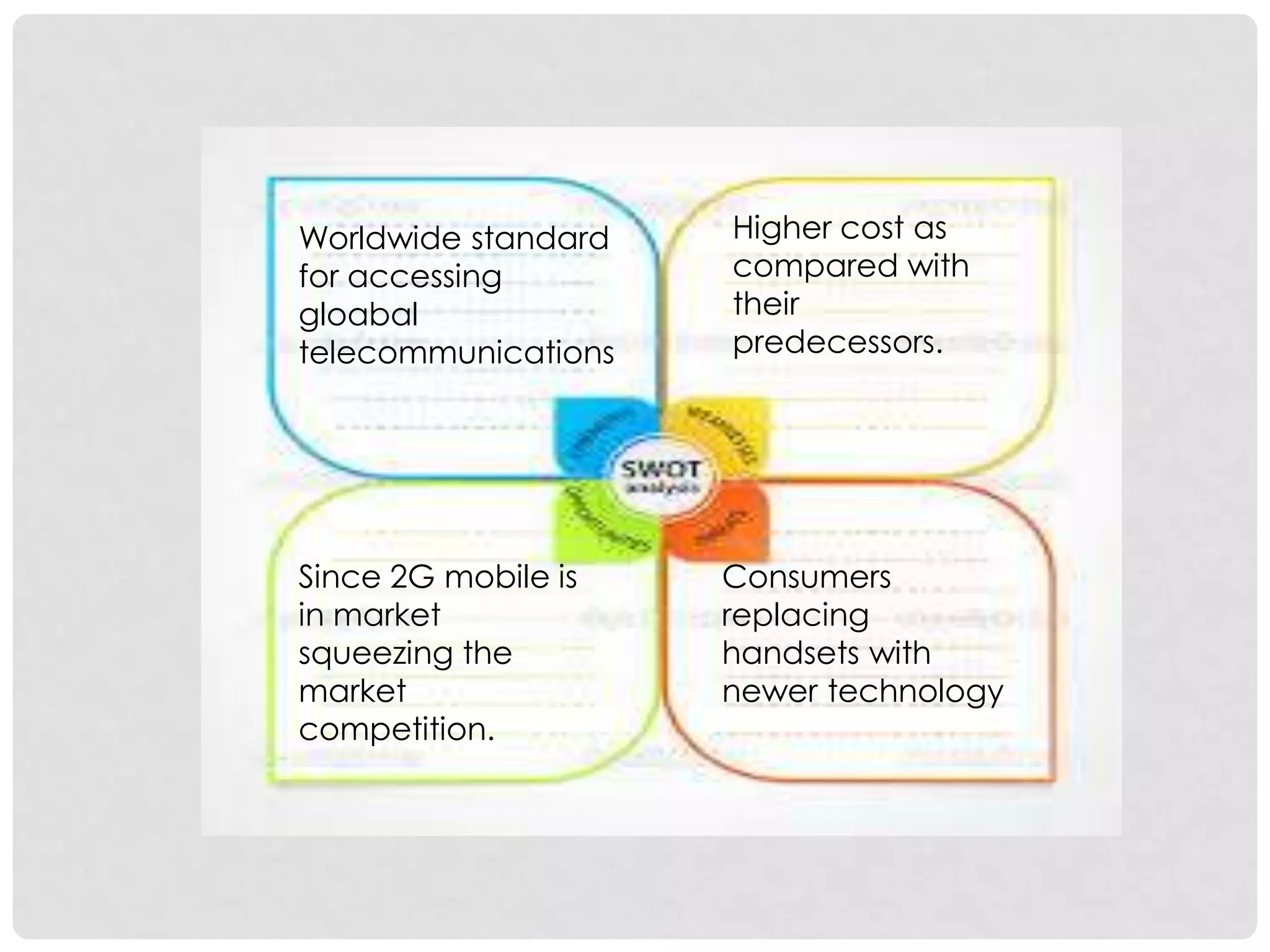
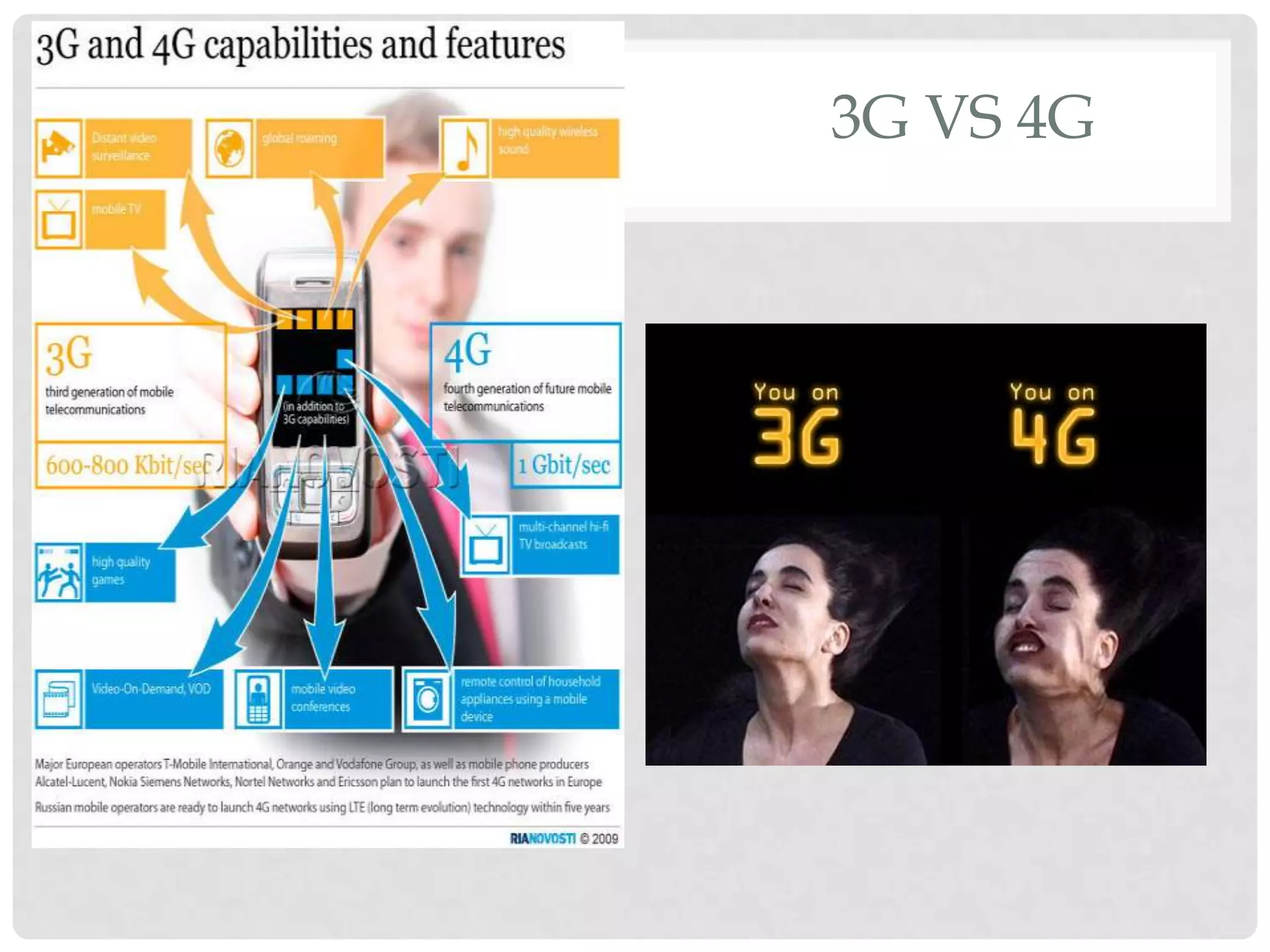
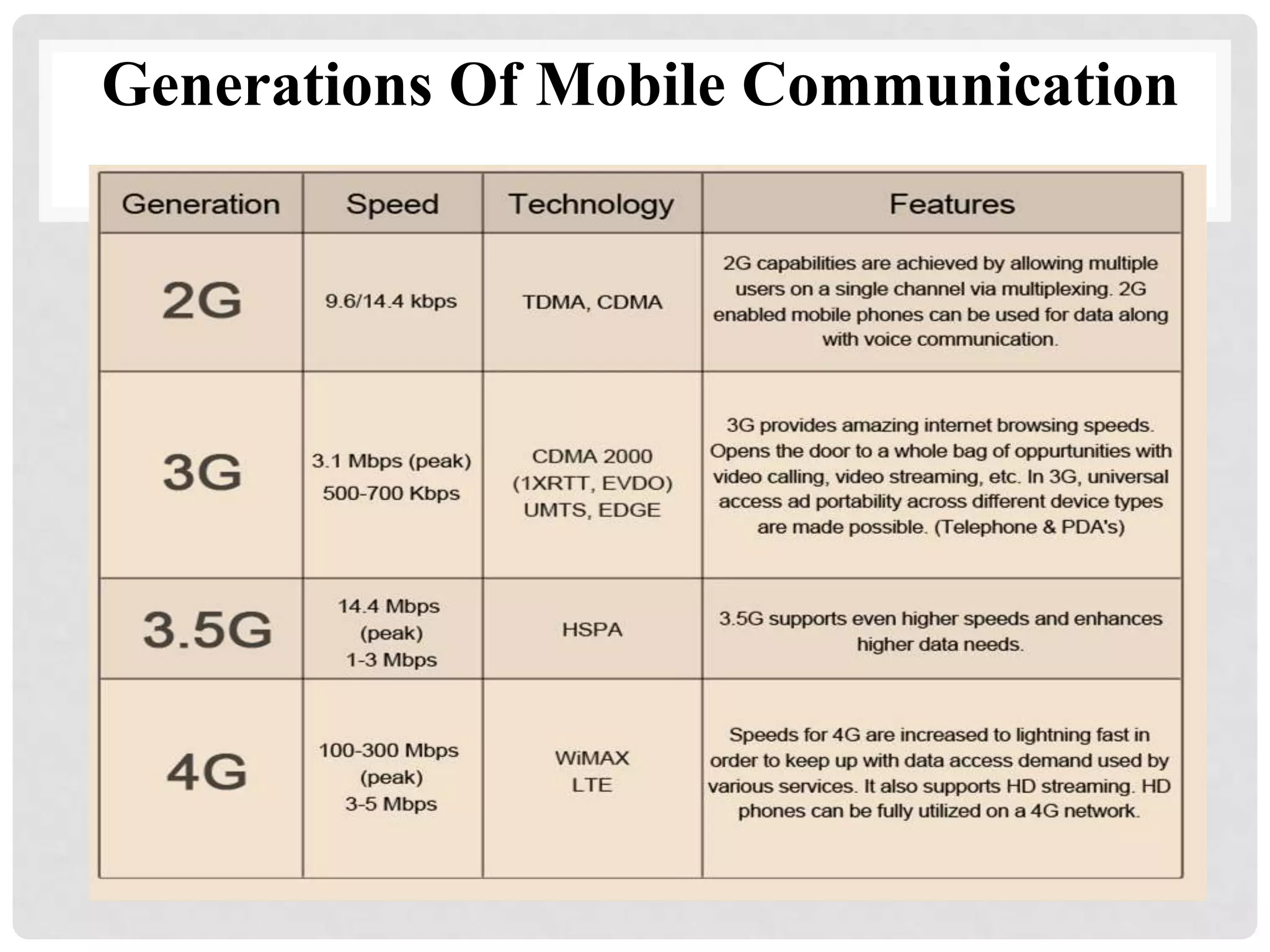
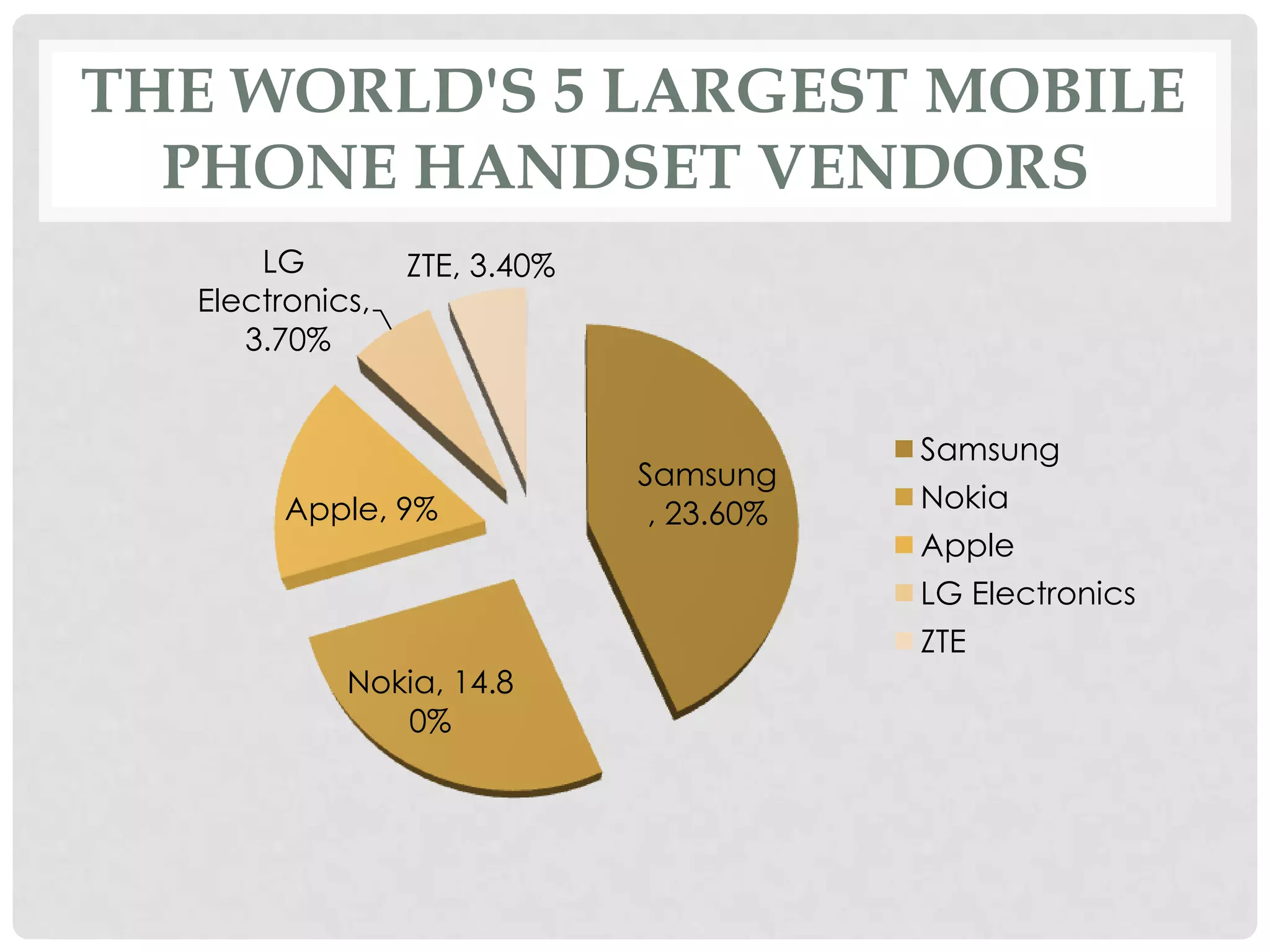
The document outlines the history and evolution of mobile communication, detailing significant milestones from the late 19th century to the introduction of 4G technology. It compares different mobile communication technologies such as GSM, CDMA, TDMA, and FDMA, and discusses their characteristics, including security concerns and data transfer rates. Additionally, it lists the largest mobile phone and telecommunications equipment vendors in the world.