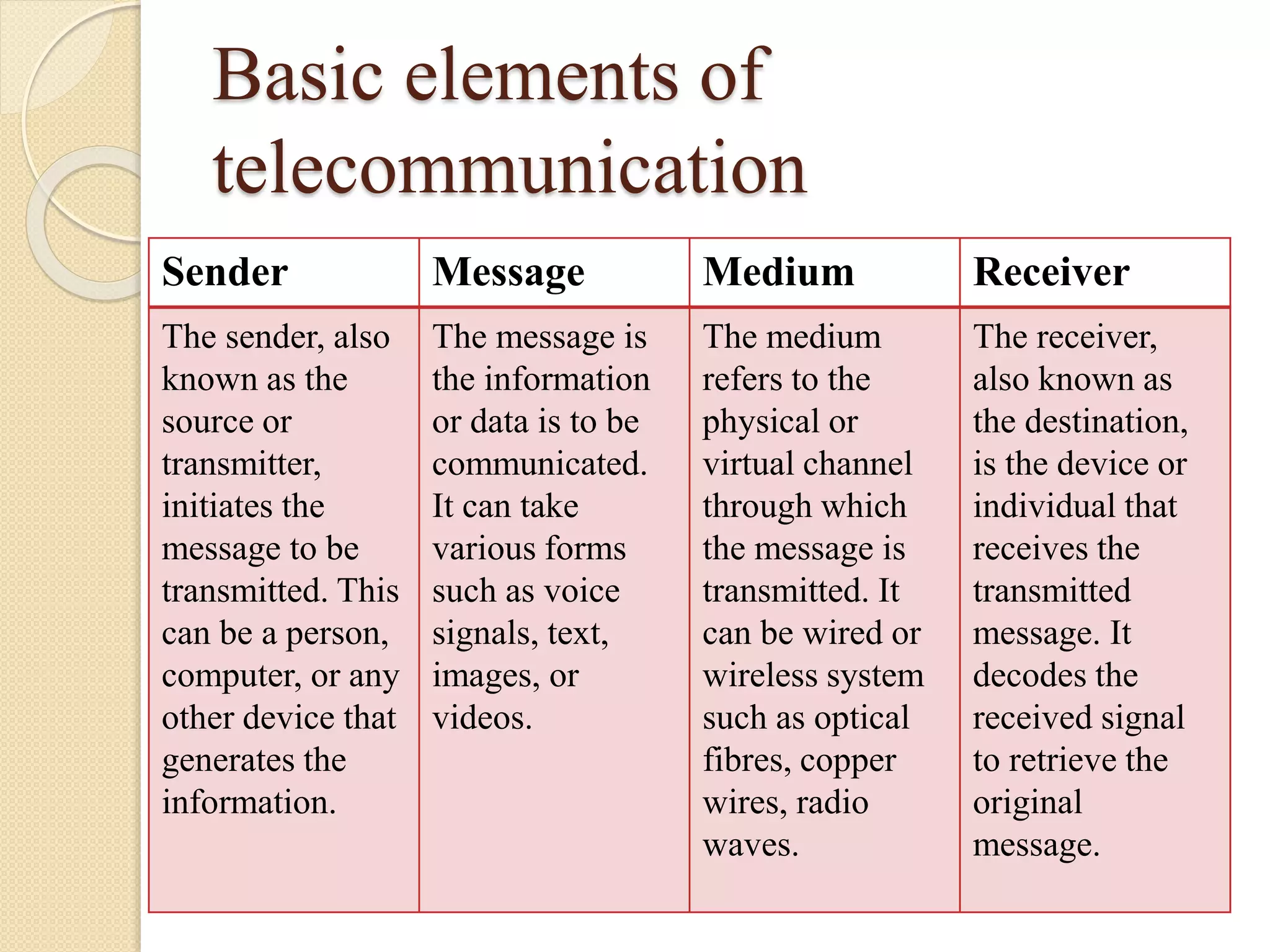
The document provides an overview of telecommunication and its evolution, specifically focusing on the advancements from 1G to 5G mobile communication systems. It discusses the basic elements of telecommunication, various transmission modes, and key features and challenges associated with each mobile generation. Additionally, it includes literature surveys from studies emphasizing the growing demand and transformation in mobile communication technologies.