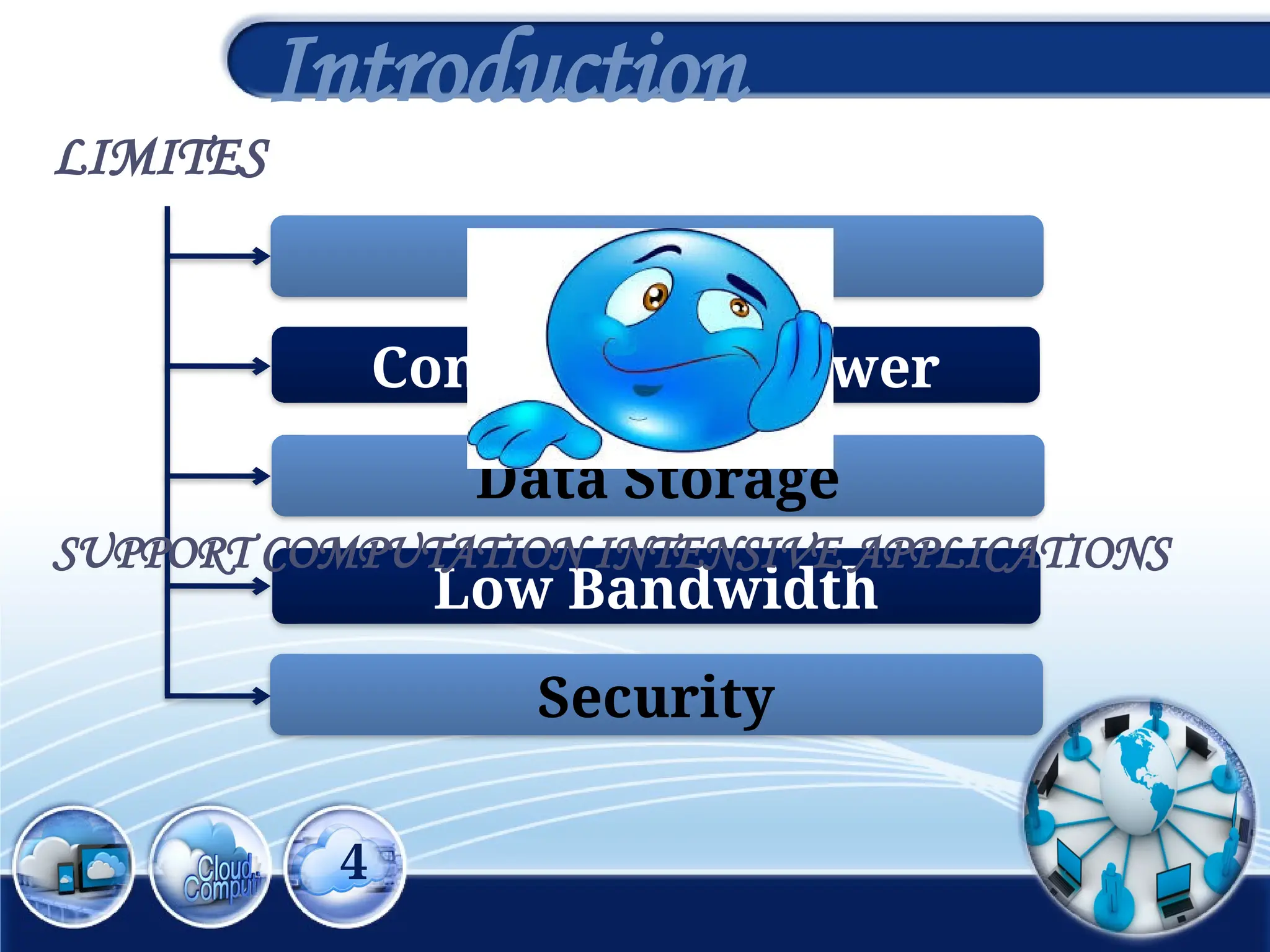
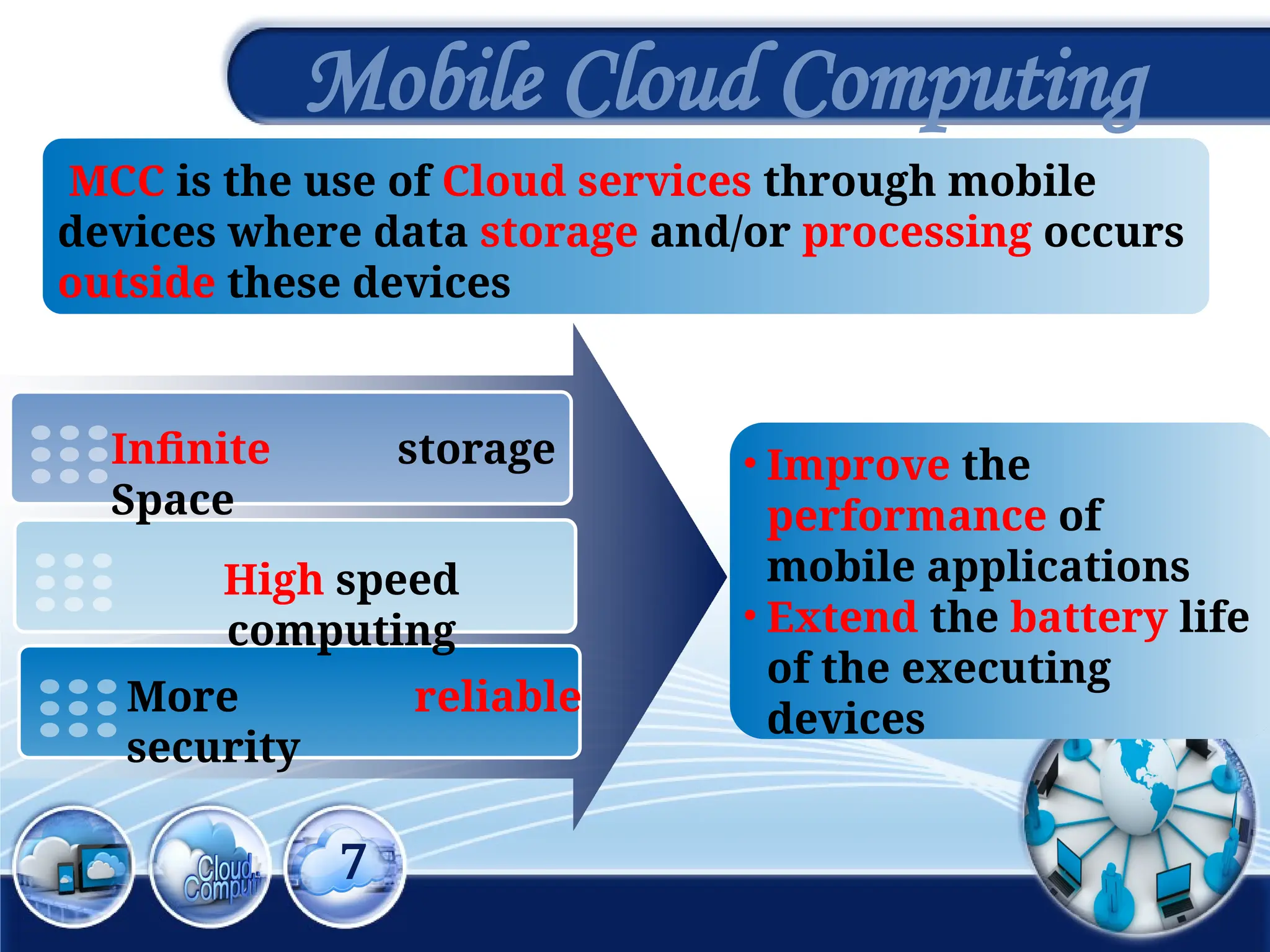
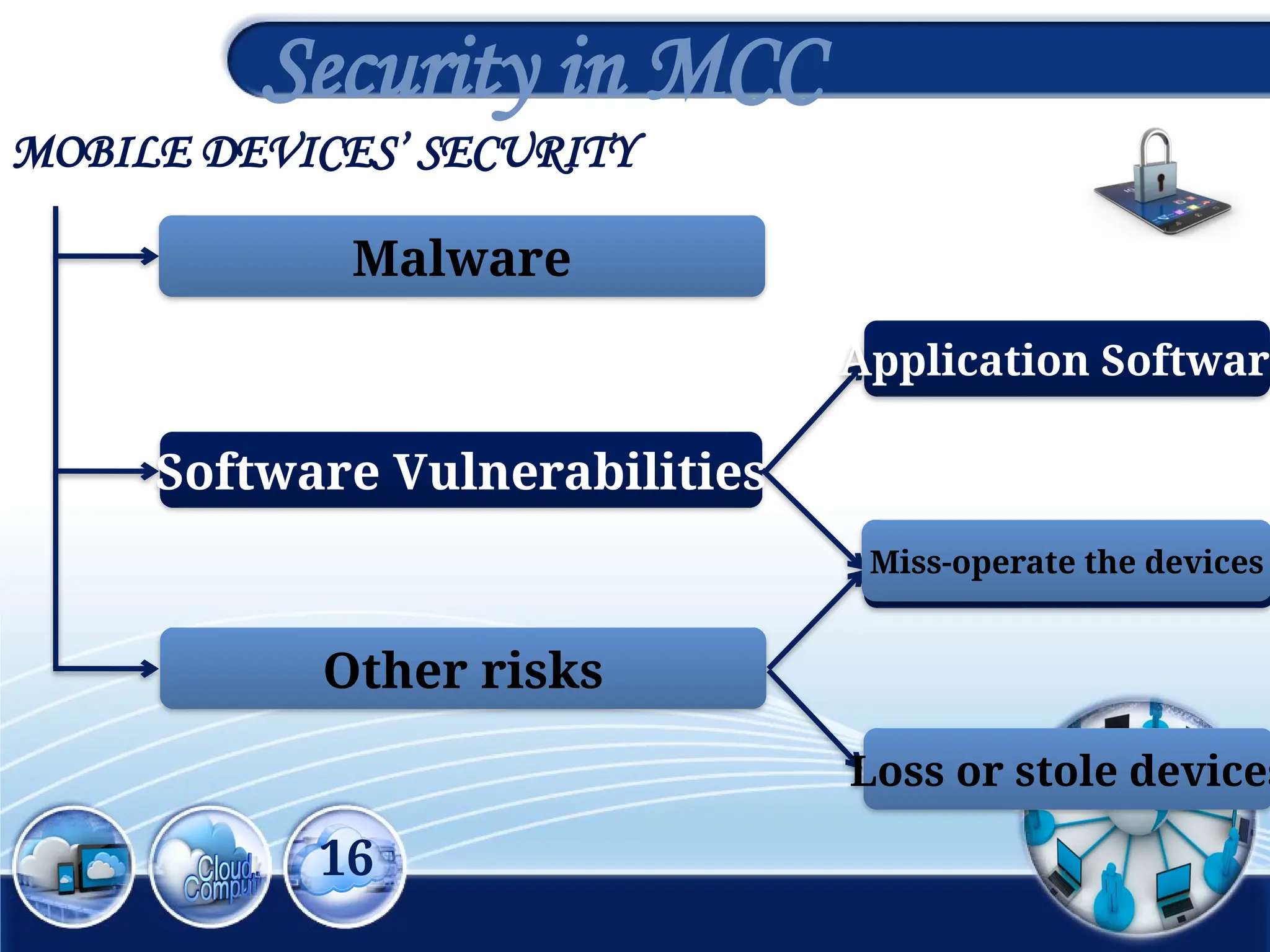
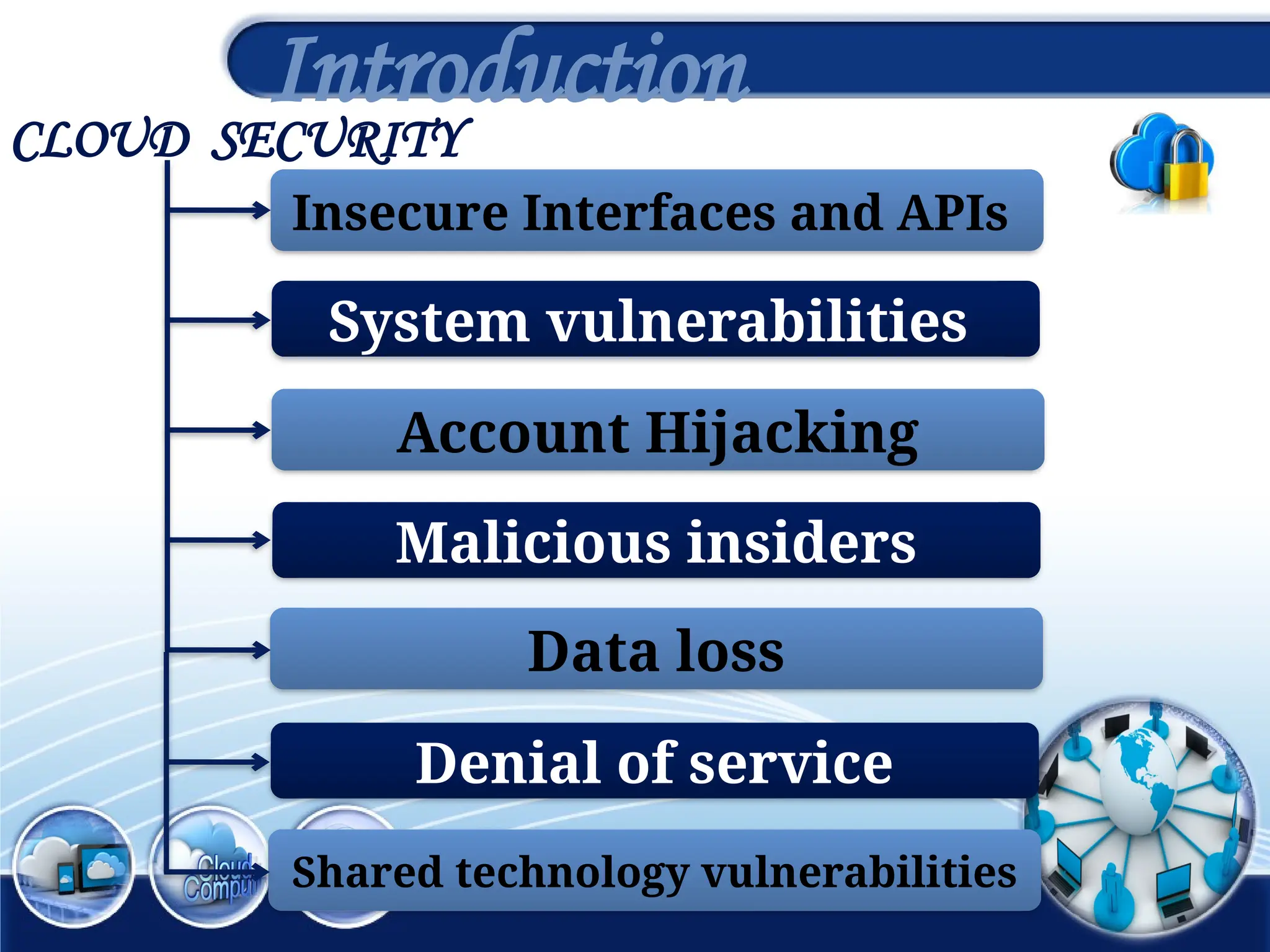
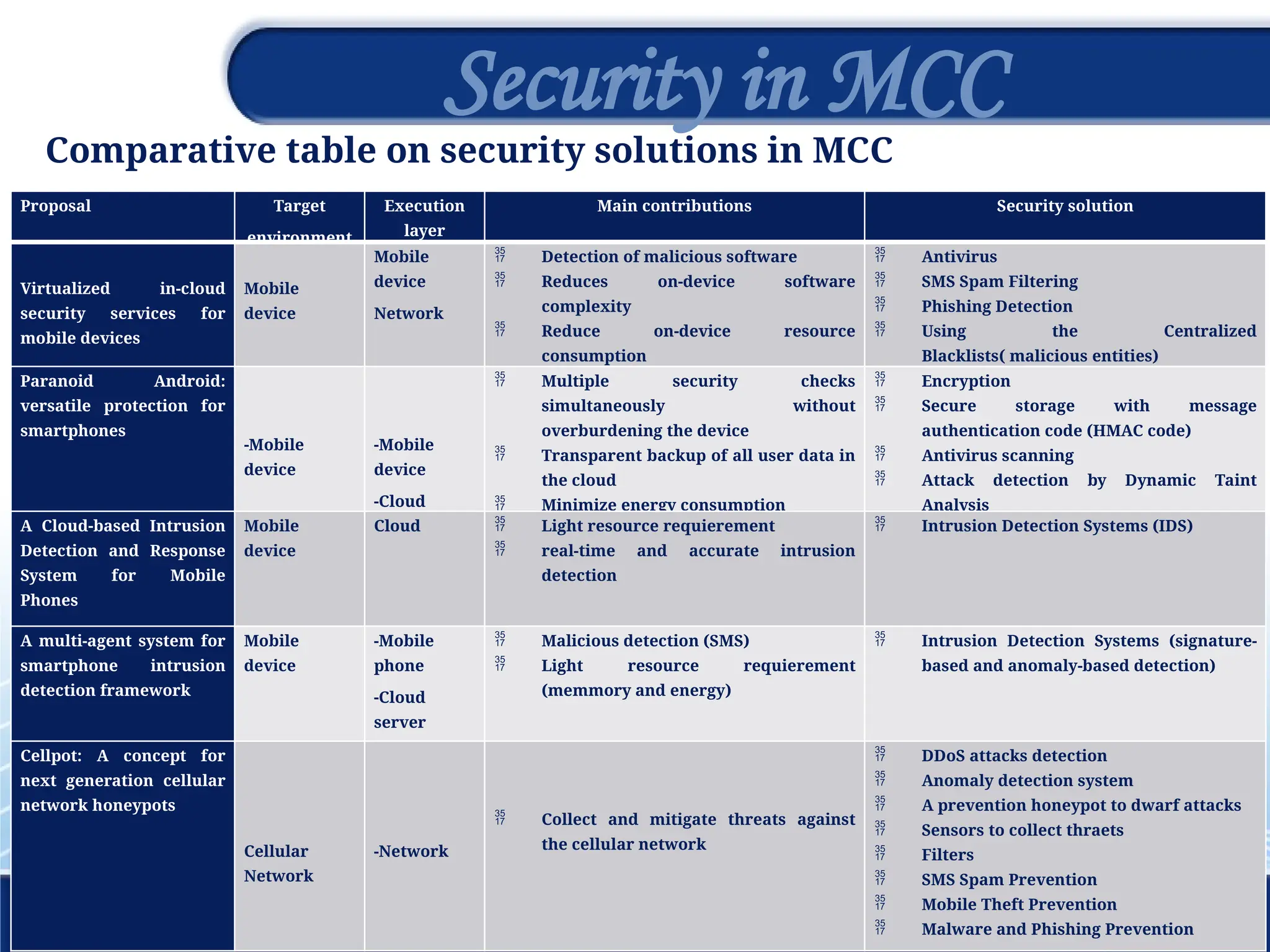
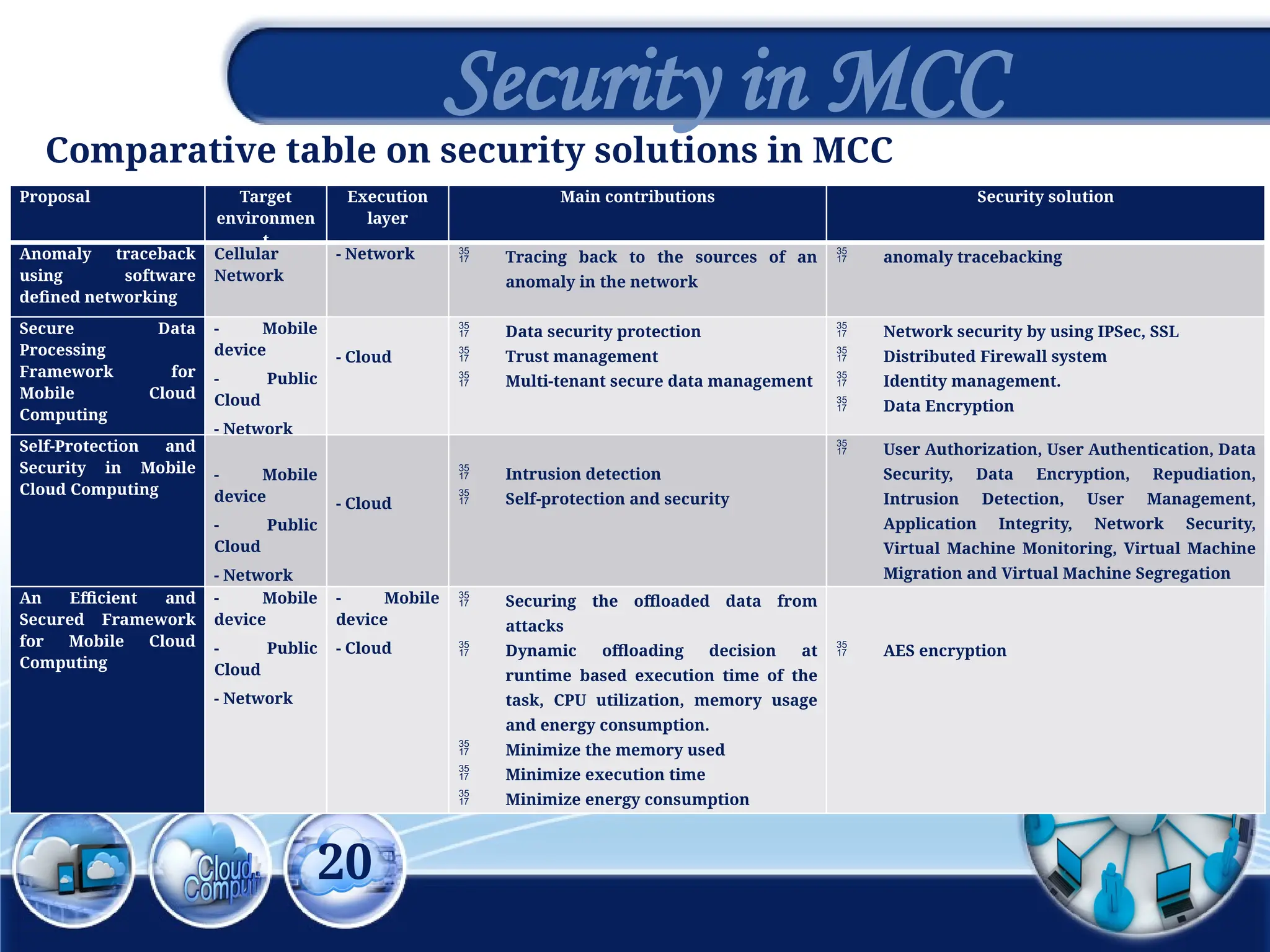
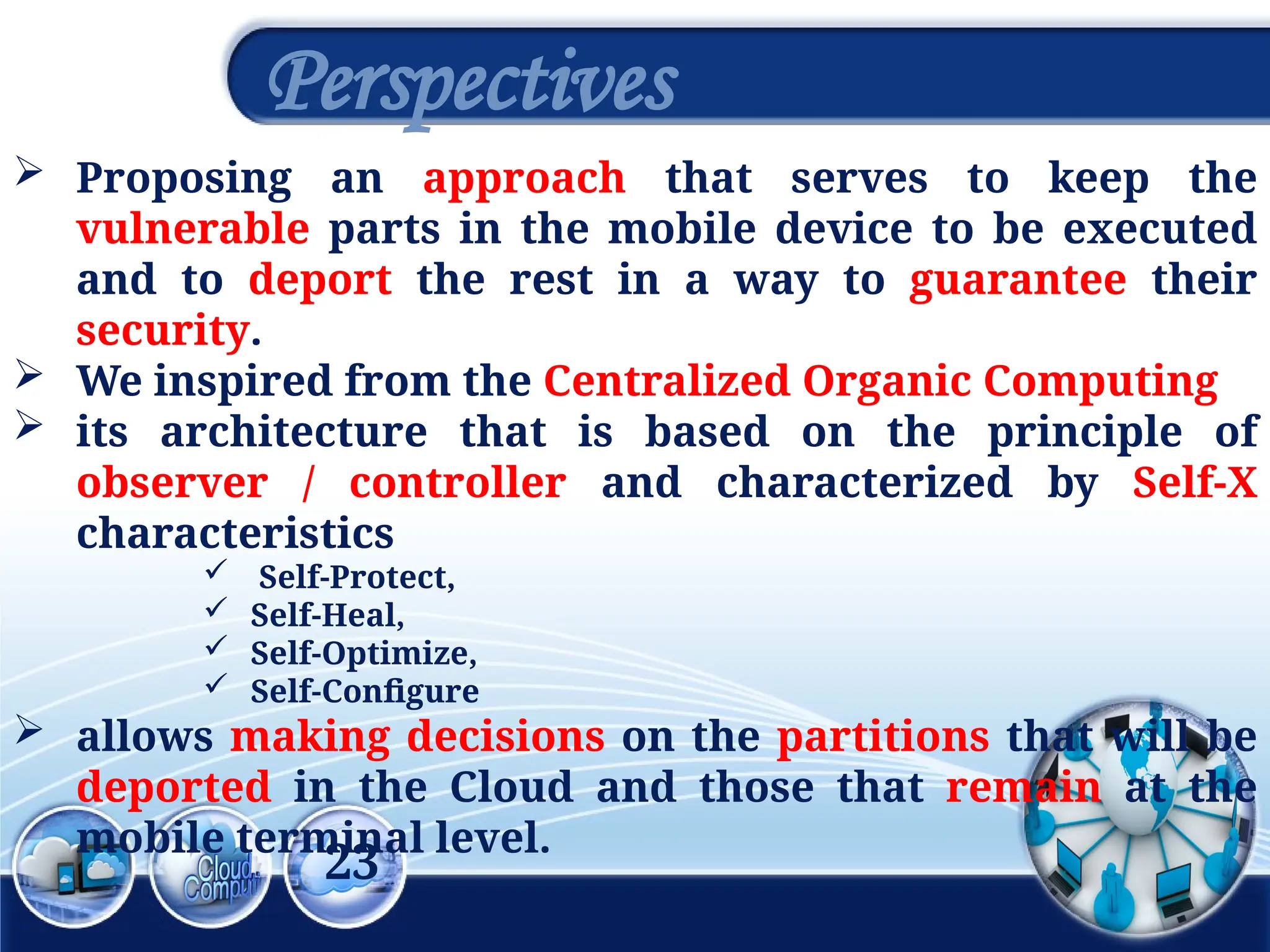
The document discusses the 3rd International Conference on Networking, Information Systems & Security, focusing on mobile cloud computing (MCC), its advantages such as improved productivity, battery life, and security issues like vulnerabilities and privacy concerns. It highlights the benefits of using cloud services through mobile devices while addressing challenges including resource limitations and security threats during data transfer. Proposed security solutions and future perspectives are presented for the development and enhancement of mobile cloud computing systems.