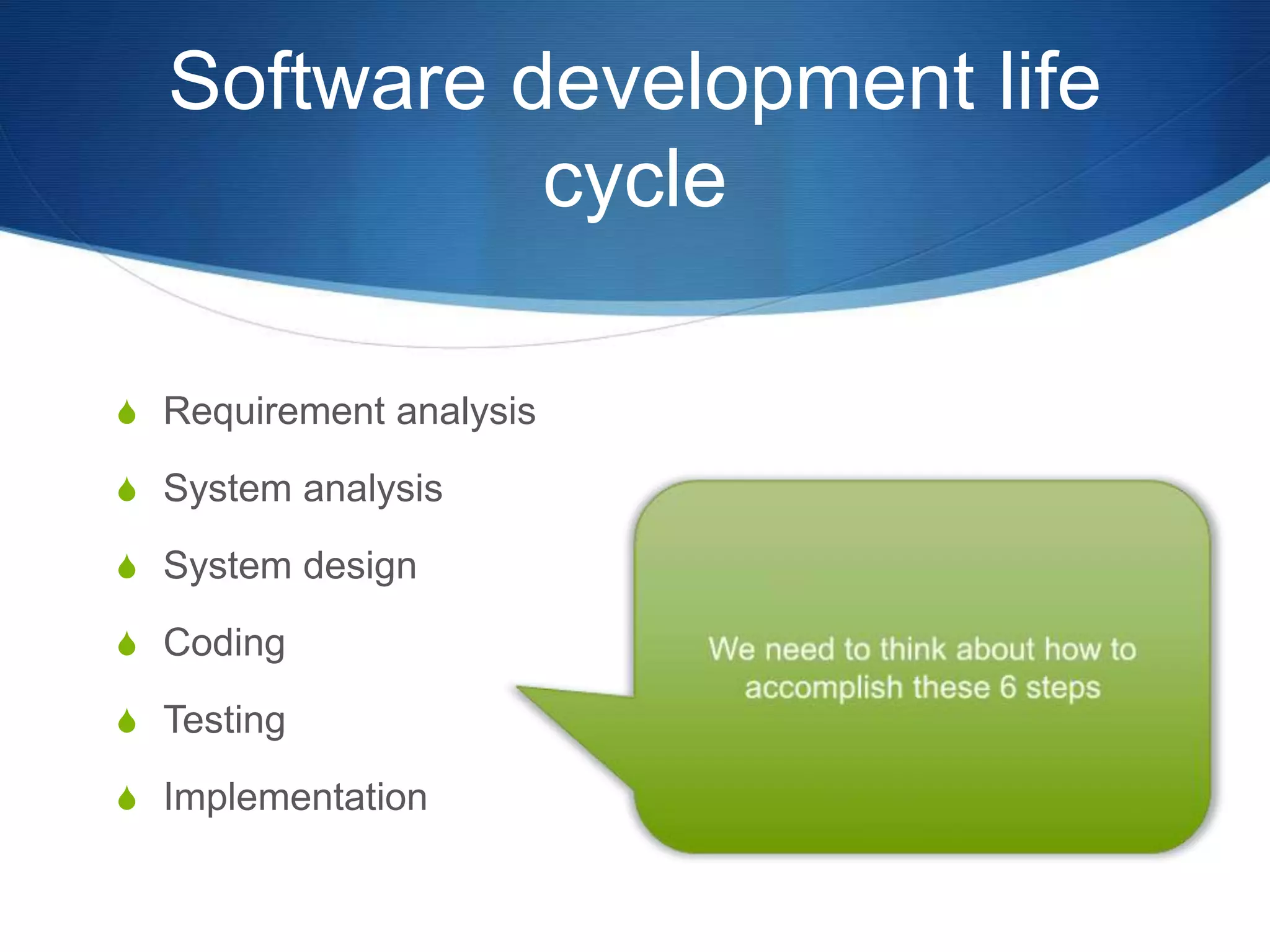
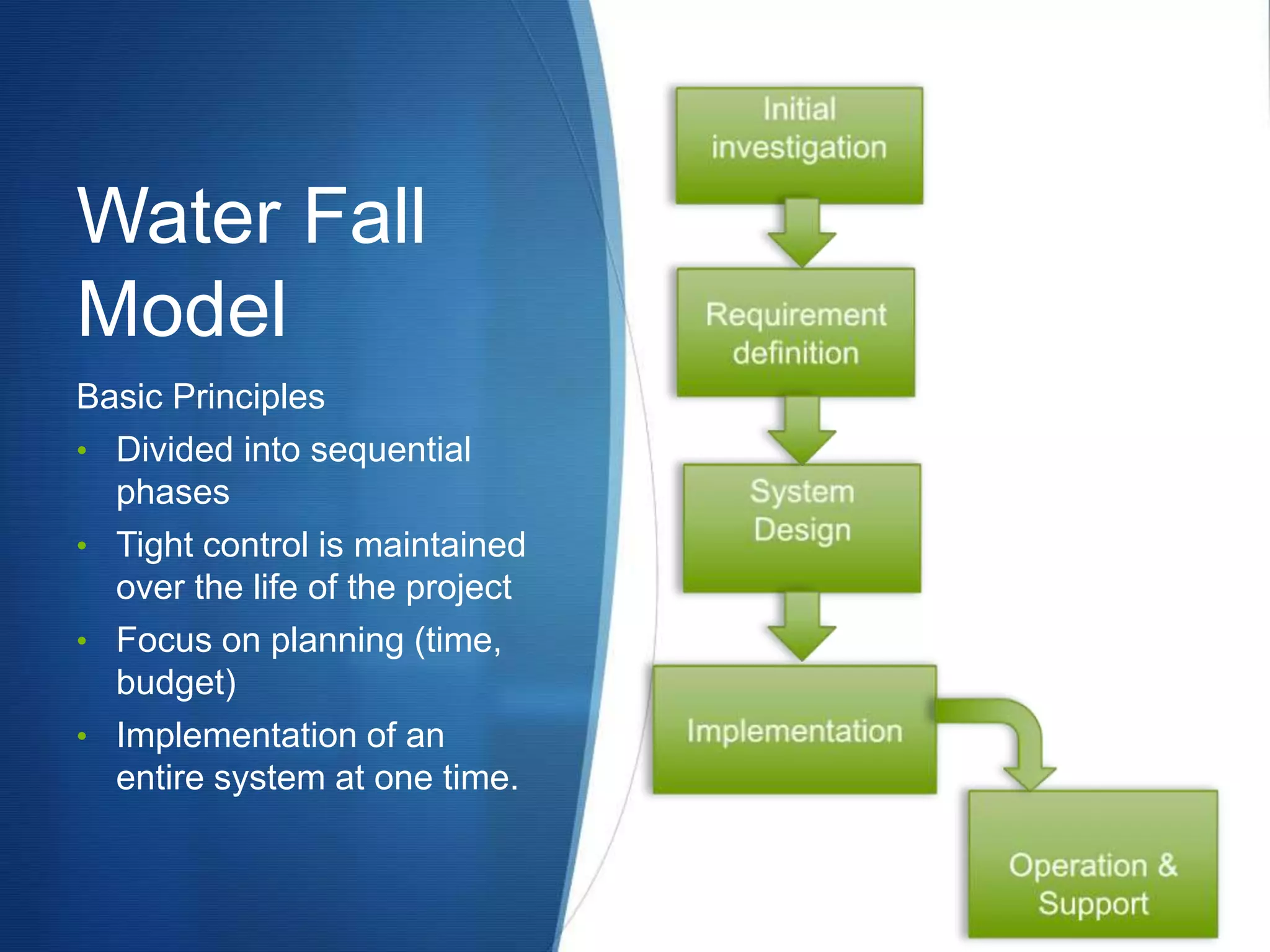
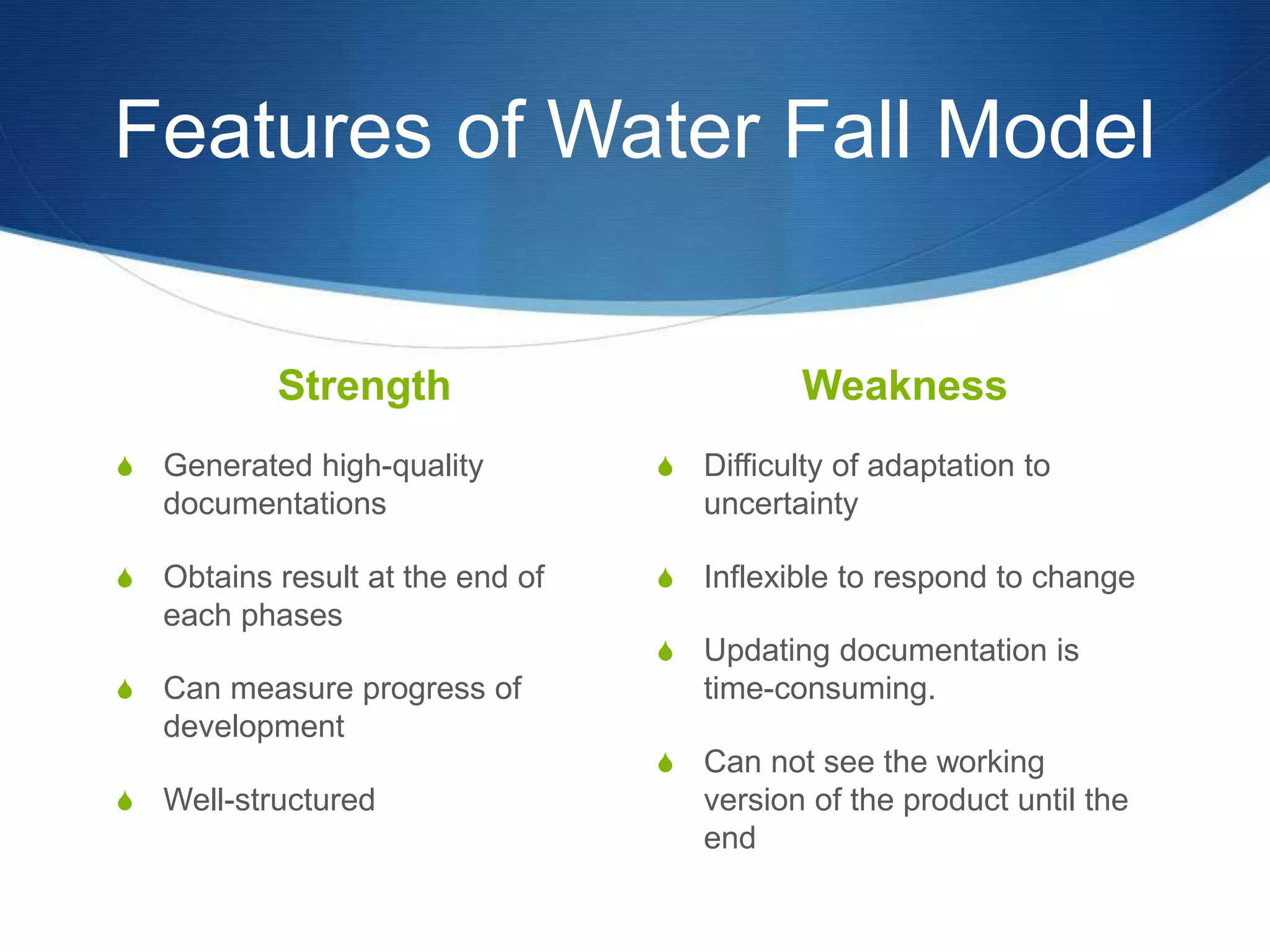
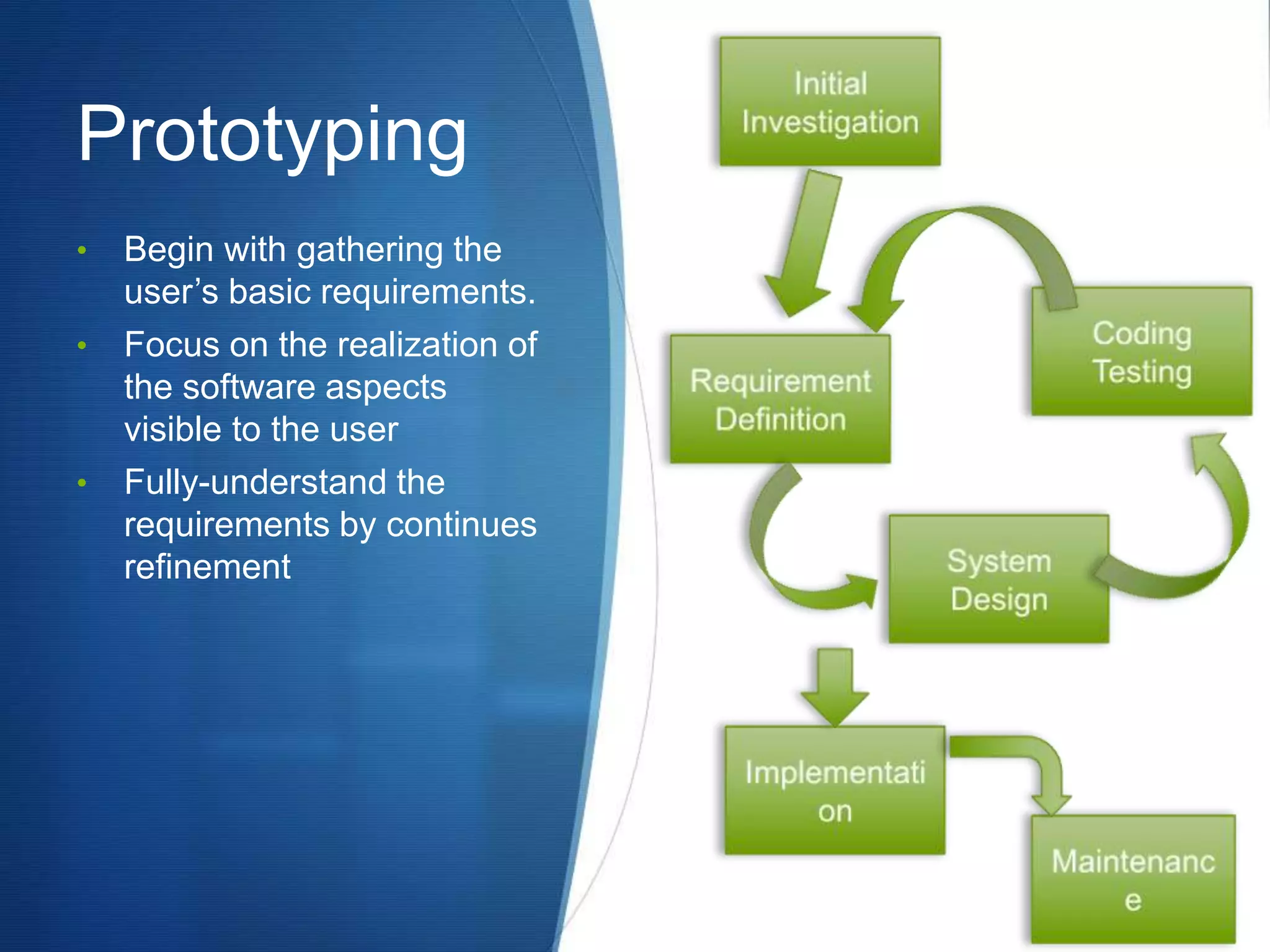
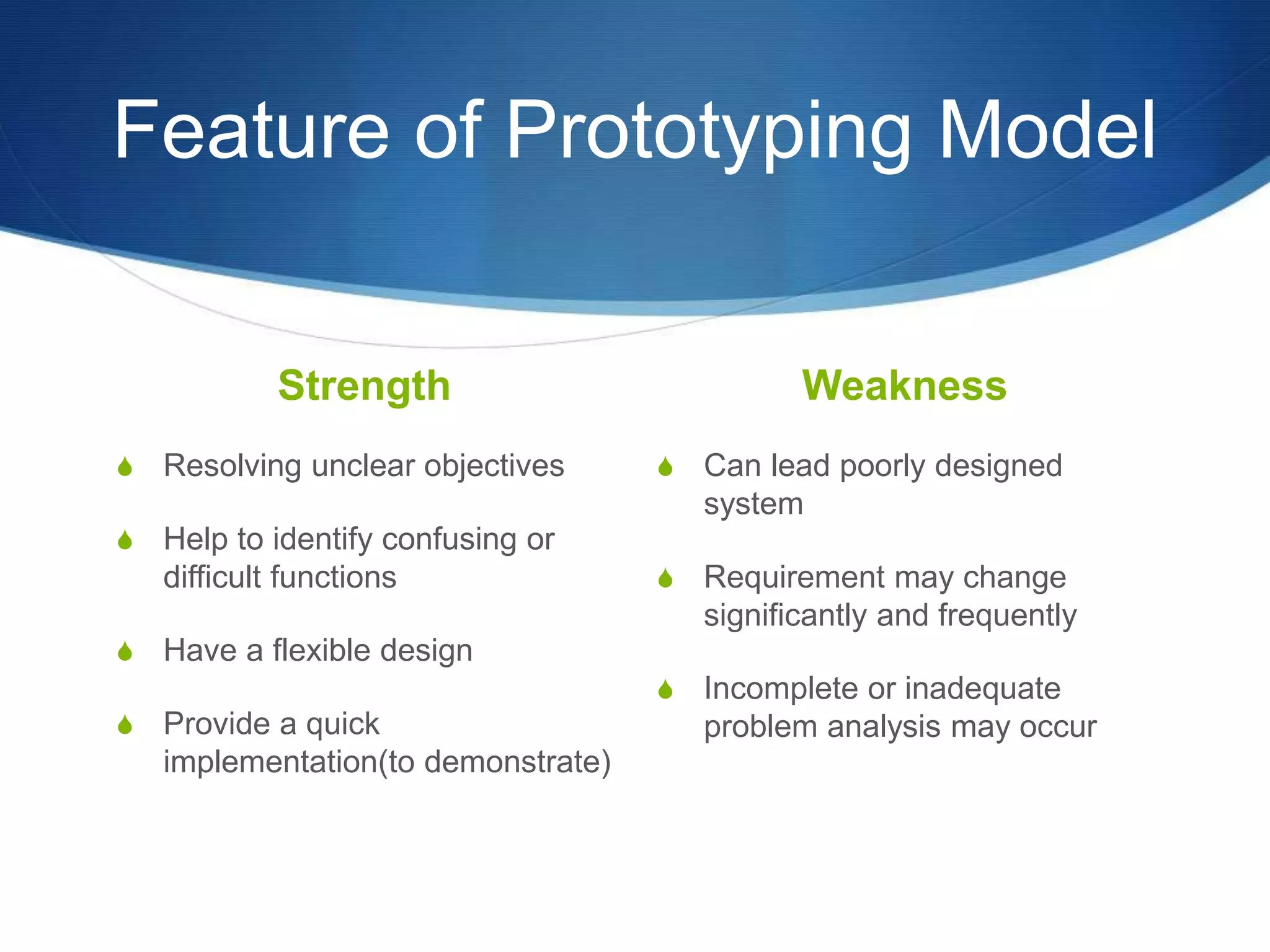
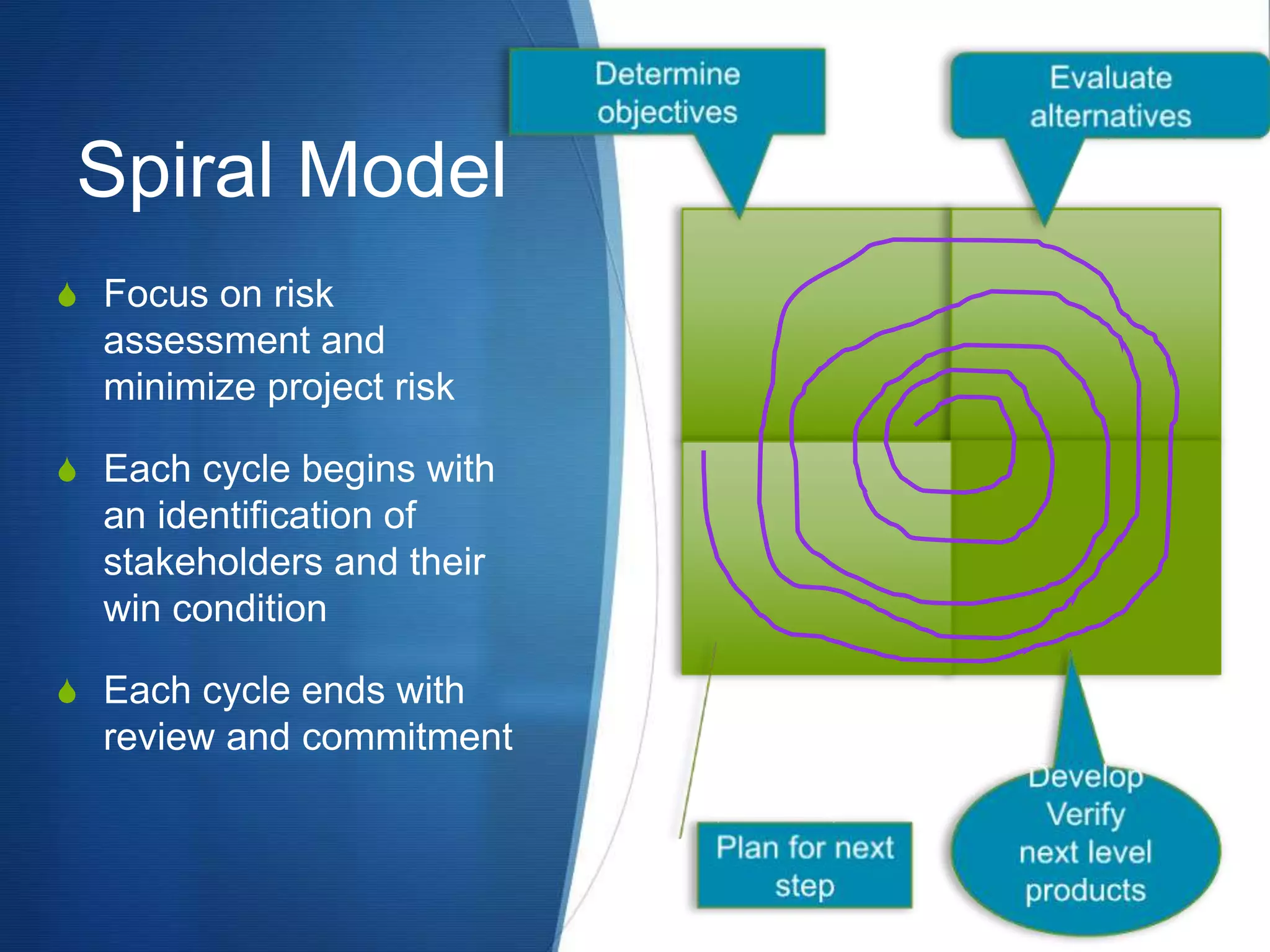
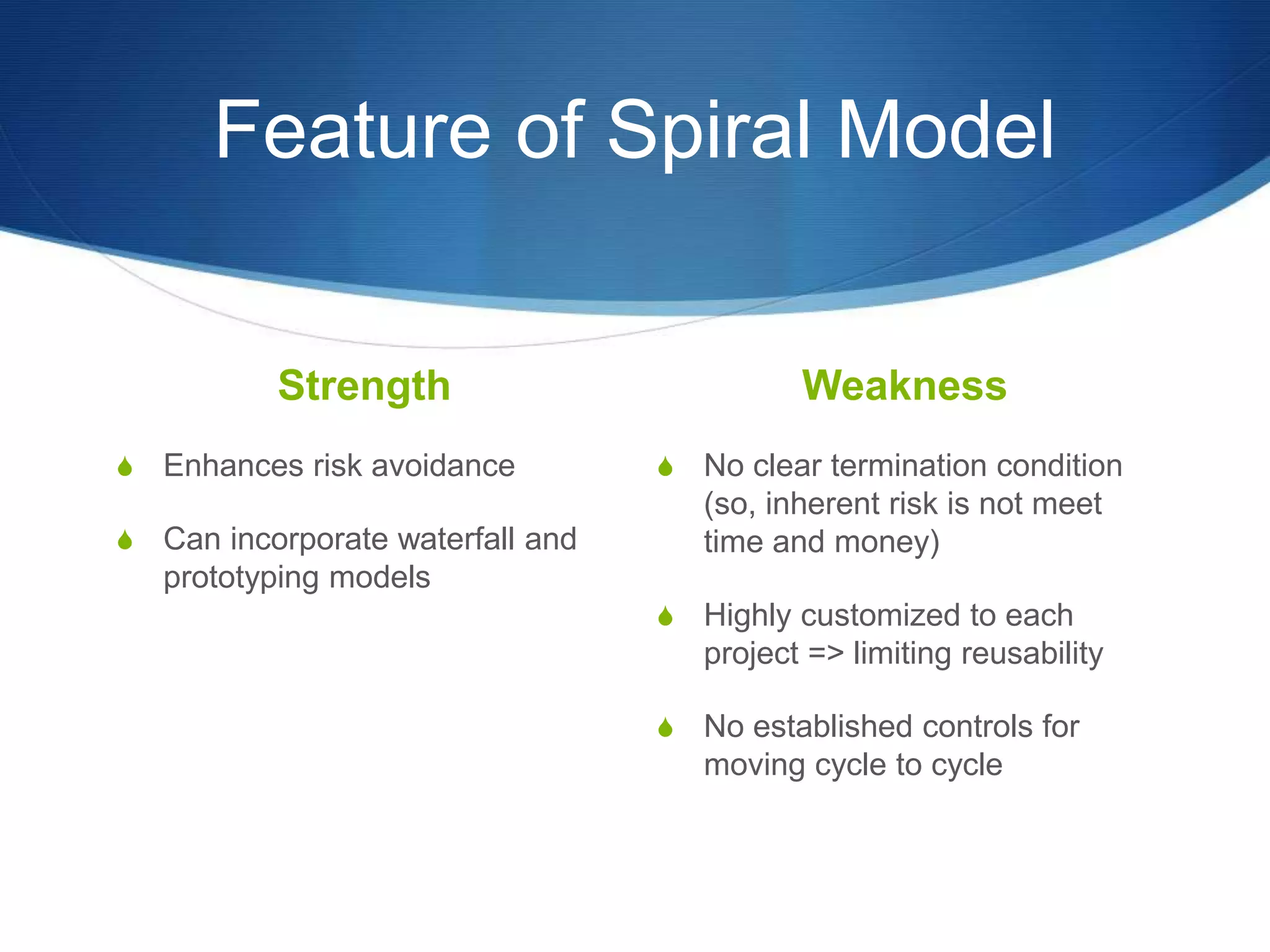
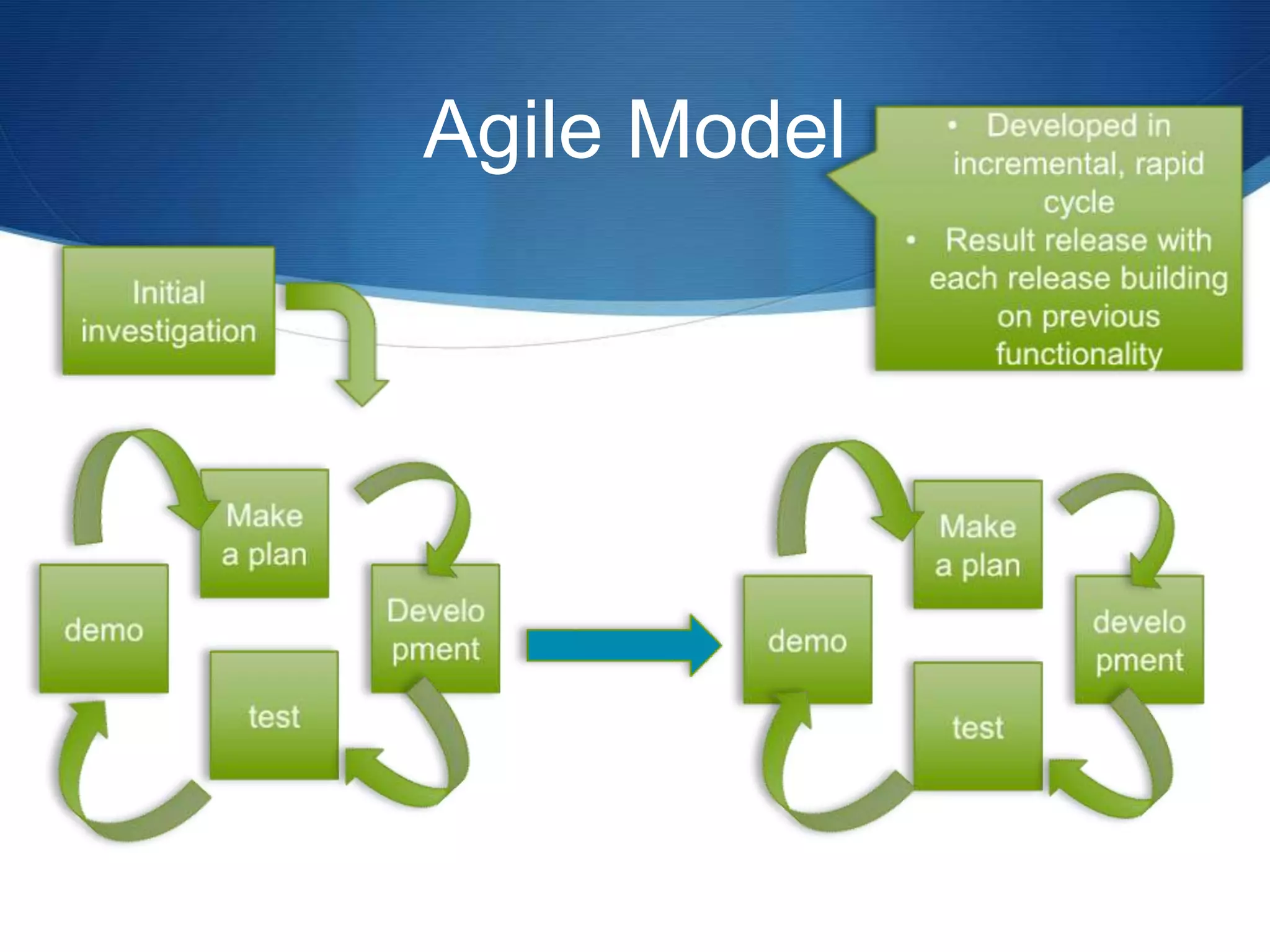
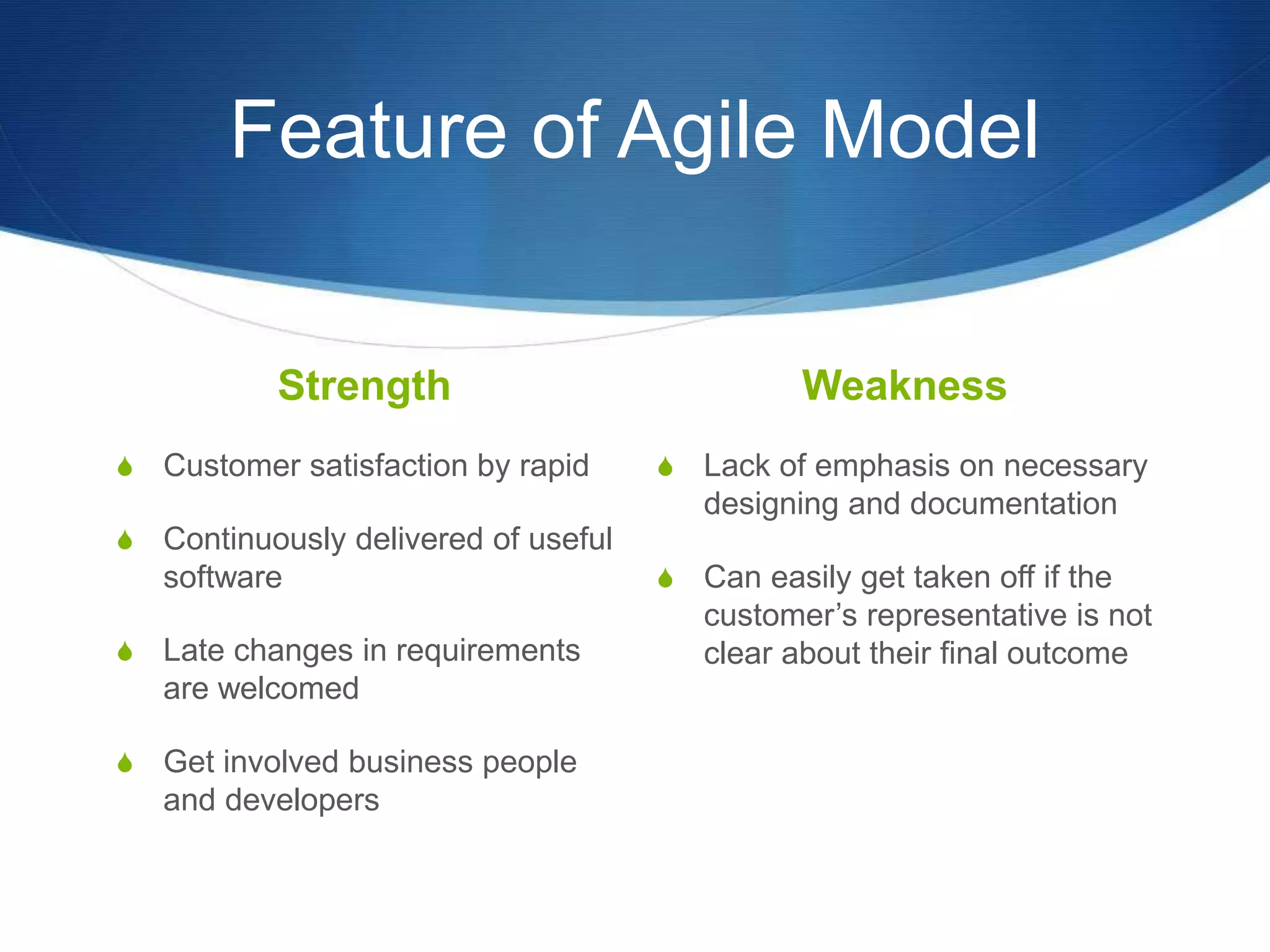
This document provides an overview of different methodologies in software engineering, including the waterfall model, prototyping model, spiral model, and agile model. It describes the key features, strengths, weaknesses, and appropriate situations for each model. The waterfall model is a sequential approach divided into phases with tight control. Prototyping focuses on user requirements through iterative refinement. The spiral model emphasizes risk assessment through multiple cycles. Agile models prioritize customer satisfaction and rapid delivery through continuous changes.