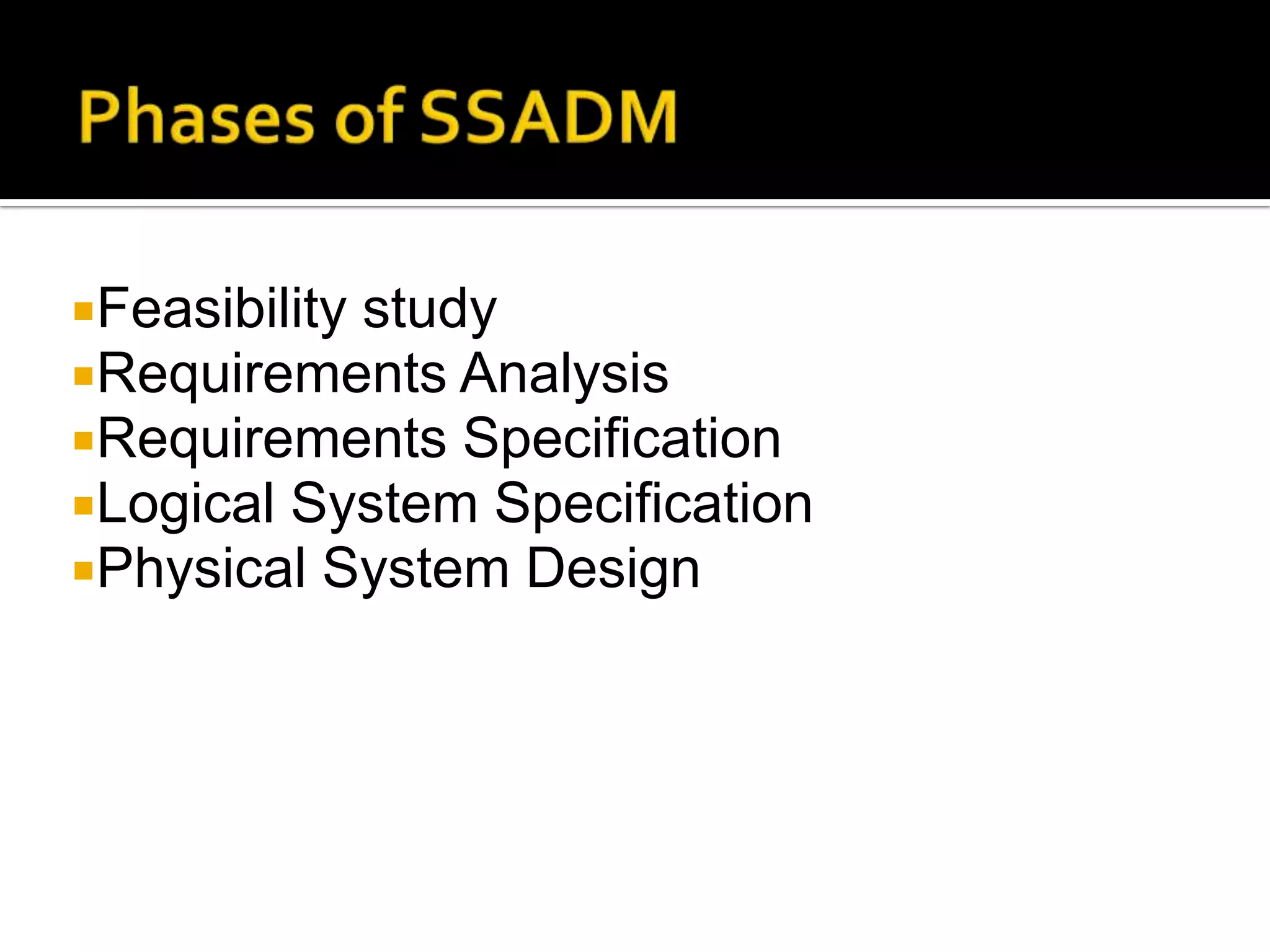
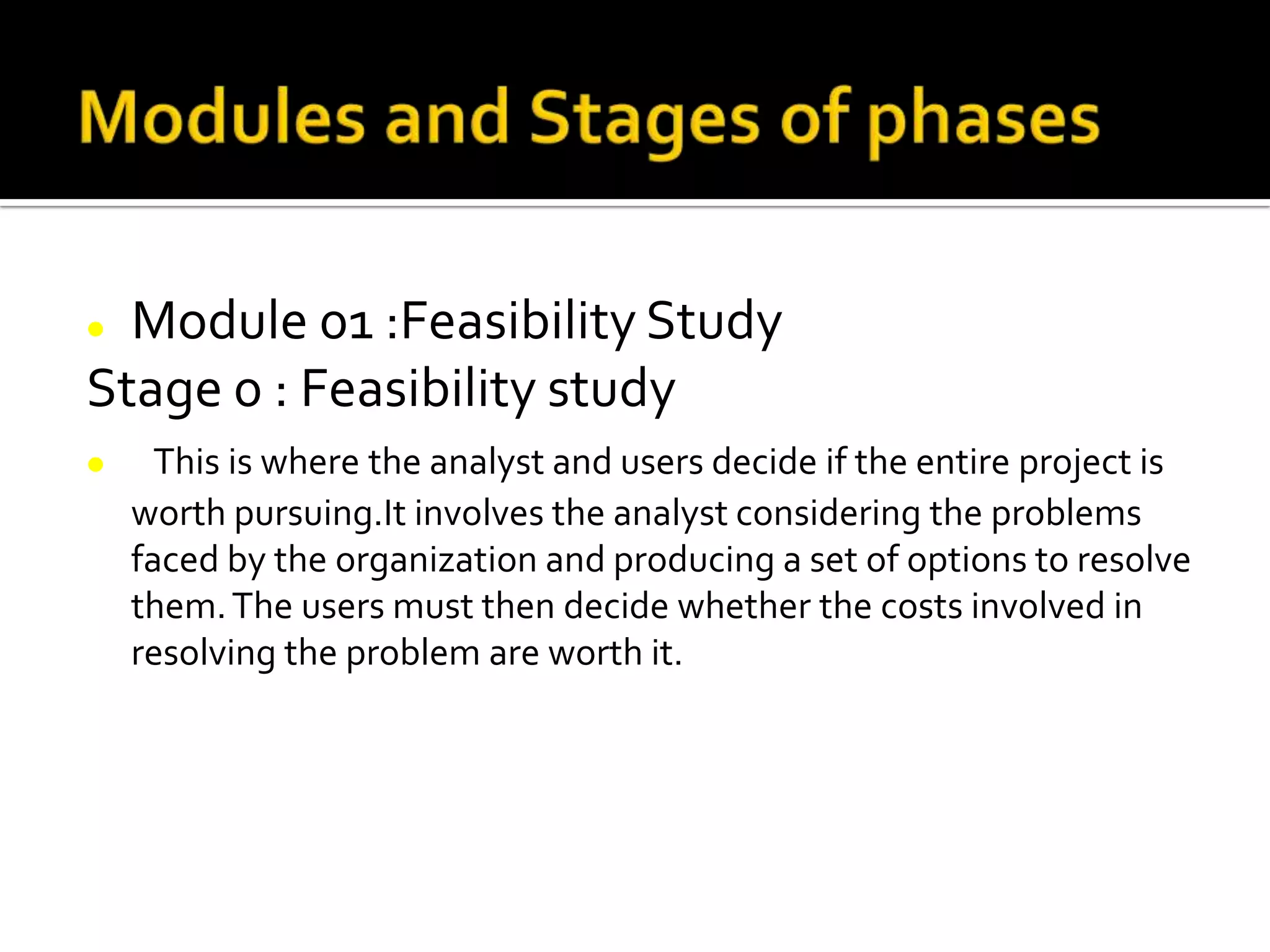
SSADM is a structured methodology for analyzing and designing computer systems. It is a waterfall approach with 5 main stages: 1) Feasibility study, 2) Requirements analysis, 3) Requirements specification, 4) Logical system specification, and 5) Physical system design. Each stage produces specific outputs and further refines the system requirements and design. SSADM provides standards and guidelines for documentation, techniques, and project structure.