The document discusses several common system analysis methodologies:
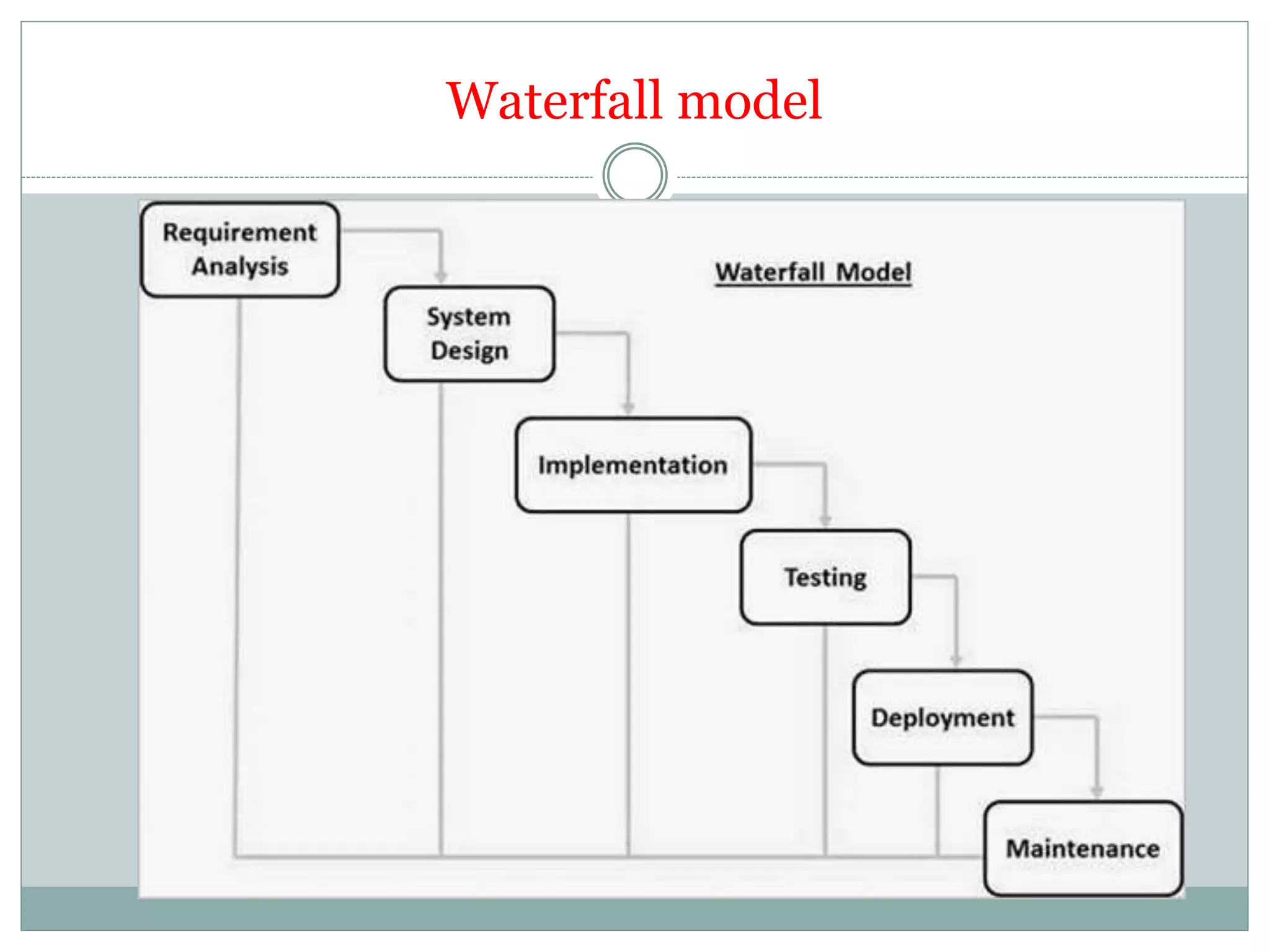
- Waterfall model is linear and sequential, best for well-defined requirements that don't change.
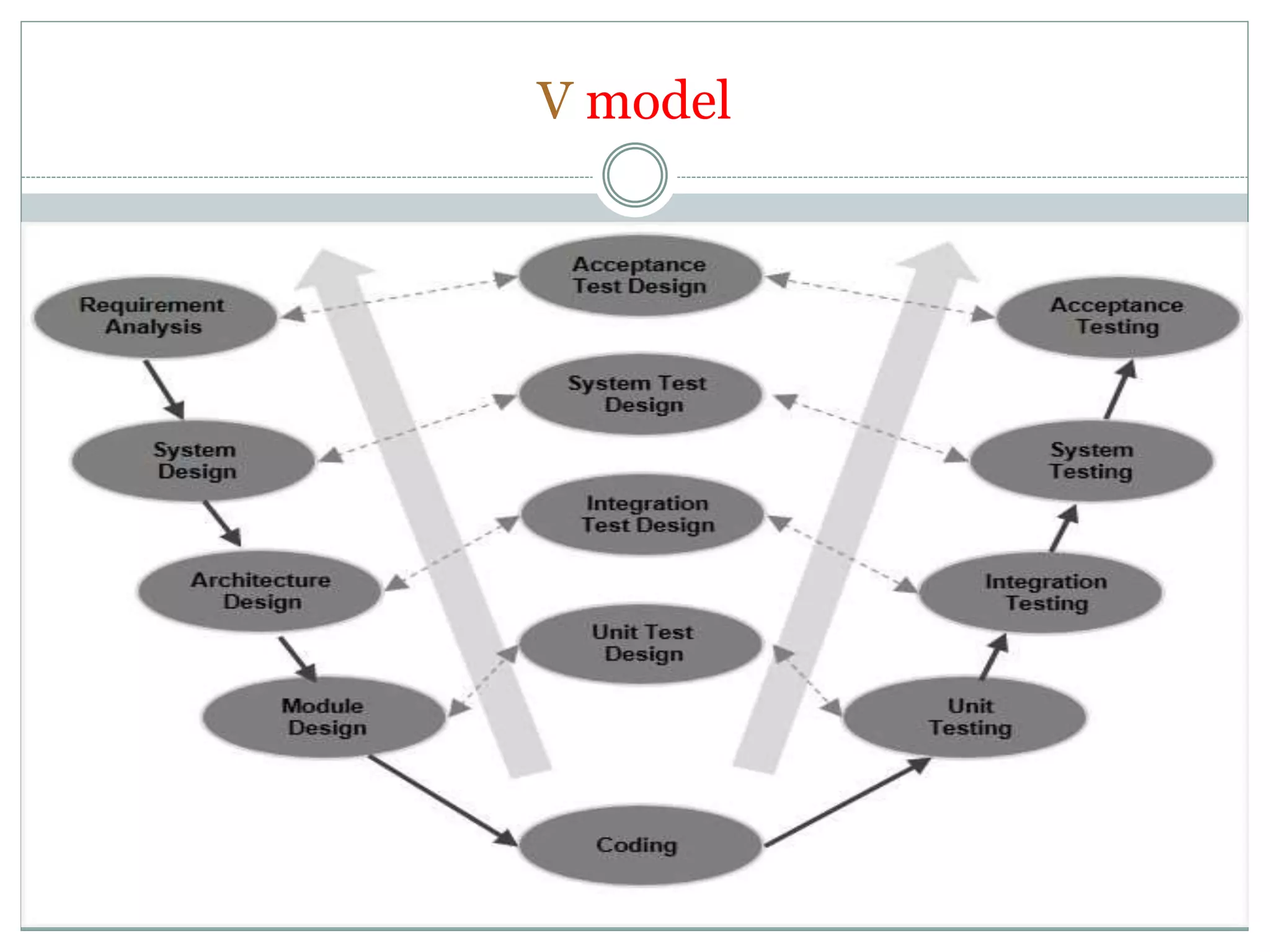
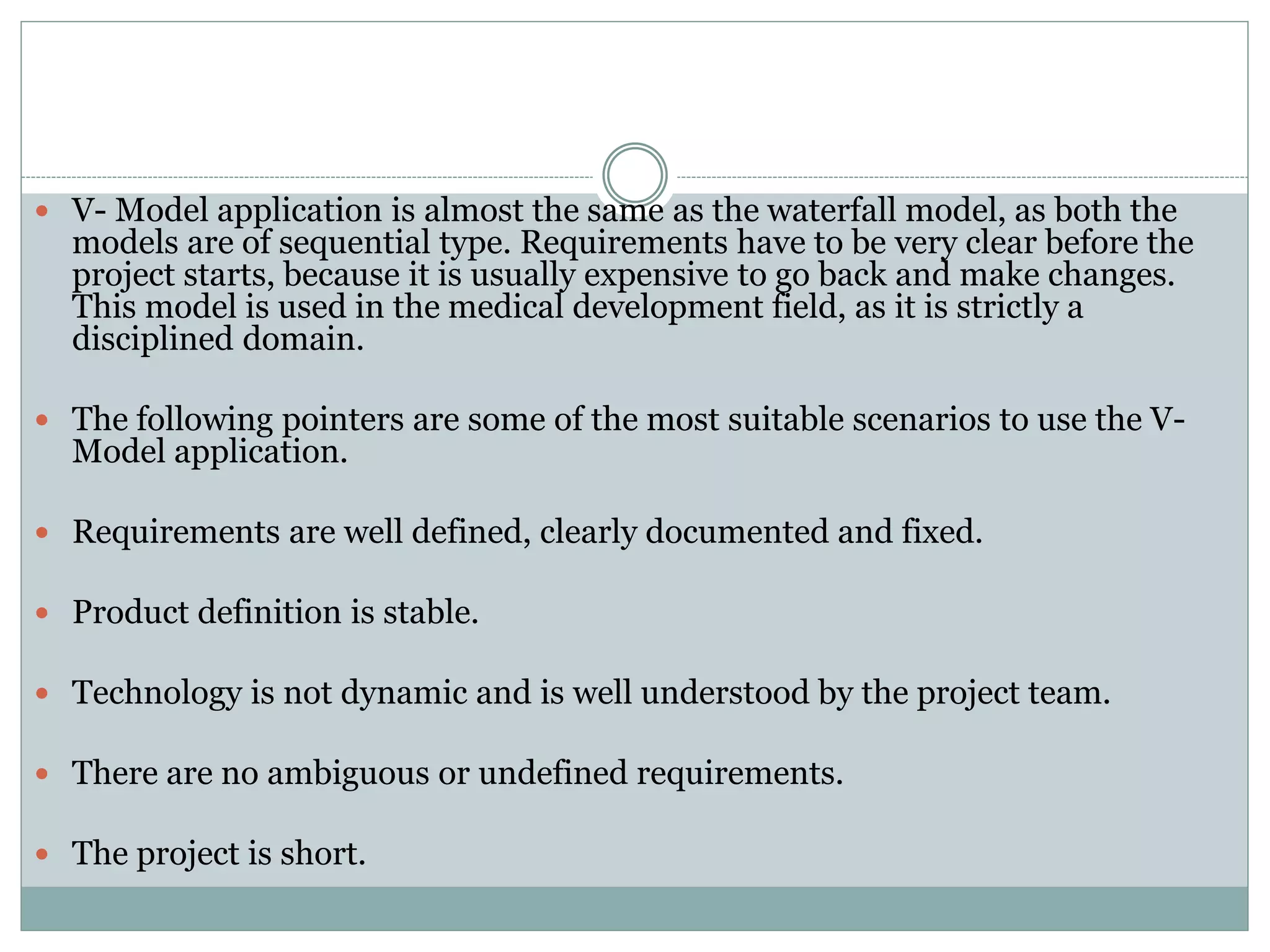
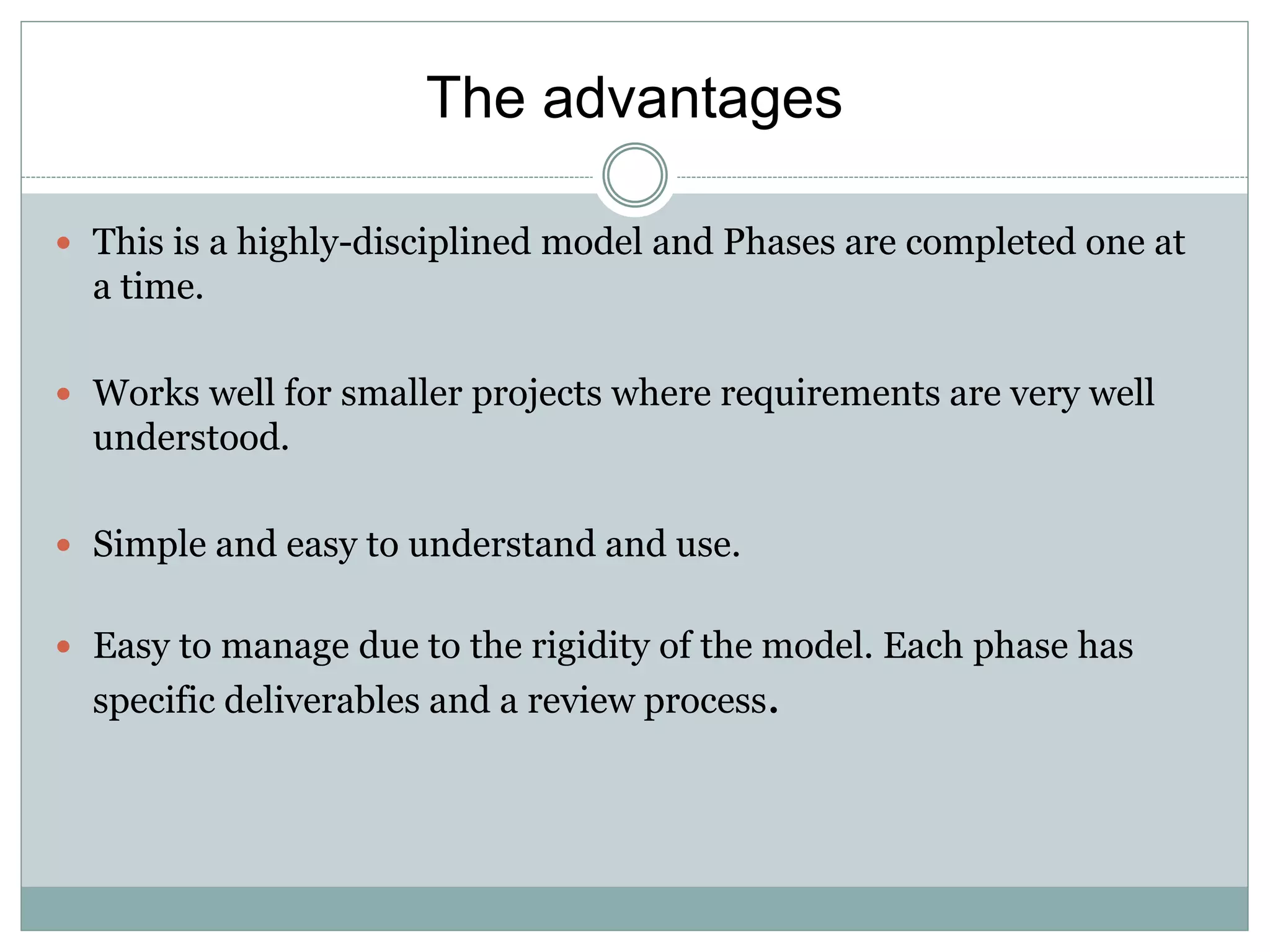
- V-model is similar to waterfall but adds testing phases to each development phase.
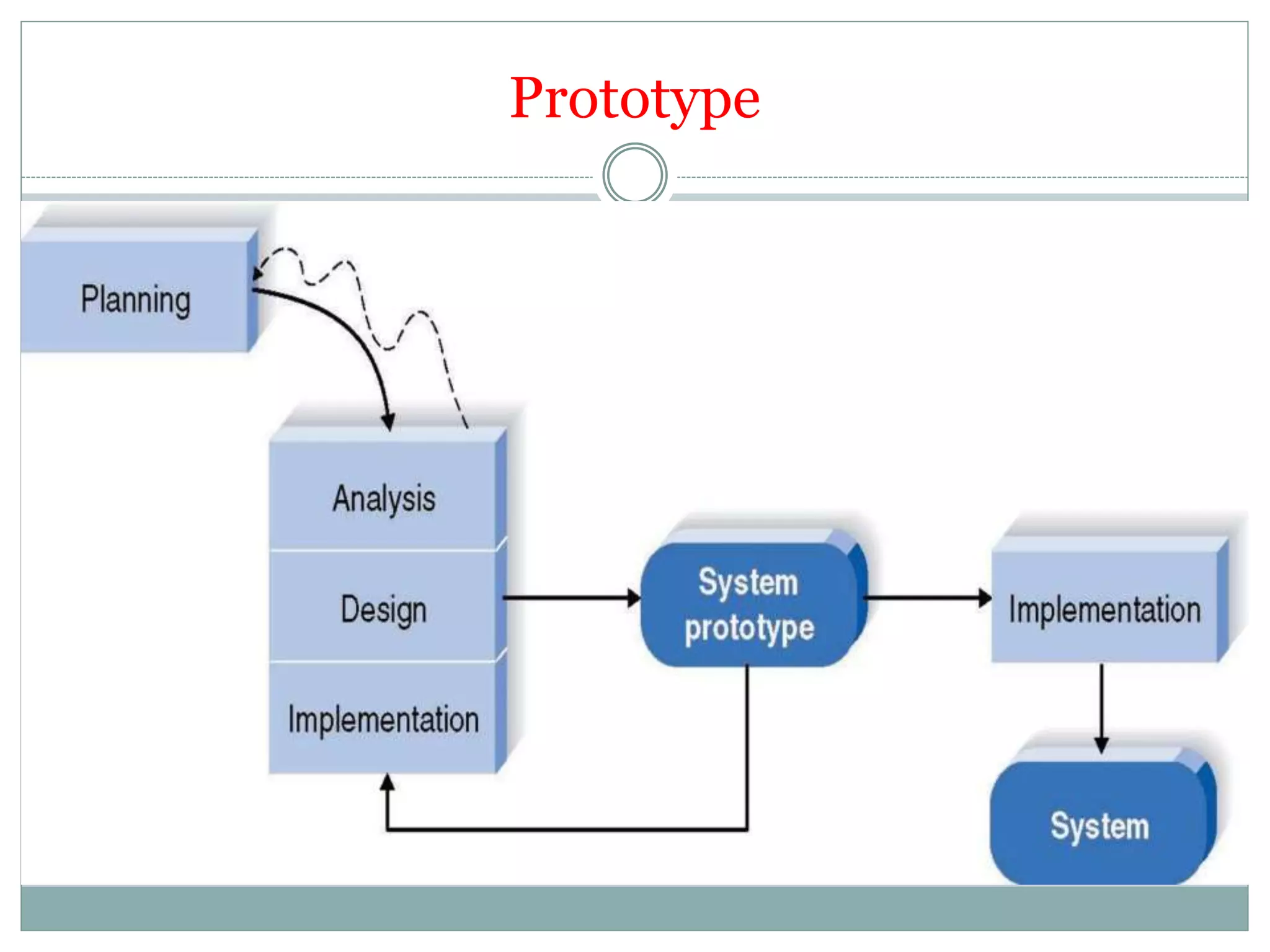
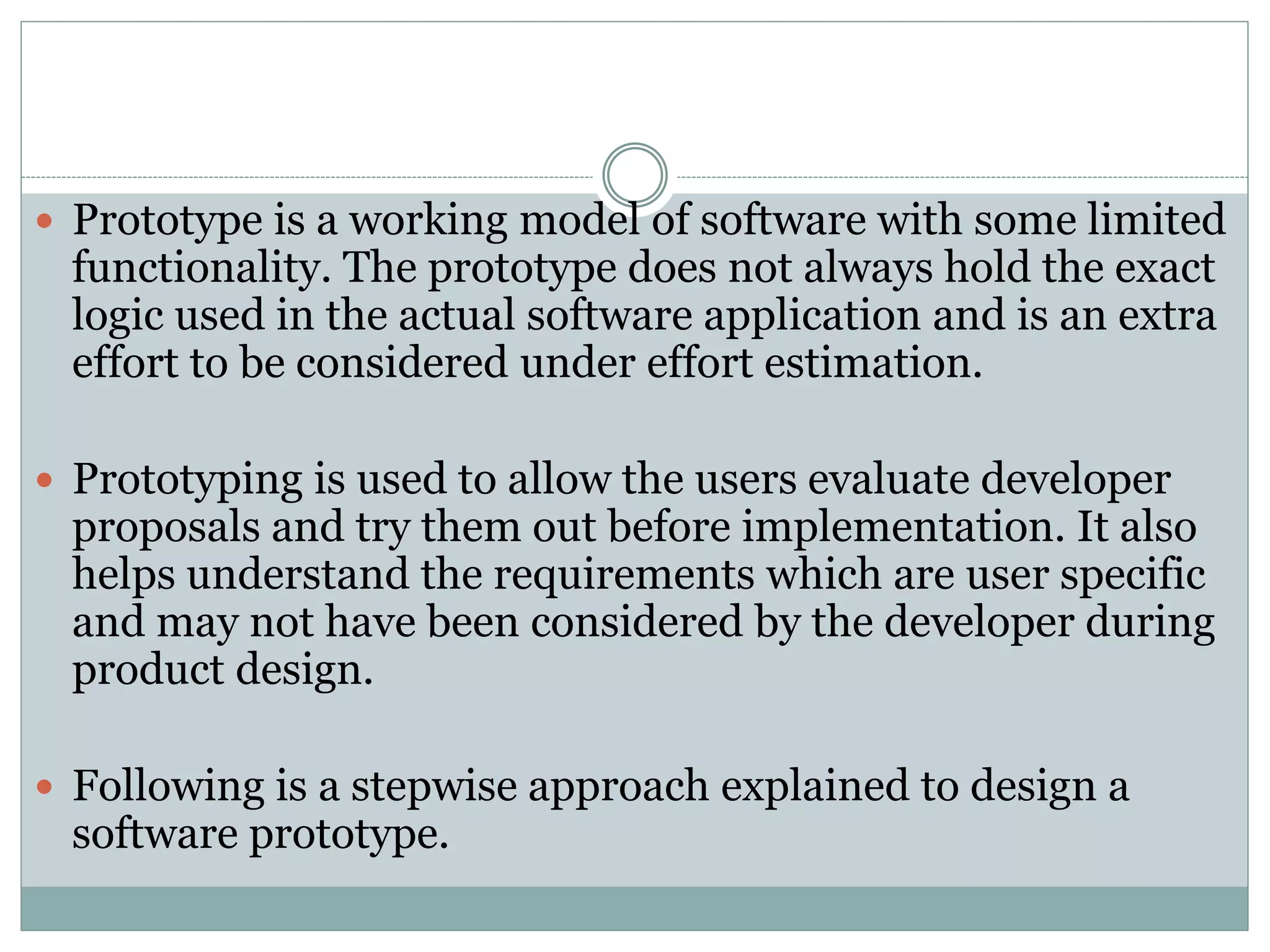
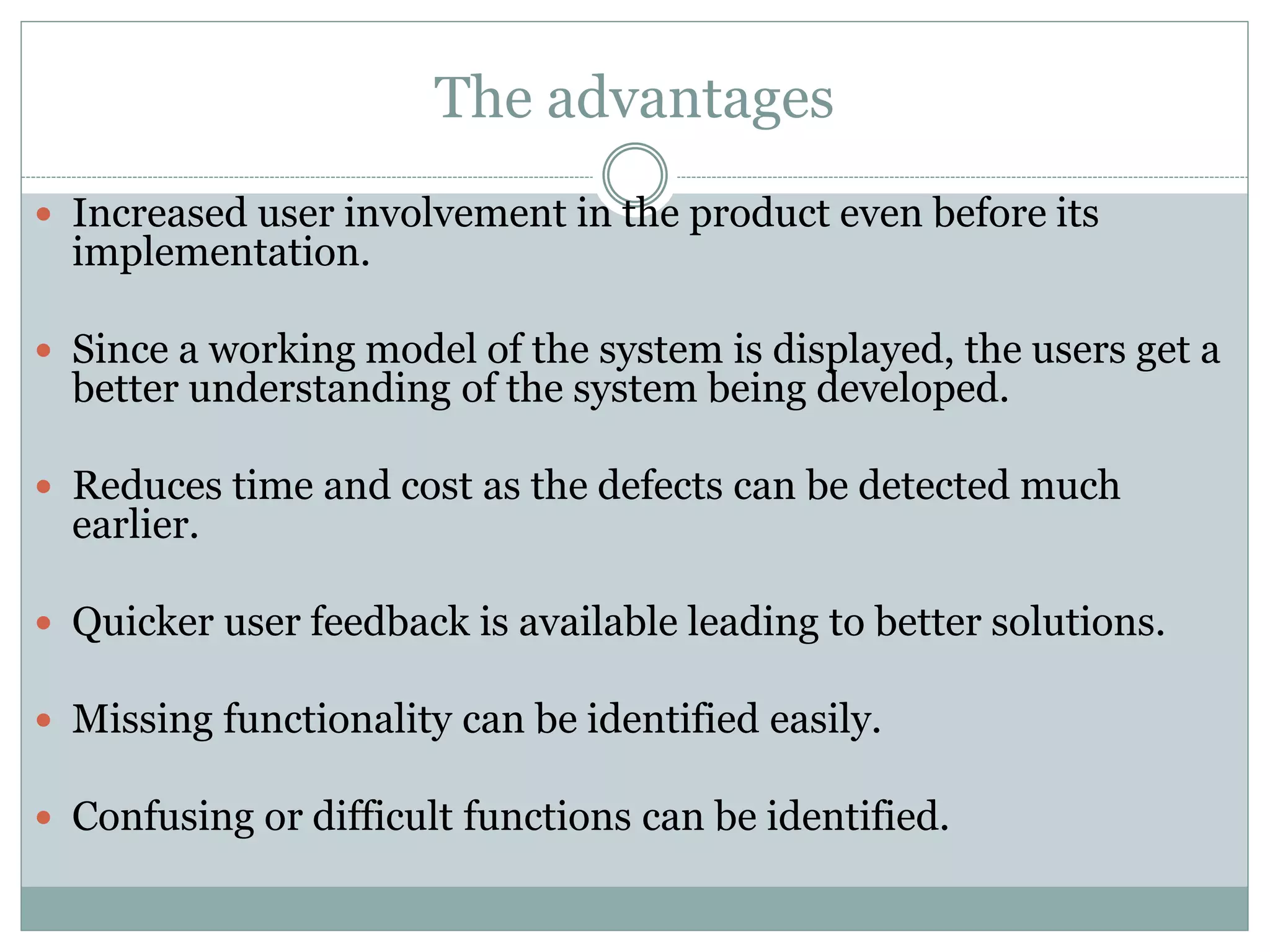
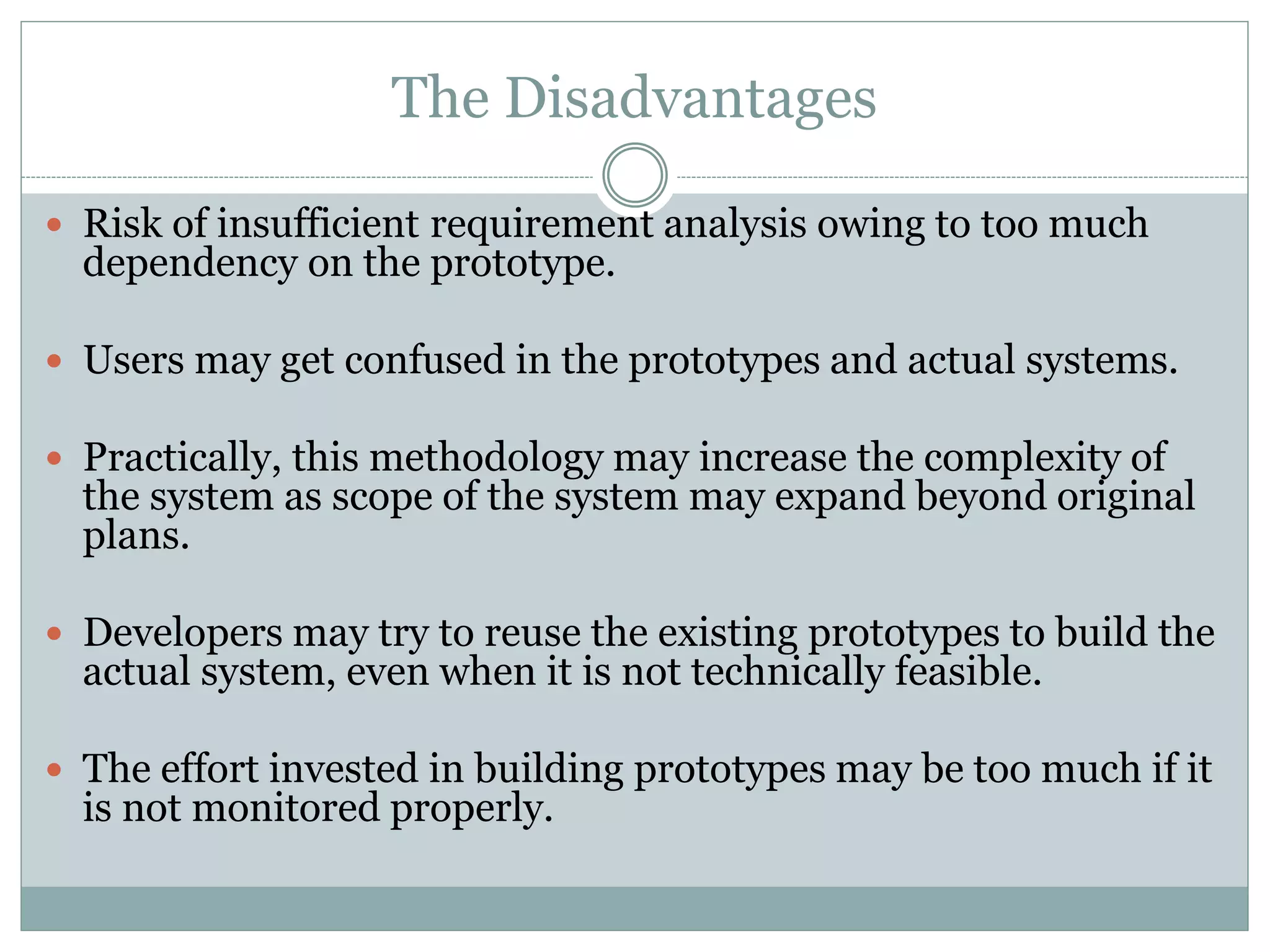
- Prototyping allows users to evaluate early versions before full development.
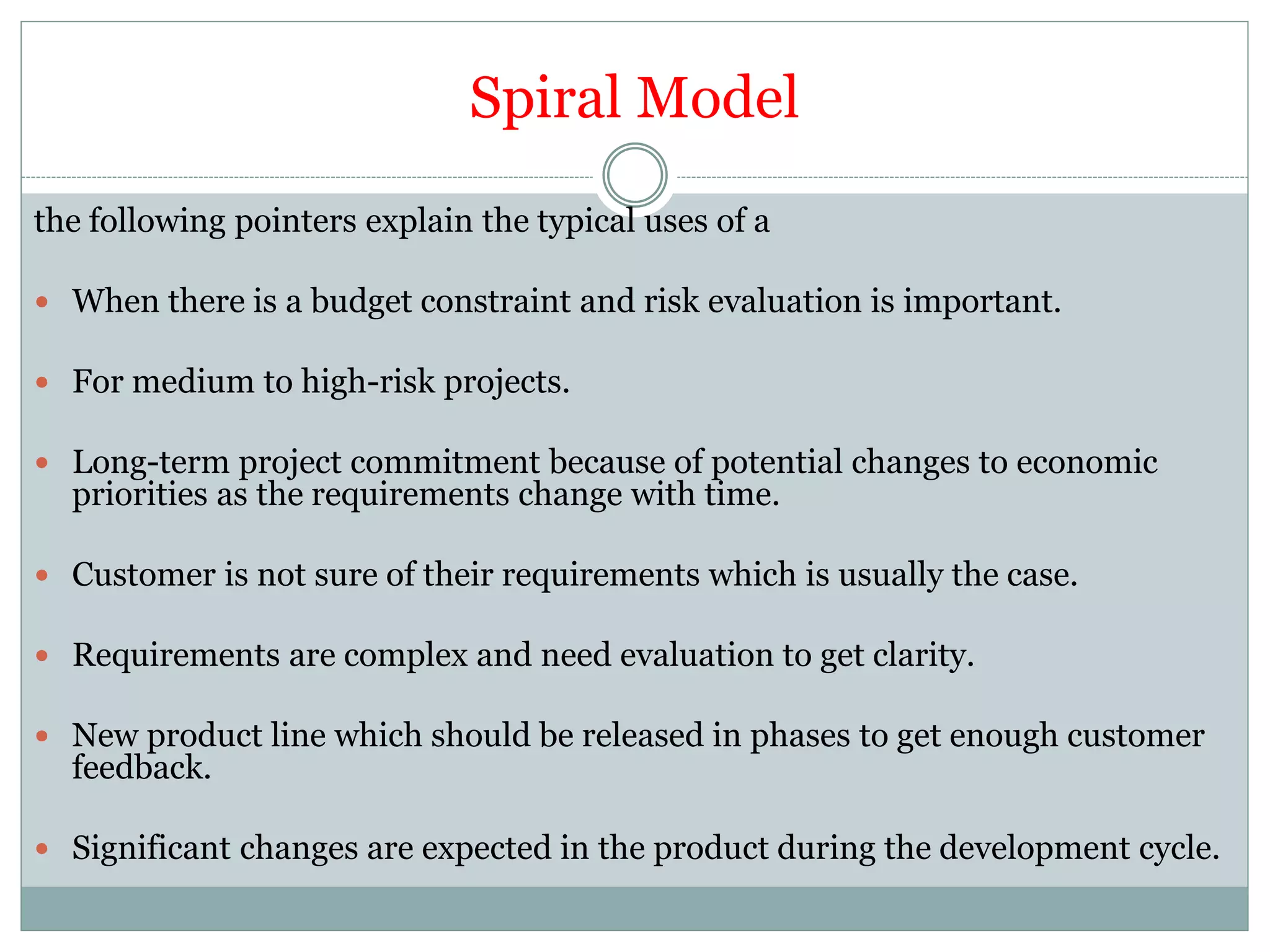
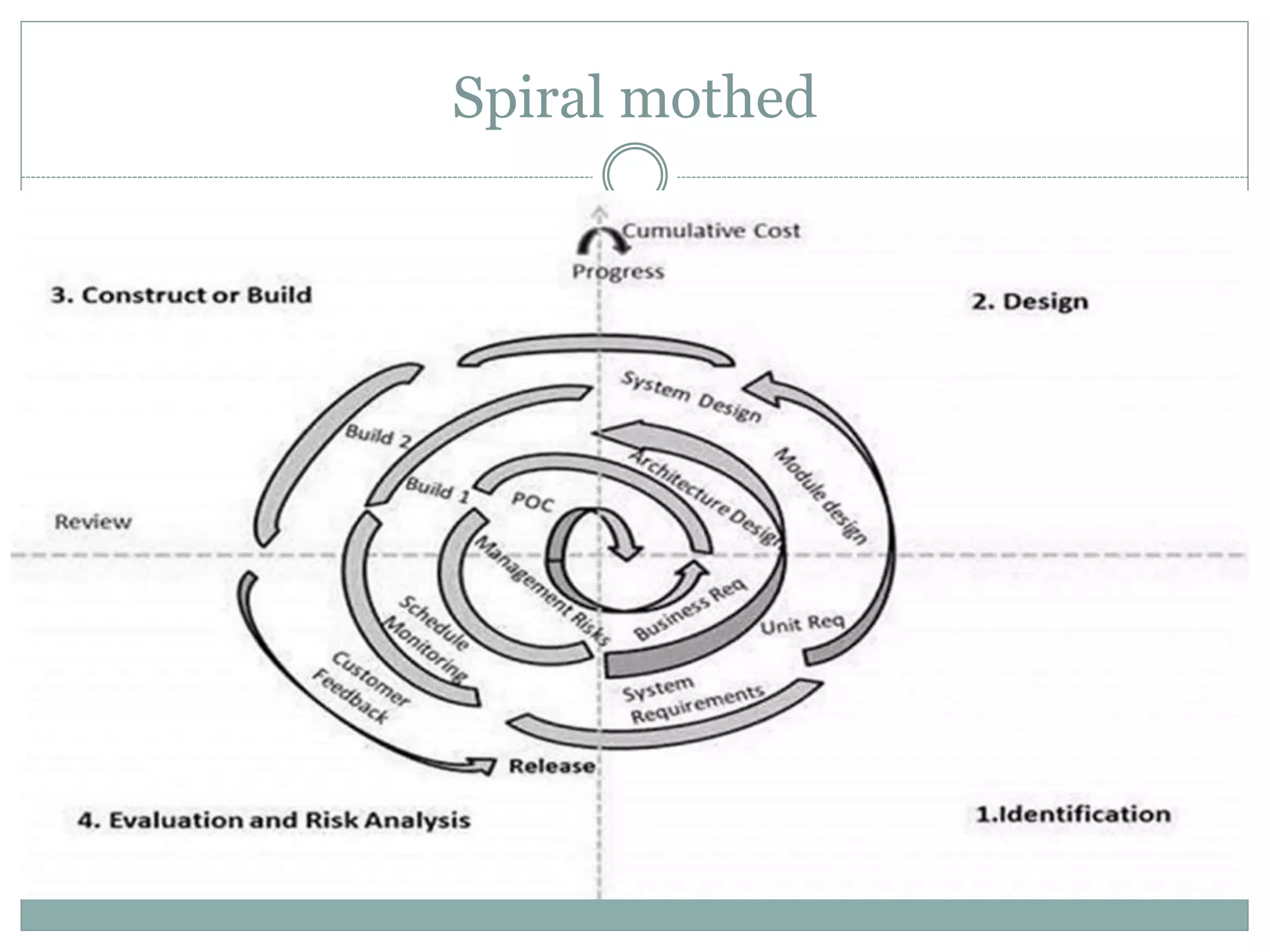
- Spiral model is iterative with risk analysis and prototypes, suitable for uncertain or changing requirements.
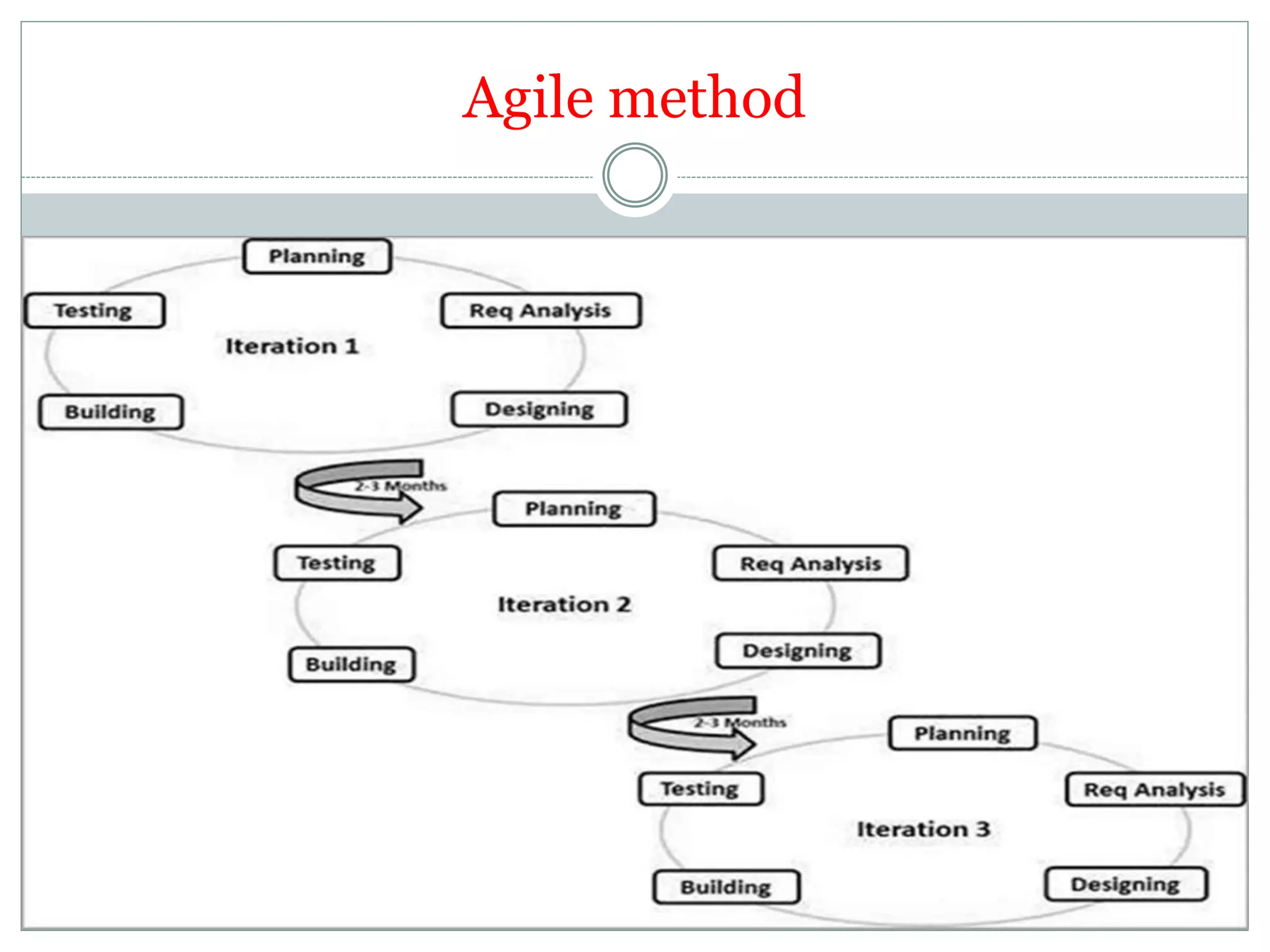
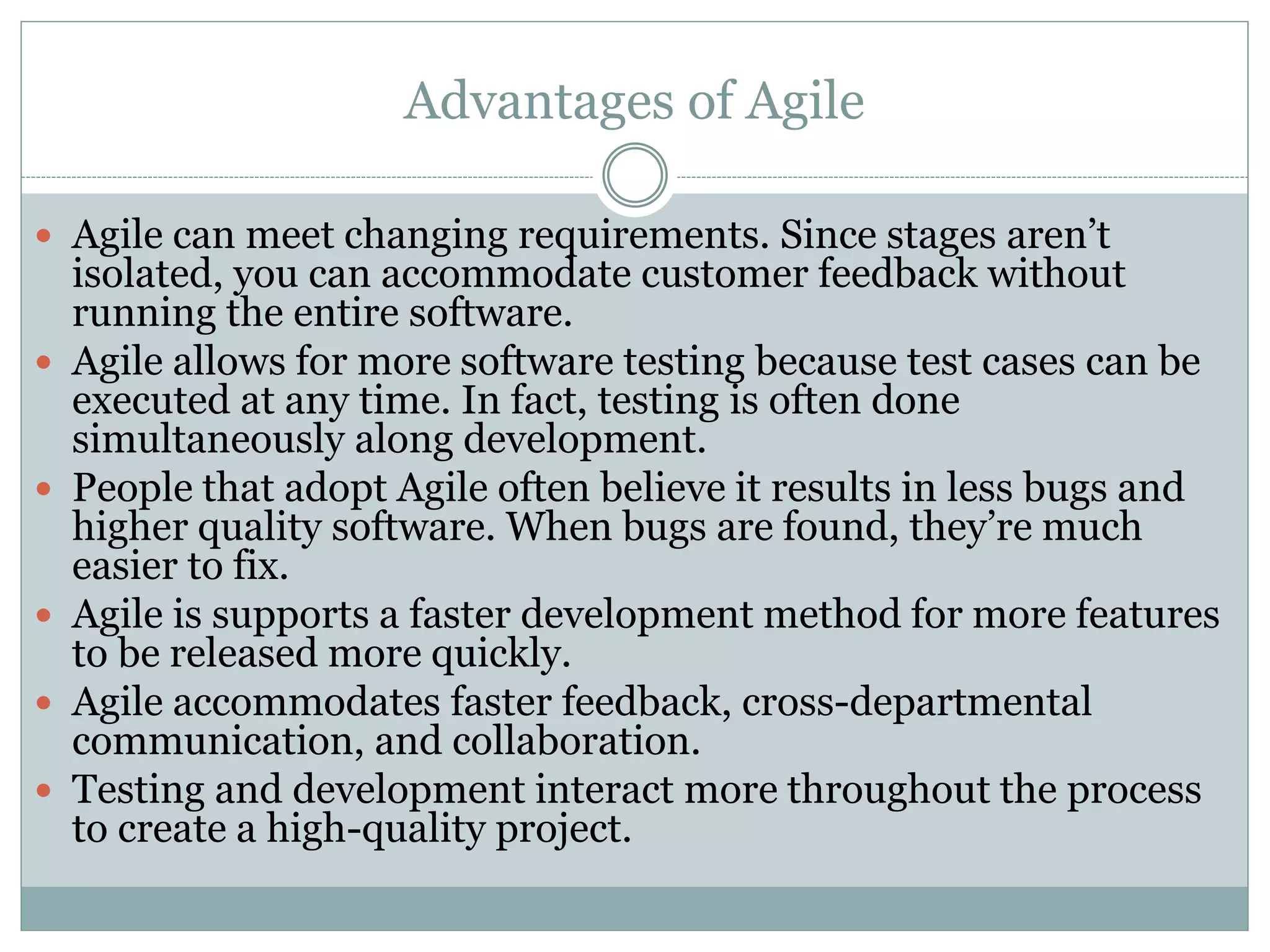
- Agile methods embrace changing needs and focus on frequent delivery of working software through collaboration.