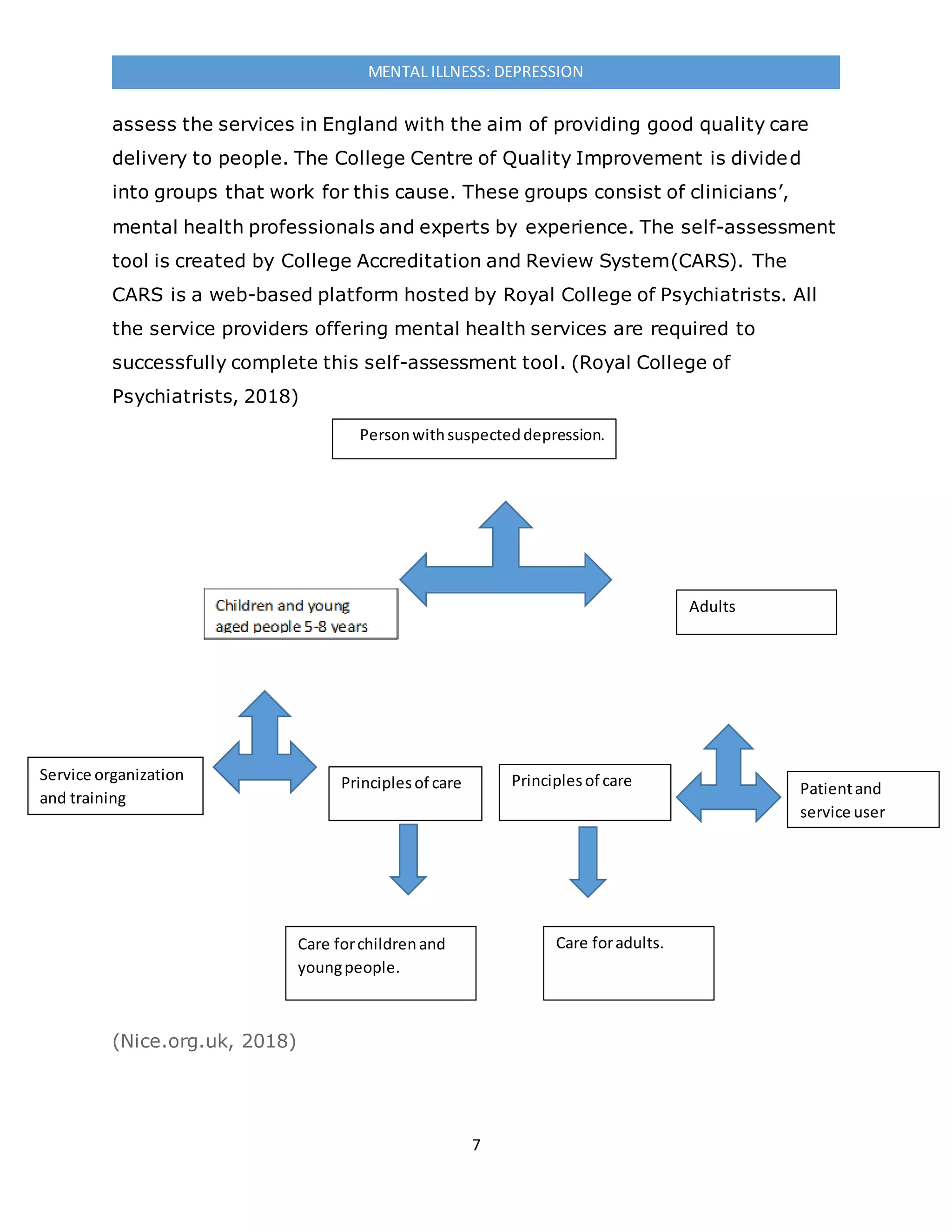
The document discusses mental health services in the UK for depression. It provides statistics on depression prevalence and details primary and secondary care systems for mental health. Primary care focuses on diagnosis, management and prevention, while secondary care handles more severe cases, like those involving psychosis or hospitalization. The document critiques gaps in primary care for mental health and outlines guidelines and pathways to improve treatment, such as increasing accessibility and using evidence-based therapies like CBT.





















![22
MENTAL ILLNESS: DEPRESSION
References:
Bloom, D.E., Cafiero, E.T., Jané-Llopis, E., Abrahams-Gessel, S.,
Bloom, L.R., Fathima, S., Feigl, A.B., Gaziano, T., Mowafi, M., Pandya,
A., Prettner, K., Rosenberg, L., Seligman, B., Stein, A., & Weinstein, C.
(2011). The Global Economic Burden of Non-communicable Diseases.
Geneva: World Economic Forum.
Bowcott, O. (2012). UK fined over mentally ill man's 'inhuman
treatment' in police custody. The Guardians. [online] Available at:
https://www.theguardian.com/uk/2012/may/03/police-fined-mentally-
ill-man-treatment [Accessed 28 Jun. 2018].
Evans, J., Macrory, I., & Randall, C. (2016). Measuring national
wellbeing: Life in the UK, 2016. ONS. Retreived
from https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/wellbei
ng/articles/measuringnationalwellbeing/2016#how-good-is-our-health
Funk, M., Ivbijaro, G. (2008). Integrating mental health into primary
care: a global perspective. Geneva: World Health Organization/WONCA
(World Organization of Family Doctors).
Goodwin, N., Dixon, A., Poole, T., Raleigh, V. (2011). Improving the
quality of care in general practice: report of an independent inquiry
commissioned by The King’s Fund. London: King’s Fund.
Gov.uk (2011). The mental health strategy for England. Policy Paper of
Department of Health and Social Care. [online] Available at:
https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-mental-health-
strategy-for-england [Accessed 26 Jun. 2018].
Guidance for commissioners of primary mental health care services.
(2012). 2nd ed. Raffertys.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mentalhealthassignment2-180717104428/75/Mental-health-assignment-2-23-2048.jpg)
![23
MENTAL ILLNESS: DEPRESSION
Gulliver, A., Griffiths, K.M. and Christensen, H., 2010. Perceived
barriers and facilitators to mental health help-seeking in young people:
a systematic review. BMC psychiatry, 10(1), p.113.
Hilton, C., 2016. Parity of esteem for mental and physical healthcare in
England: a hundred years war?. Journal of the Royal Society of
Medicine, 109(4), pp.133-136.
HM Government (2011). No health without mental health: a cross-
government mental health outcomes strategy for people of all ages.
London: Department of Health.
Humberews.co.uk. (2018). Secondary Mental Health Service |
Emotional Wellbeing Service, NHS Talking Therapies. [online] Available
at: http://humberews.co.uk/hull-services/asisst/ [Accessed 25 Jun.
2018].
Lenox-Smith, A., Macdonald, M.T., Reed, C., Tylee, A., Peveler, R.,
Quail, D. and Wildgust, H.J., 2013. Quality of life in depressed patients
in UK primary care: the FINDER study. Neurology and therapy, 2(1-2),
pp.25-42.
Miller, R., 2013. Third sector organisations: unique or simply other
qualified providers?. Journal of Public Mental Health, 12(2), pp.103-
113.
Newbigging. K. Ridley,J., McKeown,M., Machin’ K. & Poursanidou, D.
2012, “The Right to Be Heard. Review of the Quality of Independent
Mental Health Advocate (IMHA) Services in England”
NHS (2017). Mental health services in England. The Tavistock and
Portman NHS Foundation Trust. [online] Available at:
https://tavistockandportman.nhs.uk/documents/657/centre-mental-
health-report-2017.pdf [Accessed 25 Jun. 2018].
Nice.org.uk. (2018). Depression in adults: recognition and
management | Guidance and guidelines | NICE. [online] Available at:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mentalhealthassignment2-180717104428/75/Mental-health-assignment-2-24-2048.jpg)
![24
MENTAL ILLNESS: DEPRESSION
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg90/chapter/1-Guidance#care-of-
all-people-with-depression [Accessed 28 Jun. 2018].
Parkin, E. and Powell, T. (2017). Mental health policy in
England. House of Common Library. [online] Available at:
http://researchbriefings.files.parliament.uk/documents/CBP-
7547/CBP-7547.pdf [Accessed 26 Jun. 2018].
Rehm, L. (2010). Depression: Advances in Psychotherapy - Evidence
Based Practice. 1st ed. Hogrefe.
Royal College of Psychiatrists (2018). Children and Young People’s
Mental Health Care Pathways. [online] Rcpsych.ac.uk. Available at:
https://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/workinpsychiatry/qualityimprovement/men
talhealthcarepathways/cypgeneral.aspx [Accessed 28 Jun. 2018].
Schneider, M.R., 2016. Clinical and Social Contexts of Ethical Issues in
Mental Health Care. AMA Journal of Ethics, 18(6), p.567.
UK Legislation (2007). Mental Health Act 2007. [online] Available at:
http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2007/12/pdfs/ukpga_20070012_
en.pdf [Accessed 27 Jun. 2018].
Vos, T., Barber, RM., Bell, B., Bertozzi-Villa, A., Biruyukov, S.,
Bollinger, I., ...Murray, CJ.. (2013). Global, regional, and national
incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and
chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: A
systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study. The
Lancet, 386(9995), 743-800
What is primary care mental health? WHO and Wonca Working Party
on Mental Health. (2008). Ment Health Fam Med, 5(1), pp.9-13.
World Health Organization. (2018). Depression. [online] Available at:
http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
[Accessed 24 Jun. 2018].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mentalhealthassignment2-180717104428/75/Mental-health-assignment-2-25-2048.jpg)
![25
MENTAL ILLNESS: DEPRESSION
World Health Organization. (2018). Mental Health. [online] Available
at: http://www.who.int/mental_health/en/ [Accessed 24 Jun. 2018].
World Health Organization. Ten facts on mental health: fact 2.
http://www.who.int/features/factfiles/mental_health/mental_health_
facts/en/index1.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mentalhealthassignment2-180717104428/75/Mental-health-assignment-2-26-2048.jpg)