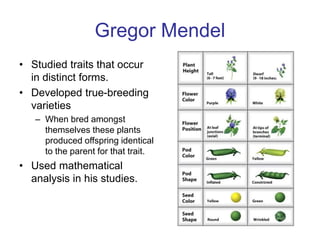
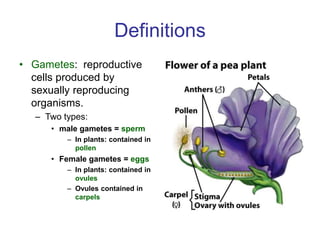
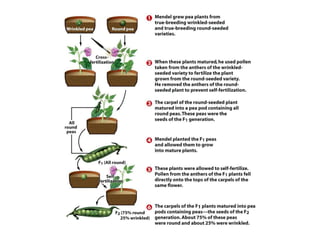
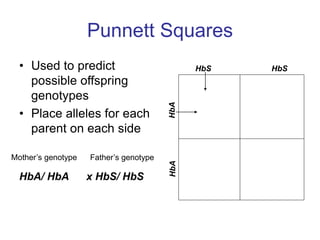
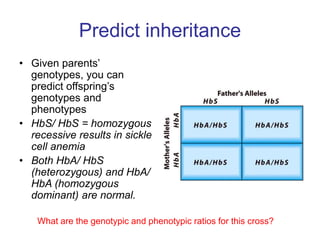
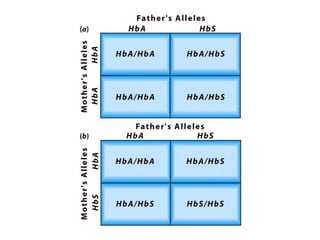
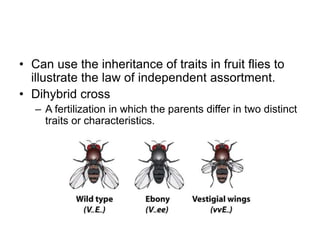
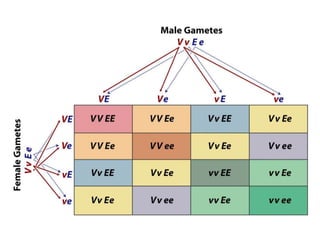
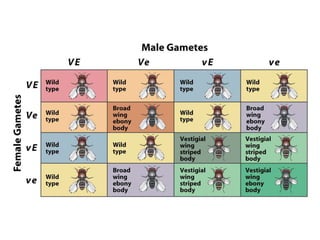
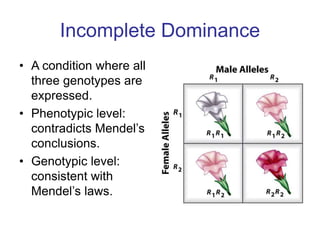
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments with pea plants to study inheritance of traits. He found that traits are inherited in distinct units (now called genes) and can exist in different forms (alleles). Through his experiments, he developed two laws of inheritance: the Law of Segregation, which states that organisms pass only one allele to offspring for each gene, and the Law of Independent Assortment, which explains that genes assort independently during gamete formation. Mendel's work established foundations of classical genetics and heredity of traits.