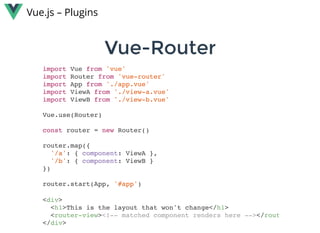
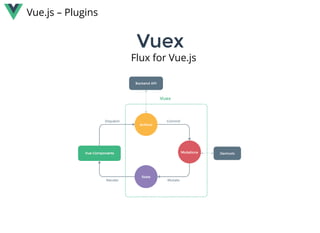
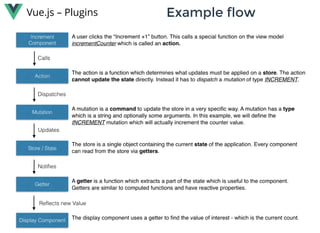
Vue.js is a lightweight, reactive component-based library for building modern web interfaces. It provides simple and flexible APIs for building reactive components and applications using templates and reusable components. Key features include:
- Reactive components using templates and data binding
- Lightweight at only 24kb minified and gzipped
- Flexible options for building full single page applications or enhancing existing projects
- Reusable components using global or local registration




















![Computed setterComputed setter
Vue.js – Features
// ...
computed: {
fullName: {
// getter
get: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
},
// setter
set: function (newValue) {
var names = newValue.split(' ')
this.firstName = names[0]
this.lastName = names[names.length - 1]
}
}
}
// ..
// When calling vm.fullName = 'John Doe', the setter will
// be invoked and vm.firstName and vm.lastName
// will be updated accordingly.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meet-vue-js-181009165745/85/Meet-VueJs-25-320.jpg)

![Vue.js – Features
List renderingList rendering
var example1 = new Vue({
el: '#example-1',
data: {
items: [
{ message: 'Foo' },
{ message: 'Bar' }
],
object: {
FirstName: 'John',
LastName: 'Doe',
Age: 30
}
}
})
<ul id="example-1">
<li v-for="item in items">
{{ $index }} – {{ item.message }}
</li>
</ul
or
<ul>
<template v-for="item in items">
<li>{{ item.msg }}</li>
<li class="divider"></li>
</template>
</ul>
<!-- Where the <template> element
won’t render -->
or
<div v-for="(key, val) in object">
{{ key }} {{ val }}
</div>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meet-vue-js-181009165745/85/Meet-VueJs-27-320.jpg)





![PropsProps
Vue.js – Components
Vue.component('child', {
// declare the props
props: ['myProp'],
// the prop can be used inside templates, and will also
// be set as `this.msg`
template: '<span>{{ myProp }}</span>'
})
<child my-prop="hello!"></child>
<!-- The prop will be passed as string -->
Remember: When using camelCased prop names as
attributes, you need to use their kebab-case equivalents.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meet-vue-js-181009165745/85/Meet-VueJs-33-320.jpg)





![MixinsMixins
Vue.js – Mixins
// define a mixin object
var myMixin = {
created: function () {
this.hello()
},
methods: {
hello: function () {
console.log('hello from mixin!')
}
}
}
// define a component that uses this mixin
var Component = Vue.extend({
mixins: [myMixin]
})
var component = new Component() // -> "hello from mixin!"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meet-vue-js-181009165745/85/Meet-VueJs-39-320.jpg)
![Mixing mixins Mixing mixins
Vue.js – Mixins
var mixin = {
created: function () {
console.log('mixin hook called')
}
}
new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
created: function () {
console.log('component hook called')
}
})
// -> "mixin hook called"
// -> "component hook called"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meet-vue-js-181009165745/85/Meet-VueJs-40-320.jpg)
![Mixing mixins Mixing mixins
Vue.js – Mixins
var mixin = {
methods: {
foo: function () {
console.log('foo')
},
conflicting: function () {
console.log('from mixin')
}
}
}
var vm = new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
methods: {
bar: function () {
console.log('bar')
},
conflicting: function () {
console.log('from self')
}
}
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meet-vue-js-181009165745/85/Meet-VueJs-41-320.jpg)
![Mixing mixins Mixing mixins
Vue.js – Mixins
var mixin = {
methods: {
foo: function () {
console.log('foo')
},
conflicting: function () {
console.log('from mixin')
}
}
}
var vm = new Vue({
mixins: [mixin],
methods: {
bar: function () {
console.log('bar')
},
conflicting: function () {
console.log('from self')
}
}
})
vm.foo() // -> "foo"
vm.bar() // -> "bar"
vm.conflicting() // -> "from self"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/meet-vue-js-181009165745/85/Meet-VueJs-42-320.jpg)