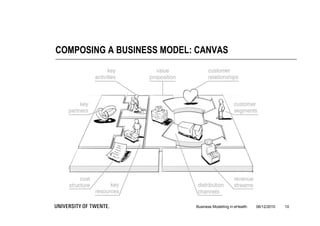
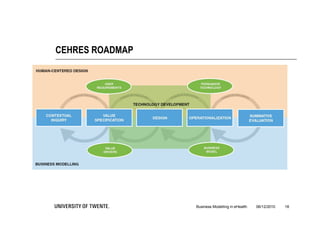
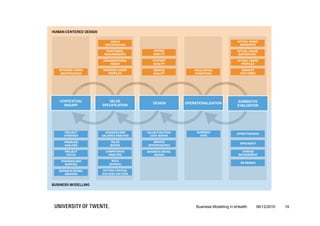
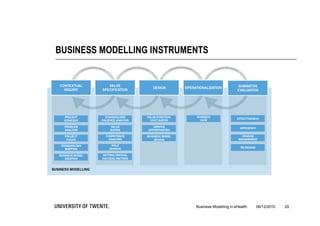
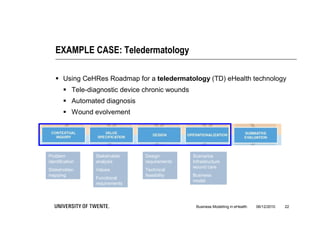
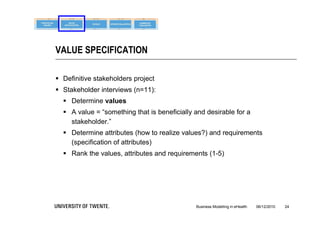
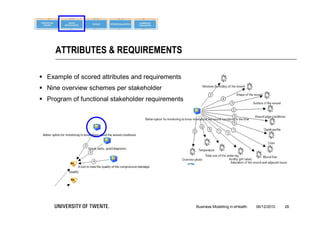
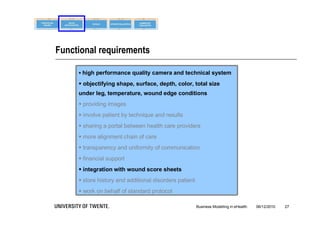
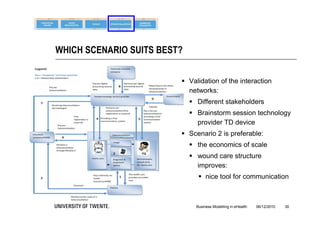
The document discusses the importance of business modeling in the implementation of eHealth technologies, emphasizing user-centered design and stakeholder involvement. It details the challenges faced in the implementation of these technologies, including the need for sustainable revenue models and support from various stakeholders. An example case of teledermatology illustrates the application of business modeling and the collaborative process necessary to meet stakeholder values and technical requirements.