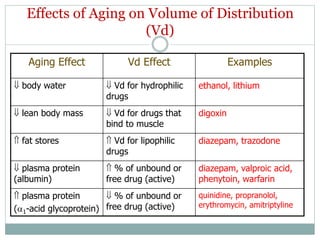
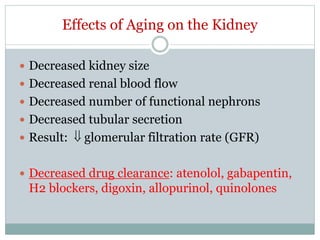
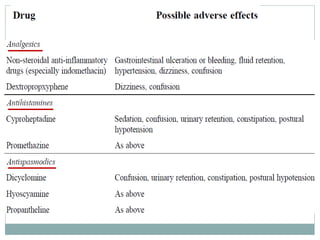
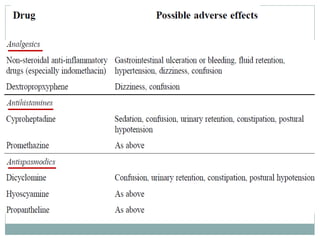
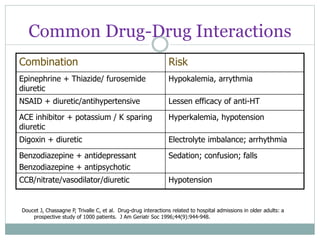
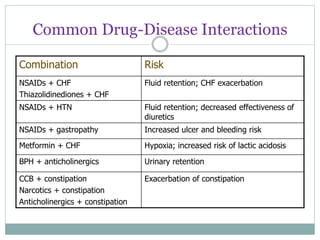
The document discusses challenges in pharmacotherapy for geriatric patients. It notes that illness is more common in older adults, leading to high rates of polypharmacy. Age-related changes can impact absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drugs. This generally results in lower clearance and increased sensitivity to medications. Drug-drug and drug-disease interactions are also more common. The document provides prescribing pearls like starting low doses and avoiding high risk medications. It emphasizes the need for careful monitoring to optimize outcomes for geriatric patients.