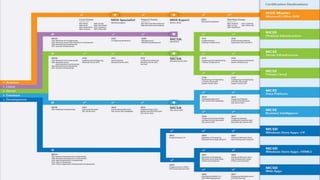
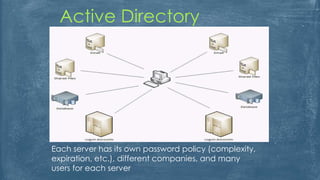
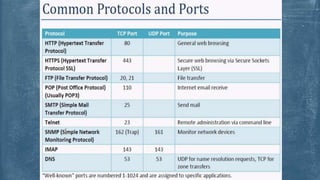
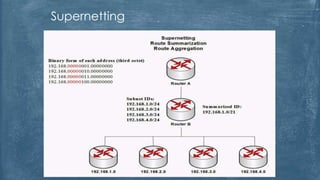
The document outlines the history and various aspects of Microsoft certifications related to server management, including topics such as Windows management, Active Directory, networking, and group policy. It also details practical exercises and configurations involving DHCP, DNS, Hyper-V, storage management, and virtualization, as well as security features like firewalls and permissions management. Essential commands and management tools are highlighted for effective administration and automation of server environments.