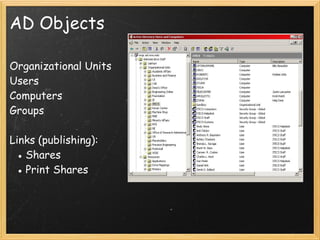
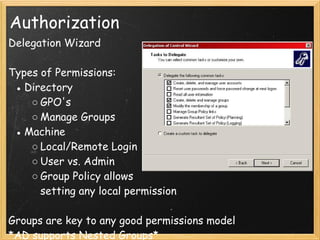
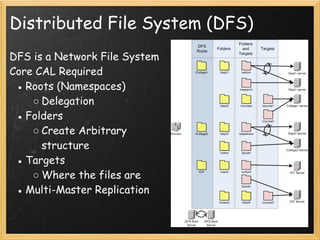
The document provides an overview of Active Directory, including what it is and is not, the tools used to manage it, authentication and authorization concepts, management concepts like organizational units and group policy, and additional Microsoft services that integrate with Active Directory like Windows Server Update Services and Distributed File System. The presentation covers the basics of Active Directory, its core functions of authentication, authorization, and centralized management, and how it is based on LDAP to store directory information that can be accessed remotely.