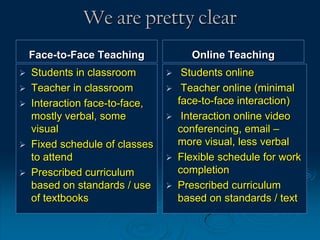
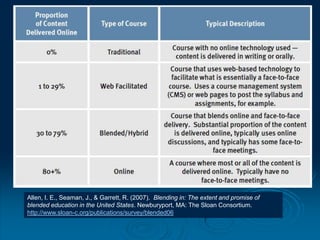
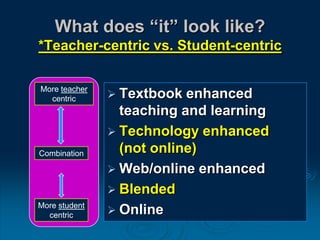
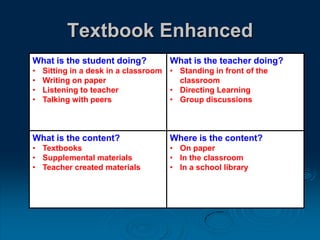
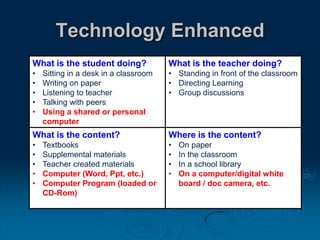
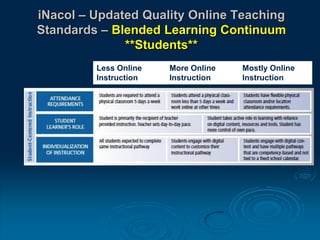
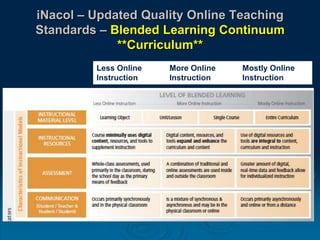
This document discusses the evolution of teaching and learning from traditional textbook-based methods to modern online and blended approaches. It begins by defining different models along a continuum from textbook to fully online, including definitions of terms like online, blended, and MOOCs. Examples are provided of what student, teacher, and content experiences might look like in textbook, technology-enhanced, web-enhanced, blended, and online environments. The importance of clear definitions and understanding how approaches differ is discussed.