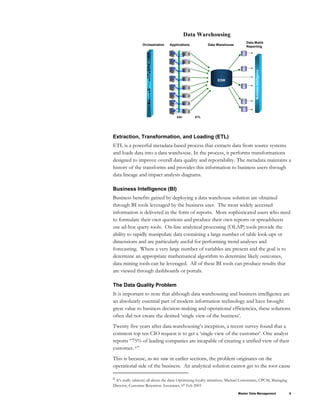
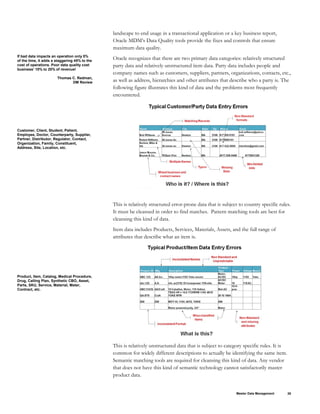
This document provides an overview of Master Data Management (MDM) and Oracle's MDM solution. It discusses the types of data in an enterprise including transactional data, analytical data, and master data. It describes how MDM solutions can manage both operational and analytical master data. The key components of Oracle's MDM solution include pre-built MDM applications to manage common master data objects, integration with operational applications and analytical systems, and tools to support data governance. The document also outlines Oracle's high-level MDM architecture and the benefits of Oracle's comprehensive Enterprise MDM solution.











































![specialized structure (available with license of Product Information Management
Data Librarian [PIMDL]) that allows companies to model their exact packaging
contents and hierarchy. Fourth, PDS provides a complete messaging solution that
is architected to the format mandated by GDSN and UCCnet.
PDS is designed to help make sure that companies avoid both the direct and
indirect costs of sending incorrect product data to UCCnet and their trading
partners. Direct costs include the fines imposed by UCCnet for sending ‘dirty data’,
and indirect costs include delayed or lost sales, etc. For example, PDS’ out-of-the-
box item attributes come with extensive data validation checks to make sure that
inputted data is clean. Similarly, PIM DH’s specialized packaging structure comes
with functions that automatically calculate and propagate certain parameters
throughout the hierarchy to eliminate errors caused by multiple re-entries of data.
And, the messaging system provides a complete transaction history of all messages
to provide a full audit trail of all communications with data pools and trading
partners.
Oracle Site Hub
Oracle Site Hub is a location mastering solution that enables organizations to
centralize site and location specific information from heterogeneous systems,
creating a single view of site information that can be leveraged across all functional
departments and analytical systems. Oracle Site Hub helps organizations eliminate
the problem of distributed, fragmented, incomplete and inconsistent site data
resulting from isolated silos of data, lack of centralized data repository, rapid
business expansion or mergers and acquisitions.
The Oracle Site Hub key capabilities include:
• Trusted Site Data Creates and maintains a unique, complete, clean and
accurate master data information across the enterprise Maintain cross-
references to source data Track historical changes
• Consolidate Mass Import Site information into a trusted global, "single
source of truth” master repository
Master Data Management 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/018876-396268-220808113708-cb182bbc/85/Master-Data-Management-46-320.jpg)














